Chapter 1 Science
advertisement

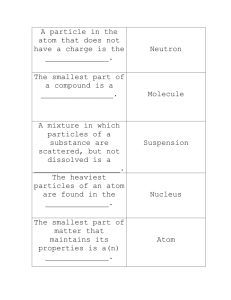
Name______________ Date_____ Chapter 1, lesson 1 What are the properties of ____________? Gold is an example of a * Elements: ______ _____________ Living things contain mostly ____________, ___________, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus. These few elements in many _________________ make up nearly _____________ known minerals on Earth. _____ of our body is carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. Our body is _______ oxygen. Oxygen is found in ___________, _____________, _____________, and ____________________________. Water: * Physical properties: Ex. Copper is shiny and solid ___________ = the amount of ____________ in an object. ___________ = the pull of gravity (scale) * Chemical properties: Ex. Wood burns and makes ash and gasses. Name______________ Date_____ Chapter 1, lesson 1 What are the properties of matter? Gold is an example of a Pure element. * Elements: are building blocks of matter They cannot be broken down into smaller pieces. Living things contain mostly carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen, sulfur, and phosphorus. These few elements in many combinations make up nearly 3,500 known minerals on Earth. 96 % of our body is carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. Our body is 60% oxygen. Oxygen is found in water, proteins, sugars and fats in our body. Water: is the most important substance to all living things. * Physical properties: what can be seen or measured without changing a material. Ex. Copper is shiny and solid Mass= the amount of matter in an object. Weight = the pull of gravity (scale) * Chemical properties: tell how the substance forms new substances when it mixes with something else. Ex. Wood burns and makes ash and gasses. Name______________ Date_______ Chapter 4, Lesson 2 What makes up matter? Diagram of an ___________ All __________ is made of atoms. Atoms are ___________ of elements. __________ combine to form _______________. *Atom: The __________ of an atom determines how the element can combine with other ____________. Pure substances such as aluminum are made up of _________ ________. Nucleus: Neutrons: Protons: Atoms are made of ___________ ________. (__________, _________, __________, and ____________) * Atomic number: Electrons: Diagram of a ____________ *Molecule: A molecule is the smallest part of a ____________ made from more than one _______ that still has the ______________ of that substance. Name______________ Date_______ Chapter 4, Lesson 2 What makes up matter? Diagram of an atom All matter is made of atoms. Atoms are particles of elements. Atoms combine to form molecules. *Atom: smallest particle of an element that has the same properties of the element. The structure of an atom determines how the element can combine with other elements. Pure substances such as aluminum are made up of tiny atoms. Nucleus: The center of the atom Neutrons: No electrical charge Protons: Positive charge Electrons: Negative charge Diagram of a molecule Atoms are made of smaller parts. (nucleus, neutrons, protons, and electrons.) * Atomic number: the number of protons in a nucleus. The atomic number is the element’s most important property. *Molecule: are formed when atoms combine. A molecule is the smallest part of a substance made from more than one atom that still has the properties of that substance. Chapter 4, lesson 2 continued _________ ___________ *Periodic Table: Similar properties are __________ ____________ _____________ of one or two letters. Each __________ is made of one kind of _________ Metals: Nonmetals: Each column is a group or _________ and has similar _________________. Metalloids: Metals such as gold and _________ are pure ___________ and made of one kind of _________. Metals that are not pure elements are made of ________ than one kind of _________. __________ are made of mixing a metal with another ___________. (steel is made from iron and _________). Chapter 4, lesson 2 continued Periodic Table of Elements Metals: usually solid, good conductors of electricity, may be hammered Nonmetals: brittle, poor conductors of heat and electricity Metalloids: some properties of both *Periodic Table: Elements are in order by atomic number and chemical properties. Similar properties are grouped together. Symbol of one or two letters. Each element is made of one kind of atom. Each column is a group or family and has similar properties. Metals such as gold and copper are pure elements and made of one kind of atom. Alloys are made of mixing a metal with another element. (steel is made from iron and carbon). Metals that are not pure elements are made of more than one kind of atom. Ch. 1, Lesson 3 What are compounds? Example of a _______________ *Compound: Most things you see around you are ______________because compounds have _________________ made of more than one kind of _______________. ____________ Every compound has a ______________ that shows how many ___________ of each ________________ are in the compound. Ex. Water H20 ____ Hydrogen ____ Oxygen Salt ____________ form by ________________ making a ________________ pattern. Ex. Cube shape Sodium Chloride= _____________ Many kinds of __________. Salts are ______________ made of particles held together by ______________ _______________. The particles may be _________ atoms. Particles with more ___________ than protons have a ____________ charge. More _____________ = a _____________ _____________ Ch. 1, Lesson 3 What are compounds? Example of a Compound *Compound: Matter made of a combination of two or more elements. Most things you see around you are compounds because compounds have molecules made of more than one kind of element. Salt Every compound has a formula that shows how many atoms of each element are in the compound. Ex. Water H20 2 Hydrogen 1 Oxygen Salt crystals form by particles making a regular pattern. Ex. Cube shape Sodium Chloride= table salt Many kinds of salts. Salts are compounds made of particles held together by opposite charges. The particles may be charged atoms. Particles with more electrons than protons have a negative charge. More protons = a positive charge Ch. 1, Lesson 4 “How can we separate mixtures?” Example of a ______________ Sometimes ___________ and _______________ are mixed together but not ______________ _________________. *Mixtures: Ex. Soup You can ___________ the materials of mixtures. *Solutions: (To dissolve means to spread evenly and not settle to the bottom.) *Solute: Ex. chocolate syrup *Solvent Ex. milk *Solubility: Ch. 1, Lesson 4 “How can we separate mixtures?” Example of a Mixture Sometimes elements and compounds are mixed together but not chemically combined. *Mixtures: different materials are placed together but they keep their own properties. Ex. Soup You can separate the materials of mixtures. *Solutions: a special kind of mixture in which a substance is dissolved. (To dissolve means to spread evenly and not settle to the bottom.) *Solute: the substance that dissolves Ex. chocolate syrup *Solvent: the substance is which the solute is being dissolved Ex. milk *Solubility: physical property of a substance