Objectives for pulmonary embolism discussion:
advertisement

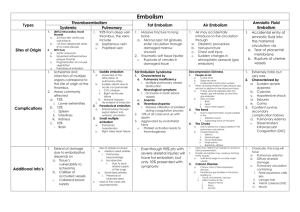
Resident Version Pulmonary Embolus Module created by Dr. David Garcia Objectives: 1) Become familiar with diagnostic algorithms used to evaluate patients suspected of having pulmonary embolism. 2) Develop an understanding of the various treatment modalities available to patients with pulmonary embolism. 3) Review the risk factors and pathophysiology associated with pulmonary embolism. 4) Be able to estimate (using a clinical prediction rule) the pre-test likelihood of PE in a patient presenting with symptoms of dyspnea or chest pain. 5) Be aware of the diagnostic clues for and the management of Heparin Induced Thrombocytopenia (HIT) References: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Wells PS, Anderson DR, Rodger M, et al. Derivation of a simple clinical model to categorize patients probability of pulmonary embolism: increasing the models utility with the SimpliRED D-dimer. Thromb Haemost 2000;83:416-20. Aujesky D, Obrosky DS, Stone RA, et al. A prediction rule to identify lowrisk patients with pulmonary embolism. Arch Intern Med 2006;166:169-75. Chagnon I, Bounameaux H, Aujesky D, et al. Comparison of two clinical prediction rules and implicit assessment among patients with suspected pulmonary embolism. Am J Med 2002;113:269-75. Perrier A, Roy PM, Sanchez O, et al. Multidetector-row computed tomography in suspected pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med 2005;352:1760-8. Buller HR, Agnelli G, Hull RD, Hyers TM, Prins MH, Raskob GE. Antithrombotic therapy for venous thromboembolic disease: the Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy. Chest 2004;126:401S-428S. Konstantinides S, Geibel A, Heusel G, Heinrich F, Kasper W. Heparin plus alteplase compared with heparin alone in patients with submassive pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med 2002;347:1143-50. Christiansen SC, Cannegieter SC, Koster T, Vandenbroucke JP, Rosendaal FR. Thrombophilia, clinical factors, and recurrent venous thrombotic events. Jama 2005;293:2352-61. Case: HPI: Pt is a 64 yo male with past medical history significant for hypertension and COPD, who presented to ER with 2 weeks of LUQ abd pain and chest pain. Pain was sharp and constant, with radiation to back, woke him from sleep, minimal relief with Pepto-Bismol. Some nausea, no vomiting or diarrhea, 10 lb wt loss, + itching, orange-colored urine, and weakness, all going on for past week. Admission work up indicated biliary obstruction, and CT scan of the abdomen revealed a mass in the pancreatic head. Subsequent ERCP diagnosed adenocarcinoma. Pt. clinically improved after stent placed, but on hospital day # 17 patient developed non-productive cough and pleuritic chest pain. Pt had been ambulating in hallways, on sc heparin, and denied calf pain. A picc had been placed in LUE on HD # 14 due to lack of iv access. Past Medical History: Chronic Back Pain Hypertension Hypertriglyceridemia Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Fibromyalgia (ICD-9-CM 729.0) Prostatitis (ICD-9-CM 601.9) Urinary obstruction (ICD-9-CM 599.6) Atypical Chest Pain (ICD-9-CM 786.59) Family Medical History: No family history of cancer, clots or DM. Social History: Served in the Air Force for ~25 years, as civil engineer and in Special Forces. Smoked 1 1/2 packs x 20 years, quit about 15 years ago. Drank from age 16-26, heavily on the weekends and while in Vietnam. Now has a beer or two a month. No IVDU. Two amateur tattoos. Exposed to Agent Orange while in Vietnam. Allergies: multiple BP meds, bactrim, statins, vicodin Medications currently: Tylenol Irbesartan Pantoprazole Ciprofloxacin Flagyl Benadryl Heparin 5000 units sc q 8 hours PE on HD # 17: Tm 98.9 bp 112/63 p 74 rr 20-28 02 sat 91-95% RA (all unchanged over last week) Gen: alert, oriented, mild distress, facial flushing, skin without jaundice Heent: Moist mucus membranes, no cervical adenopathy, no elevated JVP Lungs: coarse upper airways sounds, but no crackles, normal excursion, and prolonged expiratory phase bilaterally, no dullness to percussion, symmetric fremitus bilaterally. CV: reg, s1s2, no mrg heard, strong peripheral pulses, normal carotid upstroke Abd: normal bs, soft, mild tenderness to palpation RUQ, no obvious masses, liver at costal margin, spleen not palpable. Ext: L UE with picc line, no swelling, no edema. LE’s: negative homan’s sign, no erythema or tenderness, no cords palpated. Labs: wbc/hgb/hct/plt: 11.2/13.6/39.8/339 Chem 7 wnl, creat 1.2 LFT's: T prot 6.0, Alb 2.8, Alk phos 154, AST 43, ALT 53, Tbili 1.2 Lipase 1175 Inr 1.0 What is the next step in management of this patient? Outline for discussion: Risk factors for pulmonary embolism 1. trauma, major surgery (especially orthopedic or tumor resection) 2. acute medical illness, especially if associated with immobilization 3. pregnancy, exogenous estrogen therapy 4. "hypercoagulable