File
advertisement

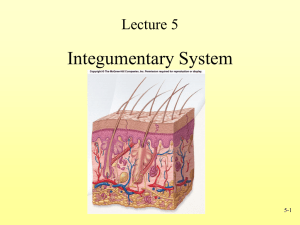
Ch. 5 Notes A&P Smart Name _________________________ Date _________________________ Ch.5 Integumentary System I. Introduction ______________________ = skin, and associated hairs, nails, and exocrine glands. ______ of your total body weight. _____________organ in the body. only organ seen everyday. Problems in other systems can be predicted by observing changes in ____________, flexibility, __________________, or sensitivity of the skin. Has 2 major components: 1) ____________________________________ Includes: 2) ____________________________________ Includes: ___________, nails, _____________________________ all which start at the dermis and protrude through the epidermis to the skin surface. Beneath the dermis, the loose connective tissue is called the ____________________________________. Also called the __________________________. It separates the integument from the _______________________ surrounding other ________________ such as muscles and bones. 1 General Functions of the skin: 1. ____________________ – of underlying tissues 2. Excretion – 3. ____________________ – of body temp 4. Synthesis – 5. _________________ – of nutrients 6. Detection – II. Epidermis __________________________ = what we call “skin cells” Thick skin covers ____________ & ___________ and is 5 skin layers thick. _________________ covers the rest of the body and is ___skin layers thick. A. Layers of the Epidermis o Stratum ________________________ Innermost o Stratum ________________________ o Stratum ________________________ o Stratum ________________________ o Stratum ________________________ Outermost 1. Stratum Germinativum Forms ____________________________ that extend into the ______________. Help _________________ surface area. 2 Ridges on soles and palms increase surface area to increase ________________ for better __________________. Fingerprints are ridge patterns which can be used to _________________ an individual. ________________________ = germinative cells which determine skin color. ________________________ = large germinative cells that dominate this layer. o Are __________________ whose divisions replace the superficial keratinocytes, which are ________ or lost at the epidermal surface. Merkel cells = ____________ sensitive specialized cells found on skin surfaces ___________________ hair. They release chemicals which stimulate nerve endings. 2. Stratum Spinosum Consists 8-10 layers of cells. Langerhans cells = stimulate _________________ against microorganisms and superficial ______________________. 3. Stratum Granulosum 3 Consists of 3-5 cell layers They begin to produce proteins _____________________ and ______________. Keratin is the basic component of ________ and ________. As keratin fibers are developing: o The cells become ______________ & ______________. o Cell membrane __________________ & becomes _____ ___________________ o Nucleus and other organelles __________________ and the cells ________. 4. Stratum Lucidum Cells are _________________, densely packed, and filled with _______________. 5. Stratum Corneum 15 - 30 layers thick The layer exposed to the skin’s surface die (become ________________), but remain tightly __________________. They are always shed in ______________. 4 It takes ___________________________ for a cell to move from the germinativum layer to the stratum corneum. Dead cells remain here for about ____________ before they are shed. Through ________________________________, you lose a __________ of water from interstitial fluids each day. If the skin is _______________ and connections between superficial & deeper layers are broken, this water will pocket forming _________________. When the skin is submersed in fresh water, the skin cells swell ______ normal size. When it is submersed in salt water, the process is reversed, so that the water moves from the cell into the salt water. This _____________________ dehydration. B. Skin Color Color is due to an interaction between 1. 2. Skin Pigmentation 1. _____________________ ______________________ pigment that accumulates in skin. Found in orange-colored vegetables. Converted to _______________ (aides vision, etc.). 5 2. _____________________ Melanocytes o Located in __________________________ o Produce melanin from aa. _____________________ o Melanin travels in vesicles called _____________________ from melanocytes to keratinocytes, which ____________________ colors the keratinocyte until the melanosome is ___________________ by a lysosome. o Whites: o Blacks: The melanosomes are _______________ and the transfer also occurs in the ______________________ making pigmentation __________________ and more persistent. o Melanin in keratinocytes protects skin from ____ radiation. Small amounts of UV radiation stimulates synthetic activity in the epidermis, but can damage DNA causing _____________________ and promoting ____________________ development. Melanosomes in the keratinocytes become _____________________ & surrounds the nucleus to ________________ the DNA from the UV radiation. 