SBI4U - Membrane Transport
advertisement

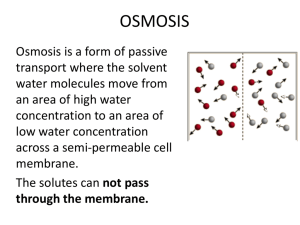
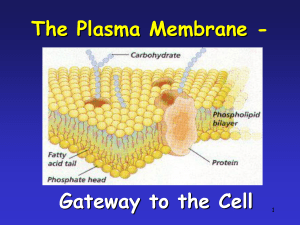
Transport Across Membranes 2.4 Importance of Transport • intake of nutrients • removal of wastes • communication with environment & other cells • blocking passage of harmful substances Passive Transport • the movement of materials across the cell membrane without the use of chemical energy (ATP) • occurs because of diffusion Diffusion • the net movement of a substance from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower • dynamic equilibrium Simple Diffusion • substances move across membrane unassisted • small non-polar molecules (O2, CO2, steroid hormones, some drugs) and small polar molecules (H2O, glycerol) • larger molecules and ions can not pass through membranes unassisted Facilitated Diffusion • diffusion across membrane assisted by integral membrane proteins called transport proteins • channel proteins vs. carrier proteins • ions, water, amino acids, sugars, etc. Osmosis • the diffusion of water across a membrane • water follows concentration gradient until equilibrium Osmosis • direction of osmosis changes depending on type of solution surrounding the cell: • isotonic solution • hypotonic solution • hypertonic solution Cell in Isotonic Solution 10% NaCL 90% H2O ENVIRONMENT CELL 10% NaCL 90% H2O NO NET MOVEMENT What is the direction of water movement? equilibrium The cell is at _______________. copyright cmassengale 10 Cell in Hypotonic Solution 10% NaCL 90% H2O CELL 20% NaCL 80% H2O What is the direction of water movement? copyright cmassengale 11 Cell in Hypertonic Solution 15% NaCL 85% H2O ENVIRONMENT CELL 5% NaCL 95% H2O What is the direction of water movement? copyright cmassengale 12 Cells and Tonicity Red Blood Cells hypotonic hypertonic isotonic hypertonic isotonic hypotonic copyright cmassengale 15 How does this impact… • …a single-celled organism living in a freshwater environment? • …a single-celled organism living in a salt-water environment? • …the roots of a plant in the spring after salt has been sprinkled during the winter? More applications… • Why can’t you water a plant with salt water? • Why do vegetables in the grocery store get sprayed with water periodically? (What would happen if they were sprayed with salt water?) Active Transport Active Transport • the movement of materials against the concentration gradient • requires cellular energy (ATP) Primary Active Transport • pumps move positively charged ions (H+, Ca2+, Na+, K+) across membranes • creates electrochemical gradient Secondary Active Transport • uses gradient established by a primary active transport pump Bulk Transport • movement of larger substances across a cellular membrane • requires energy (ATP) • exocytosis & endocytosis Endocytosis Exocytosis Credits • Slides #10, 11, 12, and 15 taken from Powerpoint presentations created by Cheryl Massengale, educator extraordinaire & creator of http://www.biologyjunction.com/