Plate Boundaries Chart
advertisement
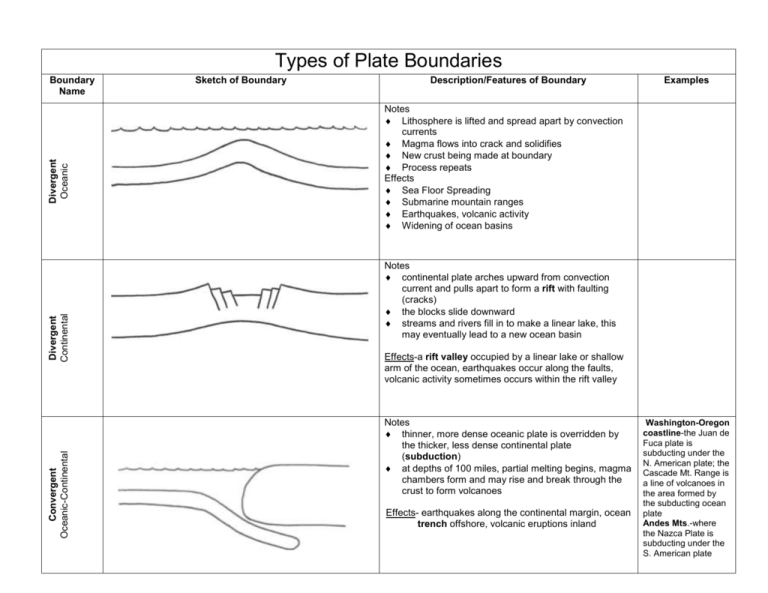
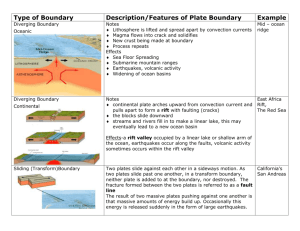
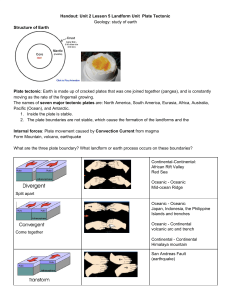
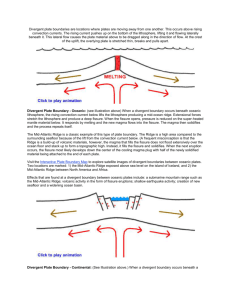
Types of Plate Boundaries Convergent Oceanic-Continental Divergent Continental Divergent Oceanic Boundary Name Sketch of Boundary Description/Features of Boundary Examples Notes Lithosphere is lifted and spread apart by convection currents Magma flows into crack and solidifies New crust being made at boundary Process repeats Effects Sea Floor Spreading Submarine mountain ranges Earthquakes, volcanic activity Widening of ocean basins Notes continental plate arches upward from convection current and pulls apart to form a rift with faulting (cracks) the blocks slide downward streams and rivers fill in to make a linear lake, this may eventually lead to a new ocean basin Effects-a rift valley occupied by a linear lake or shallow arm of the ocean, earthquakes occur along the faults, volcanic activity sometimes occurs within the rift valley Notes thinner, more dense oceanic plate is overridden by the thicker, less dense continental plate (subduction) at depths of 100 miles, partial melting begins, magma chambers form and may rise and break through the crust to form volcanoes Effects- earthquakes along the continental margin, ocean trench offshore, volcanic eruptions inland Washington-Oregon coastline-the Juan de Fuca plate is subducting under the N. American plate; the Cascade Mt. Range is a line of volcanoes in the area formed by the subducting ocean plate Andes Mts.-where the Nazca Plate is subducting under the S. American plate Convergent Continental-Continental Convergent Oceanic-Oceanic Boundary Name Sketch of Boundary Description/Features of Boundary Notes one oceanic plate will subduct, remelt at depths near 100 miles; magma chambers that are produced may start to rise and break through the surface to form a volcano; the cone will be below sea level but may eventually grow higher; produces an island chain and in time the islands grow larger and an elongated landmass is created Japan, Eastern Caribbean islands of Martinique and St. Lucia Effects- earthquakes, oceanic trench, volcanic islands Notes powerful collision occurs deformed rock, folding and faulting of plates 100’s of miles into the plate Effects-intense folding, broad folded mountain range, earthquake activity, shortening and thickening of the plates in the collision zone Notes two plates slide past one another the fracture zone is known as a transform fault Transform Examples Effects-locations of recurring earthquake activity and faulting, volcanic activity is normally not present Alpine Fault of New Zealand