Codons and Mutations
advertisement

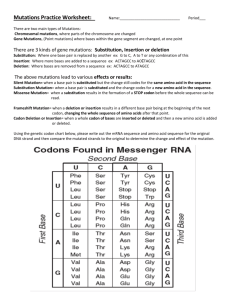
Codons and Mutations 7th Grade – Life Science S7L3a Telephone You will be given a phrase. Whisper the phrase word for word to the student right next to you until the last student in a line receives the phrase. The last person will write down the phrase. (Teacher select one of the phrases below.) "I tried bleaching my hair and it turned orange.” "The quick brown fox jumped over a lazy dog eating a hamburger.” "We have contacted your Earth governments and they refused our existence.“ “Yolanda’s aunt shared her secret sweet potato pie recipe with me.” You were asked to restate (or copy) a phrase word for word from person to person. Sometimes a task like this is done successfully. Sometimes a task like this is done with little error and the end statement is very similar to the original statement. Sometimes a task like this is done with so many errors that the end statement is nothing like the beginning statement and the statement changes in meaning greatly. When you look at a person, you see skin, eyes, hair, etc. What substance are these features made of? Write in notes: When you look at a person, you are looking at proteins. Their skin, eyes, hair, etc. When genes are being read to make proteins, the bases are read in threes. These groups of three are referred to as CODONS. Codons- A sequence of three nitrogen bases in a gene sequence that code for a specific amino acid Amino Acid- Building blocks of proteins (ie: proteins are made up of amino acids) *Each codon codes for one amino acid. *Multiple amino acids code for one protein. • For the following nucleic acids, practice groupings the bases into codons • ATTGCGTAC ATT GCG TAC • Practice - GTACCGGGTACGTAC GTA CCG GGT ACG TAC • Identify the nitrogen in the first nucleotide for the third codon for both nucleic acids above. (The correct nitrogen bases have been highlighted in red.) Do Now: When you hear the word mutation, what comes to mind? DNA is copied when new cells are made. Why do new cells need to be made? • For the organism to grow • For the repair and replacement of old or lost cells. Read : “What is a Gene Mutation and how do Mutations Occur?” When DNA is being copied, an error can be made in the arrangement of the base pairs. A mutation is a permanent change in the DNA sequence of a gene. There are different types of mutations (we have read about some of them– SANDERS Point (substitution) SNNDERS Deletion S_ _DERS Insertion SANANDERS Can mutations be harmful? Are mutations always harmful? • • • Some mutations can be harmful (such as genetic diseases). Some mutations can have no effect at all. And MANY mutations can be beneficial. The Impact of Mutations Next Step: How exactly do mutations effect the job of the gene? Video- “Finding Cures is Hard” 1. What do genes produce? (In other words, genes are recipes for making different_____________) 2. How do mutations effect the job of the gene? 3. What type of mutation is cystic fibrosis? Extension Questions 1. Variation in a species is important because it may give individuals within a species a advantage for survival. 2. In a population of polar bears, some may develop thicker fur. How? 3. The polar bears with thicker fur may have the advantage to survive. Why? “Genetic Variation” 1) Why are humans genetically so similar? 2) How will variation in humans become greater? Identify the mutation: ATGCTA ATGGCTA (Duplication) AGGCTA AGCTTA (Deletion and Duplication) ATGCTAATG ATGCTACTG (Point Mutation)