6 Melanin synthesis accelerates _______________, peaking about ____ days after the initial exposure. ______ individual can suffer skin ________________ from overexposure, but those with _______________ skin color have better ________________ protection. Over time, ____________________ damage can lead to ____________________ maintenance of the dermis, which results in premature _______________ or development of _____________ in the germinative cells or ______________________, due to _________________________ damage of these cells. o Albinos o Freckles o Liver spots o Jaundice 7 Liver can’t excrete _________ & yellowish pigments accumulate in _____________ ____________. In advanced stages, skin and eyes can turn ___________. o Vitiligo Individuals __________ their melanocytes. Believe to be due to _______________ defenses malfunction and antibodies attack _______________ melanocytes. o Moles Moles occur when ___________________________ grow in a ______________ instead of being spread throughout the skin. Moles may _______________ after exposure to the sun, during the teen years, and during pregnancy. o Skin Tags _______________________ = small flap of tissue that hangs off the skin by a connecting stalk. Skin tags are _________ dangerous. They are usually found on the __________, chest, back, __________________, under the breasts, or in the groin area. Skin tags appear most often in _________________, especially with weight gain, and in elderly people. o Birthmarks Are ______________________ on the skin that are noticeable at birth, or shortly afterwards. ____________________________ - a red, pink or purple blemish that is caused by abnormal blood vessels under the skin. 8 ____________________________ - are usually brown and are caused by the clustering of pigment cells. Dermal Circulation o Blood cells contain the pigment _____________________. o When attached to _____________, hemoglobin has a bright ______ color. This gives the dermis a _________________ which is most apparent in light colored individuals. C. The Epidermis & Vitamin D UV radiation causes skin cells in the germinativum & spinosum to convert a cholesterol steroid into _______________ which is used by the ______________ in the synthesis of _________________. Calcitriol is needed for normal ________________ & phosphorous _____________ by the small intestine. III. Dermis A. Two Layers: 1. Papillary Layer 2. Reticular Layer Lies _______________ to the ____________________ layer Dense meshwork of irregular connective tissue ________________ fibers of this layer extend into the papillary layer as well as the ___________________ layer. 9 ______________ organs of epidermal origin extend into the dermis. Nerve fibers are also in the ________________. Wrinkles & Stretch Marks Collagen fibers are strong and ___________ ______________, but are easily _________ or twisted. Our skin remains flexible, and somewhat elastic, but collagen fibers stop _____________ before tissue damage occurs. Elastin fibers allow ________________ and will recoil to their original _____________. ___________ in the skin also helps maintain _______________ and resilience. Aging, hormones, and overexposure of UV radiation permanently _____________ the amount of _____________ in the dermis, producing _____________ and sagging skin. Substantial weight gain can exceed the elasticity limits of the skin resulting in _________________________. ______________ is a derivative of _________________ which increases _______________ blood flow to stimulate dermal _____________. Therefore, the rate of wrinkle formation decreases and existing wrinkles become _______________. B. Dermal Circulation & Innervation Ulcer = _____________= may affect bedridden or immobile patients with circulatory restriction, especially when splints, casts, or bedding continuously presses against superficial blood vessels. 10 Dermatitis = ____________________________ = due to contact with strong chemical irritants producing a rash that may spread. Ex: Eczema = Diaper rash = caused by a combination of _____________, irritating chemicals from fecal or urinary _______________ and _______________________. Hives = IV. Subcutaneous Layer Aka. _________________________ Not actually part of the _______________________ _____________________ the skin’s _________________ while allowing independent movement Most infants and small children have “_____________________” for reducing ___________________, serves as an ________________ reserve, and a shock absorber for the tumbling. As we grow, subcutaneous fat distribution changes. o Men => accumulates at the ___________, arms, ________________, & over buttocks 11 o Women => accumulates at the _____________, buttocks, ________, and thighs. V. Accessory Structures A. Hair Follicles and Hair Not on the sides and soles of the ___________, palms of __________, the sides of __________ and toes, _____ and portions of the genitalia Around 5 million hairs on the body, 2% on your head. Hairs originate in complex organs called ________ ______________. Hair Production Hair Function _________________ hairs on your body 100,000 which are on your ___________ Protects scalp from _____, cushions blows to your head, and insulates the ___________. Hairs of the ears, nostrils, & eyelashes Body Hairs ____________________________, surrounding their follicles, provides early warning of _______________ injury. Have _______________________ whose contractions cause the hairs to stand erect while in ________ or in the ________. 