General Biology I: Final Exam Study Guide
advertisement

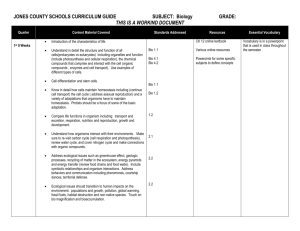
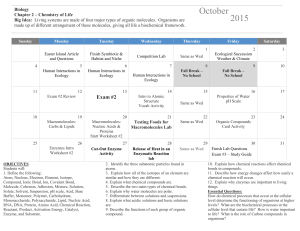
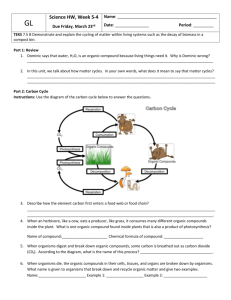
General Biology I: Final Exam Study Guide 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. Review the scientific process: Name ____________________ What is the typical sequence of scientific processes? What kinds of variables are involved in experimentation? What is a control? What is reductionism? Its disadvantages? Living organisms: Have what general characteristics? Have what levels of organization in multicellular organisms? Are mostly composed of what elements? Maintain internal balance by what process? Survive on earth by what two basic strategies? Review basic atomic structure: subatomic particles (location, charge, relative mass) filling of energy levels (higher energy electrons where?) Review the chemistry and properties of water. What is ATP? Review the chemistry of carbon and its compounds: What are the basic categories of organic compounds? What are the functions of the organic compounds? How are organic compounds formed? Broken down? What is the cause/significance of polypeptide shape? What elements are predominant in organic compounds? Review cell structure: What is the difference between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell? What structures to all cells have? What are the organelles and their functions? Why are cells generally small in size? What roles are carried out by the plasma membrane? Review cell transport: What is diffusion? Osmosis? Active transport? Facilitated transport? Endo/exocytosis? What are hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic solutions? Effects on cells? What determines the ability of a substance to enter or leave a cell? What are the parts of the cell theory? Review the types of reactions in living things: How do we define oxidation? Reduction? Energy transformations involve loss as what? What role do enzymes play in cell reactions? Factors? What are the roles of coenzymes? Review photosynthesis and cellular respiration: What are the reactants/products of each? What types of organisms carry out the reactions? What section of the EM spectrum is used during photosynthesis? What is the function of fermentation? Review cell divisions: Review chromatin and chromosome structure and numbers. What are autosomes? Sex chromosomes? What are the roles of mitosis and meiosis? What cells are diploid? Haploid? How does plant mitosis differ from that in animals? What is the significance of crossing over? What is cytokinesis? Review basic genetics: Mendel had what contributions? Review his work. Be able to predict the outcome of offspring in simple crosses. Review the patterns of inheritance. What patterns of inheritance are observed in humans? Examples? What is genotype? Phenotype? What is a carrier? What are the major functions of the genetic material? Review the historical process that established DNA as the informational molecule. What is the central dogma of biology? Review DNA and RNA: Components and arrangement? What is the bonding pattern between the bases? Review the processes of replication, transcription, and translation. How might the genetic code be described? Review gene regulation: How are genes switched “on and off” in prokaryotes? Eukaryotes? What is the role of genetic material in cancer development and control? 19. Review genetic engineering: What are the roles of vectors? Restriction enzymes? Gel electrophoresis? What are transgenic organisms? Present and future uses of them? What is transformation? Review: RFLPs, DNA fingerprinting, PCR 20. Review evolution: What scientists contributed to the development of the theory? Role of mutation? What is a population? Reducing atmosphere? Organic soup? 21. Under what conditions will the Hardy-Weinberg principle hold true? 22. Review the basic taxonomic system. What kinds of organisms are in the various domains and kingdoms. 23. What is the basic composition of a virus? Are antibiotics effective in the treatment of them? Why or why not? 24. What are the basic shapes of prokaryotes? Are antibiotics used in treatment of bacterial infections? What is a current major medical concern in regard to bacteria? 25. What does it mean for an organism to be “pathogenic”? 26. Review the characteristics of eumetazoans. 27. What are arthropods? Are they present on earth in significant numbers? 28. What is the difference between an invertebrate and a vertebrate? Common examples of each? 29. What is meant by the term “cephalization” and why is it an advantage in an animal? 30. What is the most successful plant group on earth? Why? 31. What is ecology? What are examples of important geochemical cycles on earth? This project is funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community Based Job Training Grant as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration (CB-15-162-06-60). NCC is an equal opportunity employer and does not discriminate on the following basis: against any individual in the United States, on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, national origin, age disability, political affiliation or belief; and against any beneficiary of programs financially assisted under Title I of the Workforce Investment Act of 1998 (WIA), on the basis of the beneficiary’s citizenship/status as a lawfully admitted immigrant authorized to work in the United States, or his or her participation in any WIA Title I-financially assisted program or activity. This workforce solution was funded by a grant awarded under the President’s Community-Based Job Training Grants as implemented by the U.S. Department of Labor’s Employment and Training Administration. The solution was created by the grantee and does not necessarily reflect the official position of the U.S. Department of Labor. The Department of Labor makes no guarantees, warranties, or assurances of any kind, express or implied, with respect to such information, including any information on linked sites and including, but not limited to, accuracy of the information or its completeness, timeliness, usefulness, adequacy, continued availability, or ownership. This solution is copyrighted by the institution that created it. Internal use by an organization and/or personal use by an individual for non-commercial purposes is permissible. All other uses require the prior authorization of the copyright owner.