What is Asexual Reproduction?
advertisement

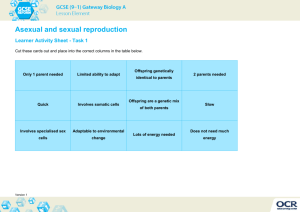
Reproduction What is Asexual Reproduction? Reproduction is the biological mechanism by which species give rise to offspring and perpetuate their genetic material. Asexual reproduction is the reproductive process that involves only one organism and results in two or more organisms. Single celled organisms, such as archaea, bacteria and protists, commonly reproduce asexually. Certain fungi and some plants do as well. An advantage of asexual reproduction is that it results in more rapid proliferation of the species. Another advantage is genetic stability. When certain desired traits are observed in commercial plants (color, disease resistance, flavor, etc.), that plant is often encouraged to reproduce asexually in order to keep those traits. Asexual: There are 3 types of asexual reproduction. They are listed and defined below. It's important to note that all forms of asexual reproduction use the genetics of one living being, therefore the offspring will be genetically similar to the parent. Budding-This process is common in plant species. A "bud" grows on the organism until it has grown enough to become its own independent organism. Regeneration- Common to invertebrates, this is the process of growing limbs, organs or other tissues to replace damaged ones. Fission- Also known as binary fission, this is the process of an organism dividing into two separate organisms such as in cellular division. What is Sexual Reproduction? Sexual reproduction involves the combination of genetic material between a male and a female of the species. Consequently, each generation is different from the previous one. This genetic variation is advantageous in that it allows the species to adapt more quickly to changing conditions in the environment. The better-adapted individuals pass their genes on to the next generation, thus influencing the genetic makeup of the entire species. This process is known as “natural selection.” Another advantage of the mixture of genetic material during sexual reproduction is the higher probability that the parents’ diseases will not be inherited by their offspring. The relative disadvantage of sexual reproduction is that it requires the participation of two parents, only one of which is capable of gestation. Even after a mate is found, there is no guarantee that the nucleus of the male gamete will fuse with that of the female, or that the fusion will result in offspring. It is also a lengthy process, subject to considerable risks, which could even endanger the mother’s life. Sexual: Requires a male and female of the species to participate in bringing together a sperm cell and an egg cell to create a new living being. This form of reproduction combines the genetics of two members of the species Adapted from http://www.thefreeresource.com/asexual-reproduction-facts-benefits-types-and-resources Asexual reproduction does not involve the interaction of two sexes. This is the primary form of reproduction for single-celled organisms, as well as some plants and fungi. One form of asexual reproduction is the vegetative method common in plants, in which parts of the plant fall off and form new ones. Another type of asexual reproduction is called the fragmentation method, in which a new organism grows from a fragment of the parent, as can be seen in some species of worms and sea stars. Unlike sexual reproducers, which are the majority in the animal kingdom, those species that reproduce asexually pass on their entire set of genes to the next generation. One of the advantages of asexual reproduction is that a lone individual can produce a new population in a new territory. Furthermore, it is more reliable because it involves less steps, and less can go wrong. However, this is outweighed by the disadvantage as regards natural selection: Since the individuals in such a species are so similar genetically, none of them bear any survival advantages compared to others. This makes it more difficult for the species to evolve in response to environmental changes and leaves them much more vulnerable to diseases that could wipe them all out at once. What are the Advantages of Asexual Reproduction? Asexual reproduction is advantageous for species that tend to remain in one place, especially where the environments are stable and do not experience any rapid changes. Stability in the environment allows the species to continue to exist even if the gene pool remains static since the reproductive process is repeated through the same organisms that are essentially clones of their parents. Nonetheless, there are certain species such as spores that engage in asexual reproduction and are somewhat adaptable to new environments. Being small and light, and sometimes with thick walls for protection, spores can be carried to new environs as well. Asexual reproduction is also an efficient process as the organisms do not have to expend energy or time looking for a mate. Rather, they can asexually reproduce at will and as needed without any restrictions. The asexual reproduction process also does not utilize great amounts of energy, allowing for ongoing forms of asexual reproduction. Another advantage of asexual reproduction is that it is a fast