Chromosomal and Gene Mutations
advertisement

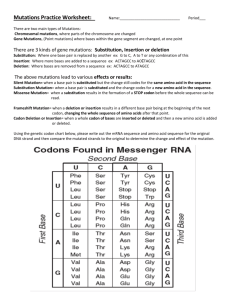
Chromosomal and Gene Mutations Proteins and Mutations: Some _____________________________ carry out functions within the cells of an organism. Other proteins are ____________________________ out of the cell for other purposes. Still other proteins are used as activators or repressors, turning ________________________________ on or off. Therefore, a change in a cell’s _______________________ could have dramatic effects on the cell’s structure or function. Changes in the ___________________________ can change the proteins synthesized by the cell. A random change in the sequence of nucleotides in DNA is called a __________________________________. Some mutations have little or no effect on the organism, others are ___________________________ and very few are ________________________________________________. There are two types f mutations: 1. ____________________________________________________ 2. ____________________________________________________ Chromosomal Mutations: Chromosomal mutations are changes in the _________________________________________ of a chromosome. Gene Mutations: Gene mutations are errors that occur within _____________________________________________________ in a chromosome. Gene mutations can involve a single nucleotide or they can affect sections of DNA that include many nucleotides. 1. The deletion or addition of nucleotides that disrupts codons is called a _____________________________________. Because mRNA is read in _____________________ (three-base sections) during translation, an addition or deletion of nucleotides can alter the sequence of bases, or reading frame, of the genetic message. Analyze the following frameshift mutation: What are the codons in the original reading frame? What are the codons in the shifted reading frame? Recall what happens when a strand of mRNA is transcribed from DNA. What might happen if one base is deleted from the DNA? The _____________________________________________________________________ would also be affected. Because each mRNA codon corresponds to an ______________________________, altering the codons may alter the amino acid sequence. The end result may be an entirely different ________________________ product. Frameshift mutations can have an enormous impact on an organism’s ________________________________________________________________. 2. A change in only one nucleotide is a ____________________________________________________. Because a point mutation affects a __________________________________________, it tends to be far less disruptive than a frameshift mutation. Some amino acids are coded for by more than one __________________________, and substitutions may simply change one codon to another codon for the same amino acid. For example: CUU = _______________________________________ Any change in the third base: CUC, CUA, CUG still codes for the amino acid ___________________________________________. About ________________________________ of all substitution mutations produce no changes in proteins. In the remaining________________________________ of point shift mutations, changed nucleotides cause a different amino acid to be incorporated into a protein. The resulting protein may function ______________________________________ or may be defective. The following diagram shows a point shift mutation and how it changes the gene from normal hemoglobin production to the production of sickle-cell hemoglobin, which in turn causes sickle-cell disease. A third and very common point mutation occurs when a codon in the middle of a gene is changed to a ___________________________________________. For example: UGC = Cysteine but UGA = Stop When genes with this mutation go through protein synthesis, translation is halted before the amino acid chain is completed.