Calculations in Year 2
advertisement

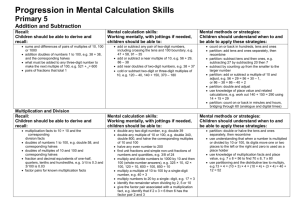
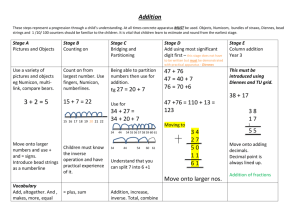
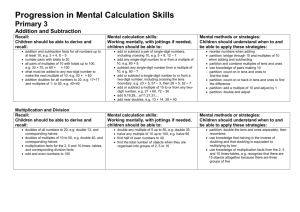
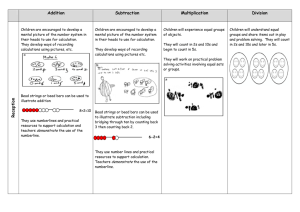
Calculations in Year 2 Addition Subtraction Continue using a range of equations as in Year 1 but Continue using a range of equations as in Year 1 but with appropriate, larger numbers. with appropriate numbers. Extend to Extend to 14 + 5 = 20 - 14 + 5 = 10 + and adding three numbers Children will begin to use empty number lines to support calculations. 32 + + = 100 35 = 1 + + 5 Children will begin to use ‘empty number lines’ themselves starting with the larger number and counting on. First counting on in tens and ones. Find a small difference by counting up 42 – 39 = 3 +1 +2 34 + 23 = 57 +10 +10 39 +1 +1 +1 34 54 55 56 57 40 42 Subtract 9 or 11. Begin to add/subtract 19 or 21 35 – 9 = 26 44 Then helping children to become more efficient by adding the units in one jump (by using the known fact 4 + 3 = 7). +1 26 25 35 34 + 23 = 57 -10 +10 +10 +3 34 44 54 57 Followed by adding the tens in one jump and the units in one jump. 34 + 23 = 57 +20 34 57 Partition into tens and ones and recombine +3 Use known number facts and place value to subtract (partition second number only) 37 – 12 = 37 – 10 – 2 = 27 – 2 = 25 27 25 -2 54 37 -10 Children are encouraged to use practical objects such as 12 + 23 = 10 + 2 + 20 + 3 = 30 + 5 = 35 refine to 23 + 12 = 23 + = = Add 9 or 11 by Numicon to subtract. 10 + 2 33 + 2 35 adding 10 and adjusting by 1 35 + 9 = 44 +10 35 44 -1 45 Children are encouraged to use practical objects such as bead strings, bricks and Numicon to count on. Multiplication x = signs and missing numbers 7 x 2 = = 2 7 x = 14 14 = x x 2 = 14 14 = 2 x x = 14 14 = x Repeated addition can be shown easily 5 x 3 = 5 + 5 + 5 5 0 1 2 Division ÷ = signs and missing numbers x 7 7 on a number line: 5 3 4 5 6 7 5 8 9 and on a bead bar: 3 times 5 is 5 + 5 + 5 = 15 10 11 12 13 14 15 or 3 lots of 5 6 6 ÷ ÷ ÷ ÷ 2 2 = = = = 3 3 3 = 6 ÷ 2 3 = 6 ÷ 3 = ÷ 2 3 = ÷ Understand division as sharing and grouping 6 2 can be modelled as: Sharing – 6 sweets are shared between 2 people. many do they have each? How or 5 x 3 5 x 3 = 5 + 5 + 5 Division can be demonstrated using a numberl ine; 5 5 5 Commutativity Children should know that 3 x 5 has the same answer as 5 x 3. This can also be shown on the number line. 5 0 1 3 2 5 3 4 3 5 6 7 3 5 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 3 3 12 ÷ 2 = 6 The first number is the number they end at and the second number is how many are in each jump. Grouping – There are 6 sweets. How many people can have 2 each? (How many 2’s make 6?) Arrays and repeated addition 0 4 x 2 or 4 + 4 2 x 4 or 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 0 Doubling multiples of 5 up to 50 15 x 2 = 30 Partition 10 + 20 10 = 4 6 2 4 6 Children should be given as many opportunities as possible for practical sharing using everyday items. 5 + 2 OR 30 OR X 10 5 2 20 10 =30 Children will develop their understanding of multiplication and use jottings to support calculation.