12 Types of Hairs 2 Major Types of Hairs 1) _____________________ = “peach fuzz” body hair 2) _____________________ = on/around head, eyes, etc. Hair Color Caused by the pigments of the ______________________ Genetically determined, but can be effected by _____________ or the ____________________. Pigment production decreases with _____ & the color lightens, turning _________ Because hair is _________, color changes are ____________ Hair Loss Avg. hair loss from head ___________________. Loss of __________________, usually something wrong. Male Pattern Baldness results from ______________ level changes in blood, which causes ______________________ production to change to ______________________ production. B. Glands in the Skin 2 types: sebaceous and sweat glands 1. Sebaceous Glands (oil glands) _________________ = a waxy, oily substance secreted onto hair follicles. It ______________ skin & hair & ____________ bacteria growth. Folliculitis = __________ = caused by blocked oil gland. 13 Sex hormone concentration causes an increase in ________ __________________. Acne results from ______________ oil building up under a clogged ______________ duct, encouraging bacterial infection. 2. Sweat Glands 2 types: Apocrine and Merocrine a. Apocrine glands Found in/around ______________, nipples & _________ Produce a ________________, cloudy, and potentially ________________ secretion. Apocrine sweat is ________________ to bacteria, which ________________ odor b. Merocrine Sweat Glands More ________________ and widely _______________ ________________ than apocrine glands. Highest concentration on ___________ and __________ Sweat is called _______________ _________________. It is __________________, but contains electrolytes, ______________ ______________, and waste products. Function of sensible perspiration 1) 2) Excrete water, ___________________ & toxins 3) _________________ harmful chemicals and discourage microbial ___________________ on skin. 14 3. Other Integumentary Glands __________________________ A cluster of ______________ or sacs, of female mammals, in which __________ is produced to feed their young. __________________________ C. Nails Protect exposed __________ helping to limit their _______________ when they are subjected to mechanical ____________. Underlying blood vessels give it its ____________. The pale crescent is due to the vessels being ______________ (or hidden). ___________ of the nail consists of __________, tightly compressed cells packed with ____________. These cells can be affected by conditions altering body __________________, so changes in the ______________, structure of, or appearance of nails can assist in diagnosis. Ex: Nails may turn yellow in patients with chronic respiratory disorders, thyroid gland disorders, or AIDS. VI. Local Control of Integumentary Function Somewhat functionally ___________________. It often responds ________________________ to local influences without the involvement of the nervous or endocrine system. 15 o Ex: when the skin is subjected to mechanical stresses, __________________ stem cells divide more rapidly increasing the tissue depth forming ________________. A. Injury and Repair The relative speed & effectiveness of skin ____________ vary according to the _____________________. 4 Stages in regeneration of skin after injury: 1) 2) Blood ___________ & __________ forms restricting the entry of microorganisms to the area. Germinativum cells ______________ down the _____________ of the wound. ____________________ cells remove debris & __________________ to the area increases. 3) A ____________ later the scab is _______________________ by epidermal cells migrating over the meshwork produced by __________________ activity. Phagocytic activity has almost ended and the fibrin clot is __________________. 4) After several weeks, the scab has been __________, and the epidermis is complete. Dermal fibroblasts continue to make _____________________ which will gradually elevate the overlying epidermis. VII. Aging and Integumentary System Epidermis __________ due to declining germinitivum ________________, which results in older people more prone to ________________ and skin _________________. Langerhans cells __________________ reducing sensitivity. 16 Vitamin D3 production ____________________. Glandular activity ___________________. Hair follicles _________ functioning or produce _________________ hairs. ______________________ level changes, changing _______ distribution, so both sexes over _______ tend to look ____________. Skin repairs proceed slowly, taking _____________ as long as it used to. 17