ALE #1
Botany 101
ALE #2 Name___________________________________ Date___________________
1.
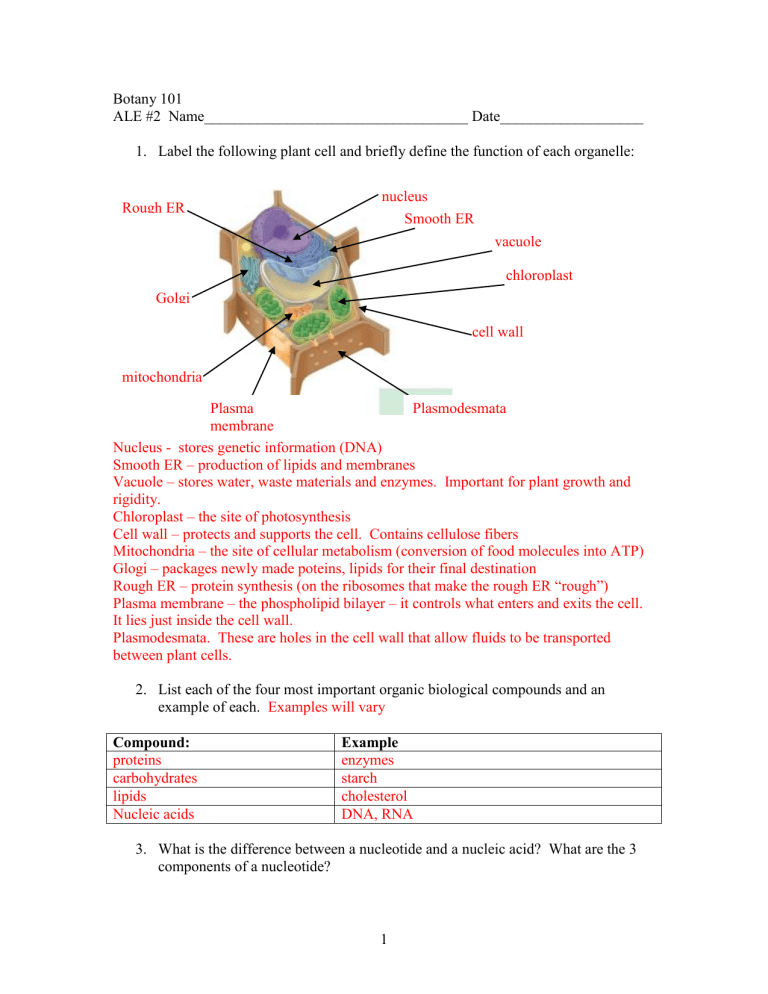
Label the following plant cell and briefly define the function of each organelle:
Rough ER nucleus
Smooth ER vacuole chloroplast
Golgi cell wall mitochondria
Plasma membrane
Plasmodesmata
Nucleus - stores genetic information (DNA)
Smooth ER – production of lipids and membranes
Vacuole – stores water, waste materials and enzymes. Important for plant growth and rigidity.
Chloroplast – the site of photosynthesis
Cell wall – protects and supports the cell. Contains cellulose fibers
Mitochondria – the site of cellular metabolism (conversion of food molecules into ATP)
Glogi – packages newly made poteins, lipids for their final destination
Rough ER – protein synthesis (on the ribosomes that make the rough ER “rough”)
Plasma membrane – the phospholipid bilayer – it controls what enters and exits the cell.
It lies just inside the cell wall.
Plasmodesmata. These are holes in the cell wall that allow fluids to be transported between plant cells.
2.
List each of the four most important organic biological compounds and an example of each. Examples will vary
Compound: proteins carbohydrates
Example enzymes starch lipids
Nucleic acids cholesterol
DNA, RNA
3.
What is the difference between a nucleotide and a nucleic acid? What are the 3 components of a nucleotide?
1
Nucleic acids are molecules that contain our genetic information – more specifically, the code for protein synthesis. DNA and RNA are nucleic acids. Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids. Each nucleotide consists of a phosphate group, a pentose sugar, and a nitrogenous base
4.
List three important functions of proteins
The three functions given in your lecture notes are: enzymes, cell membrane transporters, and structural components such as hair, nails, and muscle fibers
5.
Answer the questions below based on the following diagram of an animal cell placed in a beaker of solution. In this example, the cell’s membrane is permeable to NaCl and to water (remember, a 10% NaCl solution means there is also 90% water inside the cell)
100% H
2
0
10%NaCl a.
Is the solution hypertonic , hypotonic , or isotonic ? (circle one) hypotonic b.
Is the inside of the cell hypertonic , hypotonic , or isotonic ? (circle one) hypertonic c.
Will water move into the cell or out of the cell? ______ into _______ d.
Will NaCl move into the cell or out of the cell?____________
out __ e.
Water and NaCl will continue to move across the membrane until the solutions inside the cell and in the beaker become: hypertonic , hypotonic , or isotonic ? (circle one) isotonic
6.
What is the hypothesis of serial endosymbiosis?
This hypothesis attempts to explain the evolutionary origin of mitochondria and chloroplasts. According to this hypothesis, chloroplasts and mitochondria once both separate, independent prokaryotic organisms that were engulfed by a larger eukaryotic cell. They formed a mutualistic association with these cells, and eventually could not exist independently of these cells. The evidence in support of this hypothesis is that both mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA and divide on their own, independently from the rest of the cell (whose division is controlled by the nucleus).
7.
Describe what would happen to a plant cell that was placed in a hypertonic solution
A hypetonic solution would have a greater solute concentration then the solutions inside the cell, so the vacuole would lose water, causing the cell membrane to shrink away from the cell wall. The cell wall may also pull inward a bit.
2