process and usually involves the reproduction of a large number of offspring at once. An asexual organism’s capacity to reproduce constantly thus can lead to a rapid population growth of the species. While the species might not actually evolve in any way, asexual reproduction does allow such species to avoid forms of genetic mutations. Because they are reproducing clones, the offspring are genetically exactly like the parent, thus avoiding any inculcation of genetic deviations. It should be noted that asexual reproduction does not allow for varieties within the species since only clones are produced. While many offspring can be produced at any given time, there might be overcrowding and a greater struggle for survival among the species. As no variants are reproduced, asexually reproduced species are less able to adapt to any possible new changes in the environment. Adapted from http://www.thefreeresource.com/asexual-reproduction-facts-benefits-types-and-resources What are the Four Types of Asexual Reproduction? There are different forms of asexual reproduction. One is budding, whereby the offspring grows out of the parent’s body. This is common in jellyfish and coral as a form of asexual reproduction. Another is gemmules, or the creation of internal buds, whereby the organism releases a mass of cells that develops into an offspring. Sponges use this form of asexual reproduction. Fragmentation is another form of asexual reproduction involving the parent breaking up into different pieces from which are produced additional offspring, who in turn can also fragment into additional offspring. Certain types of small worms engage in this form of asexual reproduction. In some organisms, should a parent lose a piece of its body, there is the capacity to grow another organism from that piece. Called regeneration, it is a form of asexual reproduction that is used by starfish. Parthenogenesis involves the production of eggs that do not need to be fertilized in order to create offspring. This occurs in certain species of fish, frogs, lizards and some insects. Plants such as yeast also engage in asexual reproduction. Binary Fission The first type is binary fission. This occurs when one cell splits into two smaller cells each of which eventually grow into a full-sized cell itself. First, the DNA of the organism is duplicated. Then the two groups of nuclear material migrate to opposite sides of the cell. The cell membrane or cell wall grows inward, splitting the cell into two daughter cells, each having a nuclear body. Examples of organisms that use binary fission are all prokaryotes (cells without a membranebound nucleus) and some protozoa. Budding The second category is budding, wherein a new organism grows from the parent organism, remaining attached as it grows. In some species, such as jellyfish, the buds break away once they reach a certain size. They continue to live their own existence. But in other species, such as coral, the buds remain attached to the parent with a resulting colony of organisms. Fragmentation Yet another type of asexual reproduction is fragmentation. In this process, a new organism is able to grow from a fragment of the original one. Each of these pieces then matures into a fullsized organism. Examples of fragmentation are starfish. If the arm of a starfish is broken off, for example, that arm will grow into a new starfish. Another example is certain worms that break into a number of pieces once they reach a certain size. From each piece, a new worm arises. Parthenogenesis Parthenogenesis is another type of asexual reproduction. It is used by some species of lizards, insects such as certain types of ants, bees and wasps, some kinds of crayfish, sharks and even turkeys. An egg cell, without being fertilized, develops into a new organism. Adapted from http://www.thefreeresource.com/asexual-reproduction-facts-benefits-types-and-resources Vegetative Reproduction While most plants reproduce sexually, they all have the capability of reproducing asexually through vegetative reproduction. This involves using the leaves, stems or roots to produce new plants, instead of using the seeds or spores. A part of the parent plant is cut off and placed into water or soil. It then grows into a new plant. Sporogenesis Some algae and fungi use spore formation to reproduce asexually in a process known as sporogenesis. The fungus which produces penicillin, used as an antibiotic, is an example of this. Male Apomixis A rare form of asexual reproduction is male apomixis. This is found in the Saharan Cypress which can grow to a height of more than 60 feet. Its seeds come from the pollen exclusively, without any genetic input from a female. This type of tree is on the critically endangered list. It does not have a high reproductive rate, partially due to the manner in which the pollen cells divide. Instead of the neat division of binary fission, the cells divide into daughter cells that contain anywhere from no sets of chromosomes to four sets of chromosomes. Only those cells with two sets are able to germinate. To date, seven forms of asexual reproduction have been identified. Continued research may reveal even more. Adapted from http://www.thefreeresource.com/asexual-reproduction-facts-benefits-types-and-resources