Pulmonary Vascular Diseases

Pulmonary Vascular Diseases
Diseases
Definition
Causes
Clinical features
Pulmonary Edema
1.
Accumulation of fluid in lung parenchyme a.
Interstitium b.
Alveolar spaces
2.
Causing restrictive pattern of disease
1.
Heamodynamic disturbance
2.
Microvascular injury
Gross
1.
2.
Heavy
Congested
3.
Filled with frothy fluid
Microscopic
1.
Engorged capillary
2.
Microheamorrhage
3.
Hemosiderin laden macrophage
4.
Exudation
5.
Thickened alveolar wall
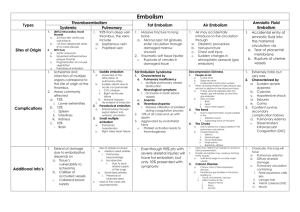
Pulmonary Embolism
1.
Blood that occludes large pulmonary arteries
2.
Embolism can be either a.
Massive (saddle embolism) b.
Medium c.
Small
3.
Embolism usually originated from a.
Deep veins of the legs especially Popliteal Vein
1.
A detached intravascular mass carried by the blood to a site in the body distant from its point of origin
2.
Can be either a.
Thrombi (most common) b.
Micellaneous i.
Fat embolism ii.
Air bubble iii.
Foreign body iv.
Tumour clump
1.
Massive embolism
(Saddle embolism) a.
Due to its massive blockage, patient dies instantaneously without even leaving an pathological mark on the lung
2.
Medium/small embolism a.
Followed by ischemia and eventually necrosis
Pulmonary Hypertension
1.
Increased in pulmonary pressure in which >1/4 of systemic pressure
2.
Most often secondary to a.
↓cross sectional of pulmonary vascular bed b.
↑pulmonary vascular blood flow
1.
Chronic obstructive/
Interstitial lung disease a.
Destruction of lung parenchyma b.
↓pulmonary vascular bed
2.
Recurrent pulmonary emboli a.
↓pulmonary vascular bed b.
↑vascular resistance
3.
Antecedent Heart Disease a.
Mitral stenosis
1.
Medial hypertrophy of arteries
2.
Thickening of the tunica
3.
4.
intima due to fibrosis
Artheromatous changes
Right ventricular hypertrophy
1.
Pulmonary Infarction
1.
Formation of tissue necrosis in the lung parenchyme due to lack of oxygen supply
2.
Characterized by coagulative type of necrosis
Obstruction of blood flow a.
Compressing tumor b.
Atherosclerosis
2.
Pulmonary embolism
Macroscopic
1.
¾ - lower lobes
2.
>½ – multiple
3.
Size – variable - barely visible to massive
4.
Shape – pyramidal (base toward the pleural
5.
surface and apex toward the hilum of the lung.
6.
Hemorrhagic, raised, red-blue area in the early stage
Microscopic
1.
Area of heamorrhage
2.
Infiltration of inflammatory cells
3.
Might present with abcess
Cor-Pulmonale
1.
Also called as pulmonary heart disease is enlargement of the right ventricle of the heart as a response to increased resistance or high blood pressure in the lungs
Acute
1.
Massive pulmonary embolism
Chronic
1.
COPD
2.
Primary pulmonary hypertension
3.
Pneomoconioses
Related to the pathological changes based on its causes