Bacteria
advertisement
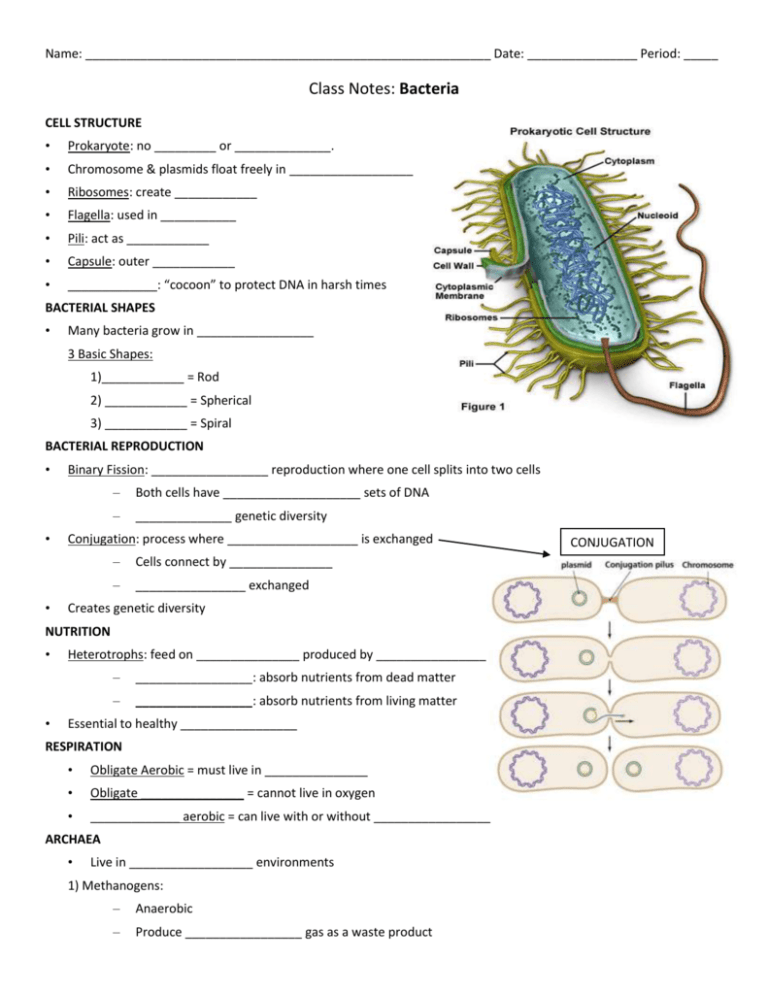
Name: ___________________________________________________________ Date: ________________ Period: _____ Class Notes: Bacteria CELL STRUCTURE • Prokaryote: no _________ or ______________. • Chromosome & plasmids float freely in __________________ • Ribosomes: create ____________ • Flagella: used in ___________ • Pili: act as ____________ • Capsule: outer ____________ • _____________: “cocoon” to protect DNA in harsh times BACTERIAL SHAPES • Many bacteria grow in _________________ 3 Basic Shapes: 1)____________ = Rod 2) ____________ = Spherical 3) ____________ = Spiral BACTERIAL REPRODUCTION • • • Binary Fission: _________________ reproduction where one cell splits into two cells – Both cells have ____________________ sets of DNA – ______________ genetic diversity Conjugation: process where ___________________ is exchanged – Cells connect by _______________ – ________________ exchanged Creates genetic diversity NUTRITION • • Heterotrophs: feed on _______________ produced by ________________ – _________________: absorb nutrients from dead matter – _________________: absorb nutrients from living matter Essential to healthy _________________ RESPIRATION • Obligate Aerobic = must live in _______________ • Obligate _______________ = cannot live in oxygen • _____________ aerobic = can live with or without _________________ ARCHAEA • Live in __________________ environments 1) Methanogens: – Anaerobic – Produce _________________ gas as a waste product CONJUGATION – Habitat: Swamps, sewage, ________________ 2) Thermophiles • ______________and _____________ loving bacteria • Habitat: Deep sea vents, volcanoes, _________________ (230°F) 3) Halophiles – Thrive in areas of high ______________concentration • – _______________ normally ________________ organisms Use ____________to make ___________________ EUBACTERIA (MODERN BACTERIA) • _______________ to most environments on Earth • Identified by ________________ test – – Gram negative: • stains __________ • ____________ to treat Gram positive: • stains _____________ • ____________ to treat • Treatments differ depending upon _______________ • Cyanobacteria: _________________ bacteria • Evolutionary Importance – Early life lived in _____________ (no ______________) – Cyanobacteria released ____________ into the _______________ – ___________recombined into ozone (________) in the _________________ – Protective layer allowed life to _____________on ______________ HELPFUL BACTERIA • • Helpful in nature – _______________: create ________ – Decomposers: ______________ Carbon – ______________ fixing bacteria Bacteria have been ______________ for human uses: – Food: ___________, ______________, yogurt, cabbage, sauerkraut – Medicine: ________________ – Industry: insecticides, fuel, __________________











