plant nucleotide
advertisement

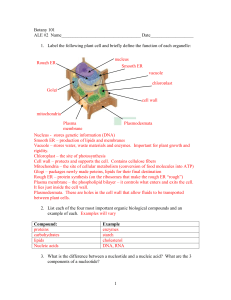
GREEN RIVER COMMUNITY COLLEGE BIOLOGY ALE#2 Name______________________________________ Date_________________ 1. List each of the four most important organic biological compounds and an example of each. Examples will vary Compound: proteins carbohydrates lipids Nucleic acids Example enzymes starch cholesterol DNA, RNA 2. What is the difference between a nucleotide and a nucleic acid? What are the 3 components of a nucleotide? Nucleic acids are molecules that contain our genetic information – more specifically, the code for protein synthesis. DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. Each nucleotide consists of a phosphate group, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base 3. List three important functions of proteins The three functions given in your lecture notes are: enzymes, cell membrane transporters, and structural components such as hair, nails, and muscle fibers 4. Answer the questions below based on the following diagram of an animal cell placed in a beaker of solution. In this example, the cell’s membrane is permeable to NaCl and to water (remember, a 10% NaCl solution means there is also 90% water inside the cell) 100% H20 10%NaCl a. Is the solution hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic? (circle one) hypotonic b. Is the inside of the cell hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic? (circle one) hypertonic c. Will water move into the cell or out of the cell? ______into_______ d. Will NaCl move into the cell or out of the cell?____________out__ e. Water and NaCl will continue to move across the membrane until the solutions inside the cell and in the beaker become: hypertonic, hypotonic, or isotonic? (circle one) isotonic 2/16/2016 5. Define and contrast the following transport processes. Provide examples using living systems where possible. a. Diffusion - movement of solute from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration. No energy is required in this process. Example: diffusion of oxygen across the cell membrane for cellular respiration. b. Osmosis - diffusion of water into areas with higher solute concentration. Water acts to dilute! Example: Diffusion of water into a plant cell to create turgor pressure. c. Passive Transport - transport of molecules by way of diffusion (no energy required). Diffusion down a concentration gradient. Ex. Diffusion of oxygen into a cell. d. Active Transport - movement of molecules against their concentration gradient: from areas of low concentration into areas of high concentration. Energy is required. Example: pumping protons across a membrane to create an electrochemical gradient that is used to drive cellular work. 6. List the major function(s) for each organelle a) Nucleus stores DNA b) Smooth ER makes lipids c) Ribosomes make proteins d) Rough ER modifies proteins e) Golgi apparatus processes and packages proteins into vesicles for transport f) Vesicle transports proteins within or out of the cell g) Lysosome digests food and worn out cells/organelles h) Cytoskeleton reinforces and organizes cell structures i) Mitochondria - use oxygen to metabolize sugars to create ATP to drive cellular work 7. List the three additional parts of a plant cell and their functions. cell wall – provide support/rigidity for the plant cells vacuole – large central water-filled organelle. Maintains the plant’s turgor pressure and assists in plant growth. chloroplast – site of photosynthesis, the sunlight-driven conversion of carbon dioxide into carbohydrates (food). 2 8. What is the difference between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell? Prokaryotic cells lack true organelles. They are also much smaller than a eukaryotic cell. Eukaryotic cells are larger and have true organelles. 9. Review your notes on cells and membrane transport. Write 3 multiple choice questions regarding the material in this section. Circle the correct answer to each question. Answers will vary. Be creative! 3