Handout Unit 2 Lesson 5 Landform Unit Plate Tectonic
advertisement
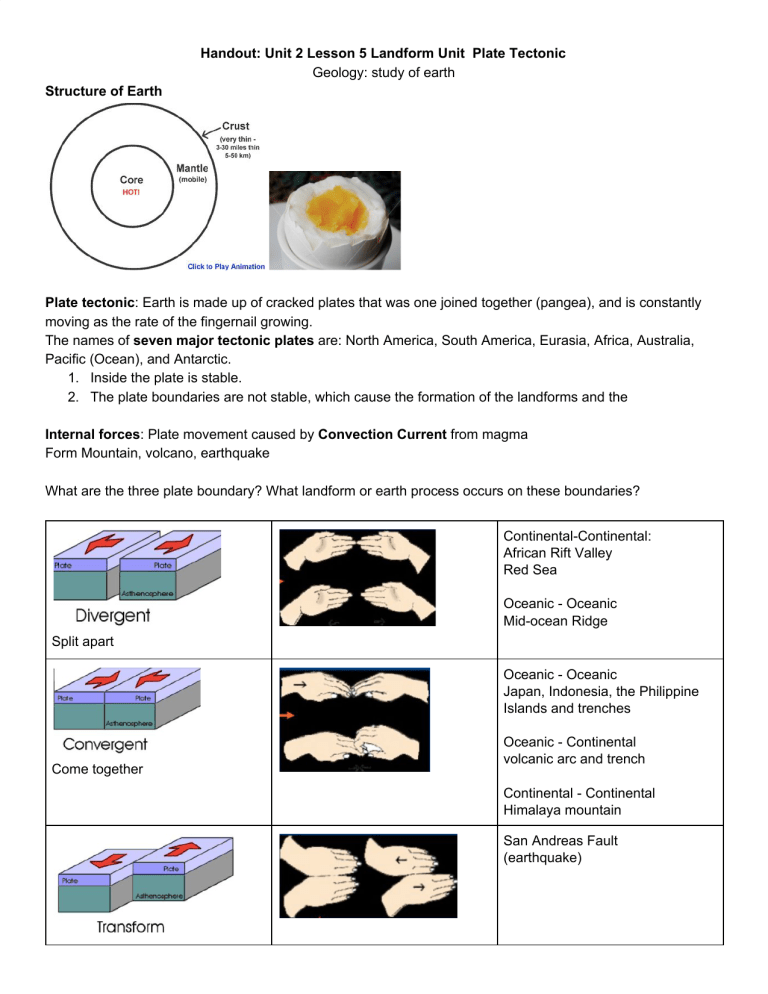
Handout: Unit 2 Lesson 5 Landform Unit Plate Tectonic Geology: study of earth Structure of Earth Plate tectonic: Earth is made up of cracked plates that was one joined together (pangea), and is constantly moving as the rate of the fingernail growing. The names of seven major tectonic plates are: North America, South America, Eurasia, Africa, Australia, Pacific (Ocean), and Antarctic. 1. Inside the plate is stable. 2. The plate boundaries are not stable, which cause the formation of the landforms and the Internal forces: Plate movement caused by Convection Current from magma Form Mountain, volcano, earthquake What are the three plate boundary? What landform or earth process occurs on these boundaries? Continental-Continental: African Rift Valley Red Sea Oceanic - Oceanic Mid-ocean Ridge Split apart Oceanic - Oceanic Japan, Indonesia, the Philippine Islands and trenches Come together Oceanic - Continental volcanic arc and trench Continental - Continental Himalaya mountain San Andreas Fault (earthquake) Slide sideways External (outside) Force: Caused by water, wind, sunlight Weathering, erosion and deposition Find the plate boundaries in the diagram. Activity: Gram cracker Boundary Demonstrate a convergent, divergent and transform boundary What does Gram cracker represent? What does whip cream represent? Volcanic eruptions Volcanoes are mountains with openings in Earth’s crust through which magma, gases, and ash reach Earth’s surface. When the magma erupts from the volcano the top of the mountain can be changed, either built up or exploded off. The lava and ash can destroy forests and bury fields. Volcanic eruptions can even change Earth’s weather patterns. Volcanic eruptions also occur under the oceans; these volcanoes that are built up are called Seamounts. If the seamount rises above the ocean surface it is called a volcanic island (for example Hawaii or Japan). Activity: Play-doh Volcano What causes the volcanic eruption? Earthquakes Earthquakes are vibrations on Earth’s surface caused by sudden movement in Earth, often along a fault ,a break in Earth’s surface. Some earthquakes cause little damage and some cause a lot of damage. Large earthquakes can cause landslides. Earthquakes under the ocean can cause huge waves, called tsunamis t hat destroy land and cause great damage if they come ashore. STEM Activity: Paper model on Earthquake Fault Landslides Landslides are mass movements of land due to gravity. Landslides can cause buildings to fall, or power and gas lines to break. Landslides even occur on the continental slope in the ocean. Google Earth Project Pick one landform and find it in google earth, mark the latitude, longitude and attitude. What boundary is the landform at? Find an interesting fact about the landform. Hawaii island Japan island Himalaya Mountain Mariana Trench Mid-ocean Ridge African Rift Valley Red Sea San Andreas Fault 1. Locate This map shows Earth’s plates on your textbook, Find the plate you live on. What is the name of that plate? 2. SEP (Science & Engineering Process) How fast do the plates actually move? Why are their borders jagged? These are just some of the many questions we could ask about these plats. Good scientific questions can give us ideas for scientific investigations. Write two question you might have about Earth’ plates. Try to think of questions that can be answered through research. 1. CCC (Cross-cutting Concepts) Cause and Effect What might cause a rapid change in Earth’s surface? 2. Classify Read about the land feature in the diagram. Then write the type of plate boundary that forms each feature. 3. SEP Construct an Explanation Use the illustration on these pages and tell about the results of constructive and destructive forces. 4. Explain Do you think the volcano in this picture is an example of a constructive or deconstructive force? Explain. 5. Sequence What is often the first step in the formation of a volcano? https://www.learner.org/interactives/dynamicearth/structure/






![PLATE_TECTONICS_Final[1].doc](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/015313348_1-7ec864f97697e782157c2eaf1e3db4d9-300x300.png)