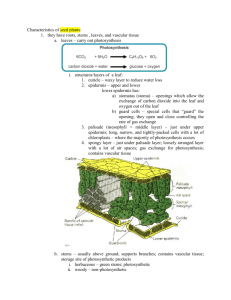
Chapter 6 – Plants
advertisement
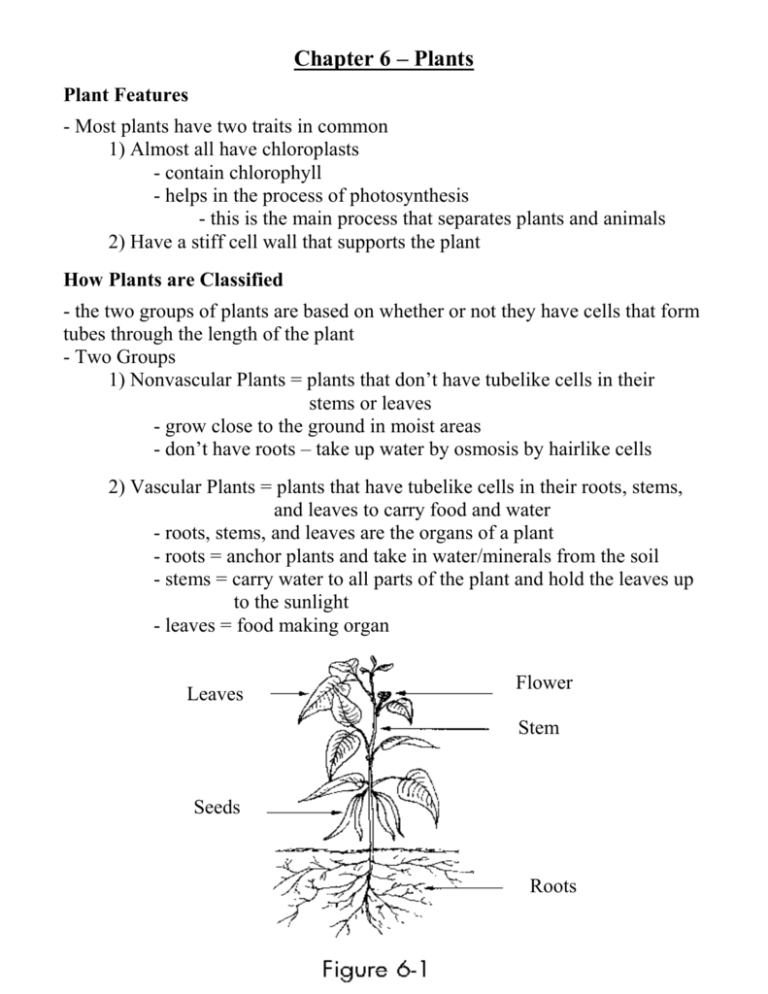
Chapter 6 – Plants Plant Features - Most plants have two traits in common 1) Almost all have chloroplasts - contain chlorophyll - helps in the process of photosynthesis - this is the main process that separates plants and animals 2) Have a stiff cell wall that supports the plant How Plants are Classified - the two groups of plants are based on whether or not they have cells that form tubes through the length of the plant - Two Groups 1) Nonvascular Plants = plants that don’t have tubelike cells in their stems or leaves - grow close to the ground in moist areas - don’t have roots – take up water by osmosis by hairlike cells 2) Vascular Plants = plants that have tubelike cells in their roots, stems, and leaves to carry food and water - roots, stems, and leaves are the organs of a plant - roots = anchor plants and take in water/minerals from the soil - stems = carry water to all parts of the plant and hold the leaves up to the sunlight - leaves = food making organ Leaves Flower Stem Seeds Roots Nonvascular Plants - examples: mosses and liverworts - moss = a small, nonvascular plant that has both stems and leaves but no roots - are fixed to the ground or tree trunks by hairlike cells that take up water - the leaves are only one to two cells thick and will quickly dry out if taken from their moist environment - are food for some animals (worms and snails), help soil from washing away, and create soil by breaking down rocks Vascular Plants - most of the plants you see everyday - have tubelike cells that carry food and water throughout the plant - two tubelike cells: 1) xylem = carry water and dissolved minerals from the roots to leaves 2) phloem = carry food that is made in the leaves to all parts of the plant Types of Vascular Plants 1) Fern = vascular plant that reproduces by spores - grow in moist, shaded areas 2) Conifer = a vascular plant that produces seeds in cones - seed = the part of the plant that contains a young plant and stored food - the young plant is an embryo = an organism in its earliest stages of growth - called evergreens = keep their leaves throughout the year - pine trees produce male and female cones - male cones produce pollen = tiny grains of seed plants in which sperm develop - female cones contain the egg cells - seeds form in between the scales of the cone - supply 3/ 4 of the lumber that is used in the world (building, paper) 3) Flowering Plant = a vascular plant that produces seeds inside a flower - flower = the reproductive part of the plant - produce pollen - the female flower parts develop into the fruit that protects the seeds - examples: tomato plants, roses, grasses