Bacteria and Viruses Outline – Teacher Guide (Key)
advertisement

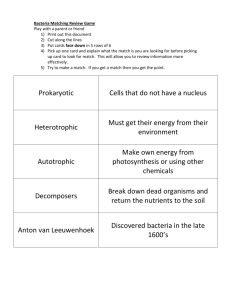
Name __________________________________ Period __________ Bacteria and Viruses Outline Bacteria Bacteria are __________________, ________________ (one-celled) organisms that lack a _______________ membrane. Bacteria can live on land, in water, and in the air. – They also live in and on both _______________ and ____________ plants and animals Most bacteria are _____________________. – _____________ are organisms that _______ make their own food. Shapes of Bacteria Structure of Bacteria A bacterium is made up of a ______________________ that encloses and protects ________________________. Bacterial Nutrition Some bacteria live separately and others remain together to form _________________. – Colonies are __________________ of bacteria. There are bacteria that live as _________________. – A parasite absorbs ____________________ from other living organisms called their _______________. Others digest and absorb food materials from ____________ organisms. – These bacteria are called ______________________. Beneficial Bacteria Most bacteria are _______________ (_______________) to humans. Bacteria are __________________ that cause decay. – Decomposers are organisms that _____________________ dead organisms and ______________________ to the soil. Many bacteria are used to produce ________ and life-saving ________. – Bacteria are used to make cheese, pickles, yogurt, vinegar, and sauerkraut. By using methods of _______________________, bacteria have been encouraged to ________________ substances such as insulin. The human intestinal tract contains millions of _______________. – Many of these bacteria help the ______________ process and others produce __________________. Bacteria are also used in the _______________ of leather, the ________ of tobacco, and the _____________________ of food for feeding cows. Harmful Bacteria Some bacteria are ________ beneficial to man. Bacteria spoil food by secreting _______ into the food causing it to rot. Along with enzymes, other substances produced by bacteria are released into the food. Some of these substances are ____________, making the food __________________ to humans and other organisms. Bacteria in large numbers can ____________ (dirty) lakes, streams, and drinking water. During ________________, bacteria reduce the dissolved oxygen content in water supplies. Many bacteria are ______________________. A pathogen is an Some bacterial ________________ of humans are tuberculosis, tetanus, and strep throat. Controlling Harmful Bacteria ________________, _______________, and ________________ are used to control pathogenic bacteria. – An antibiotic is a _______________ that can __________ the growth of some bacteria. – Bacteria are able to produce types that are ______________ to certain antibiotics. – When this happens, __________ antibiotics must be developed. Bacteria can also be ____________in foods by – pasteurization, – canning, – chemical preservatives, – radiation, – steam/pressure, – salt curing, – dehydration (drying). Harmful Anaerobic Bacteria Some bacteria can live ____________________ and cause botulism. A dangerous type of _____________________, in foods that have not been properly canned. Two other anaerobic bacteria can cause _________________ diseases Gonorrhea (causes sterility) Syphilis (can result in death). A venereal disease is a contagious disease that a person gets through _______________________. Both diseases can be _______________ successfully by ____________ if detected early enough. Viruses A virus is not a ________________. It is made up of ________________ material inside a ___________coat. Viruses do not carry on most __________________ activities. They can only _____________ inside a living cell called the _____ cell. Outside the host cell, a virus is “________” and often exists as a crystal. A virus has no means of _______________________. Virus Diagram Negative Virus Influences They cause __________________ in both plants and animals. Some viruses cause ______________ and _____________. They also _______ cells and are responsible for human diseases such as – polio, – measles, – mumps, – influenza, – hepatitis, – colds, – AIDS. Influenza virus - Flu Papilloma virus - Warts Rabies Virus Human Immunodeficiency Virus AIDS Positive Virus Influences Certain viruses are used in the ________________ of insect pests. Others are used in ______________________. Scientists have been able to use viruses to biologically __________________ caterpillars of the European pine sawfly and the gypsy moth. Bacteria and Viruses Outline – Teacher Guide (Key) © Lisa Michalek Bacteria Bacteria are microscopic, unicellular (one-celled) organisms that lack a nuclear membrane Bacteria can live on land, in water, and in the air – They also live in and on both living and dead plants and animals Most bacteria are heterotrophs. – Heterotrophs are organisms that cannot make their own food Shapes of Bacteria Coccus - round or sphere shaped Bacillus – rod shaped Spirillum – spiral shaped Structure of Bacteria A bacterium is made up of a thick cell wall that encloses and protects cellular material Bacterial Nutrition Some bacteria live separately and others remain together to form colonies – Colonies are large groups of bacteria There are bacteria that live as parasites – A parasite absorbs food materials from other living organisms called their hosts Others digest and absorb food materials from dead organisms Beneficial Bacteria Most bacteria are beneficial (helpful) to humans Bacteria are decomposers that cause decay – Decomposers are organisms that break down dead organisms and return the nutrients to the soil Many bacteria are used to produce food and life-saving drugs – Bacteria are used to make cheese, pickles, yogurt, vinegar, and sauerkraut By using methods of gene transplanting, bacteria have been encouraged to produce substances such as insulin The human intestinal tract contains millions of bacteria – Many of these bacteria help the digestive process and others produce vitamins Bacteria are also used in the tanning of leather, the curing of tobacco, and the production of food for feeding cows Harmful Bacteria Some bacteria are not beneficial to man Bacteria spoil food by secreting enzymes into the food causing it to rot – Along with enzymes, other substances produced by bacteria are released into the food – Some of these substances are toxic, making the food poisonous to humans and other organisms Bacteria in large numbers can pollute (dirty) lakes, streams, and drinking water During respiration, bacteria reduce the dissolved oxygen content in water supplies Many bacteria are pathogenic – A pathogen is an organism that causes disease and/or infection – Some bacterial diseases of humans are tuberculosis, tetanus, and strep throat Controlling Harmful Bacteria Antiseptics, disinfectants, and antibiotics are used to control pathogenic bacteria – An antibiotic is a chemical that can stop the growth of some bacteria – Bacteria are able to produce types that are resistant to certain antibiotics – When this happens, new antibiotics must be developed. Bacteria can also be killed in foods by – pasteurization – canning – chemical preservatives – radiation – steam/pressure – salt curing – dehydration (drying) Harmful Anaerobic Bacteria Some bacteria can live anaerobically and cause botulism – A dangerous type of food poisoning, in foods that have not been properly canned Two other anaerobic bacteria can cause venereal diseases – Gonorrhea (causes sterility) – Syphilis (can result in death) A venereal disease is a contagious disease that a person gets through sexual contact Both diseases can be treated successfully by antibiotics if detected early enough Viruses A virus is not a cell It is made up of genetic material inside a protein coat Viruses do not carry on most metabolic activities They can only reproduce inside a living cell called the host cell Outside the host cell, a virus is “lifeless” and often exists as a crystal A virus has no means of locomotion Negative Virus Influences They cause infections in both plants and animals Some viruses cause tumors and warts They also destroy cells and are responsible for human diseases such as – polio – measles – mumps – influenza – hepatitis – colds – AIDS Positive Virus Influences Certain viruses are used in the control of insect pests Others are used in genetic research Scientists have been able to use viruses to biologically control caterpillars of the European pine sawfly and the gypsy moth