state", especially antiphospholipid syndrome 5. active malignancy Pathophysiology of pulmonary embolism 1. typically caused by or associated with proximal deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities (can also be caused by proximal DVT of the upper extremities) 2. hypoxemia results from V/Q mismatch and/or "shunt" caused by a vasoconstrictor response seen in the pulmonary vascular tree 3. shortness of breath and/or cough may result from irritation of J receptors 4. hypotension and reduction in cardiac output may result from sudden increase in pulmonary artery pressures (hemodynamic collapse is more likely to occur in patients with pre-existing heart or lung disease) Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism 1. assess pretest probability [consider using a clinical prediction rule (1),(2,3)] - the absence of an alternative diagnosis to explain the patient's symptoms is important 2. for outpatients with a low pretest probability of disease, a normal d-dimer result excludes pulmonary embolism 3. D-dimer levels which are "abnormal" do not necessarily increase the probability of PE 4. for most patients whose pretest probability of disease is moderate or high, C. T. angiography of the chest should be ordered first (exceptions: for patients allergic to contrast by or at high risk of dye associated nephrotoxicity, a VQ scan may be preferable) 5. a negative CT scan excludes PE with adequate certainty in most patients (4) - if CT is negative and clinical suspicion is very high, one may consider compression ultrasonography of the legs as an adjunct test Treatment of pulmonary embolism 1. for patients with normal renal function, low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) or a pentasacchride (e.g. fondaparinux) are usually the treatments of choice (5) 2. note: because of insufficient evidence, outpatient therapy of acute pulmonary embolism cannot be recommended 3. unfractionated heparin (UFH) with a target PTT 1.5-2.5 times control is an effective therapy which may be preferable in some circumstances a. Patient is being considered for thrombolytic therapy (see below) b. Patient has a substantial risk for major bleeding (e.g. a postoperative patient) and the short half-life and easy “reversibility” of UFH may be advantageous 4. Thrombolytic therapy should be strongly considered for patients who have hemodynamic compromise and no obvious contraindications 5. Whether thrombolytic therapy should be used in patients without hemodynamic collapse remains controversial (6) 6. Surgical embolectomy should be considered in cases of massive pulmonary embolism with hemodynamic consequences where thrombolytic therapy is contraindicated 7. Inferior vena cava interruption is best reserved for patients in whom anticoagulation is absolutely contraindicated (e.g. a patient who suffers pulmonary embolism within several days of an operative procedure) 8. Any patient who experiences a new (or worsening) thrombosis (arterial or venous) while receiving heparin or LMWH therapy should be evaluated for heparin induced thrombocytopenia (HIT). Patients suspected of having HIT should have all heparin or LMWH products discontinued immediately. The hematology service should be consulted for alternate anticoagulation options. Considerations for long-term therapy of PE (5) 1. In cases of idiopathic or unexplained PE, warfarin (target INR 2.0-3.0) should be prescribed for a minimum of 6 months. 2. Anticoagulation for > 6 months should be considered in patients who a. have had more than one DVT or PE b. have a well documented “hypercoagulable state” (NB: the value of performing hypercoagulability testing in all or most patients is questionable (7)) c. have significant pre-existing heart/lung disease (these patients are more likely to suffer death or significant morbidity if they have recurrence after discontinuing warfarin) d. are ideal candidates for warfarin therapy (excellent adherence to monitoring, close follow-up, few drug-drug interactions, low risk for bleeding) 3. In cases where the PE has been ‘provoked’ by a time-limited risk factor (e.g. pregnancy, post-operative state, etc.), a shorter duration (e.g. 3 months) of warfarin therapy MAY be acceptable Review Questions 1. You are consulted about a 37 year-old woman who is on the trauma service. Several days ago she was involved in an automobile accident that resulted in multiple bone fractures and an emergent splenectomy. Four hours ago she developed pleuritic chest pain and dyspnea. Computed tomography of the chest demonstrates to filling defects in the main branches of the right pulmonary artery and a similar defect in a subsegmental branch of the left pulmonary circulation. On physical examination, the heart rate is 124 beats per minute, respiratory rate is 28 permanent and blood pressure is 89/60 mm Hg. Which of the following is the most appropriate intervention at this time? A. Tissue plasminogen activator B. Low molecular weight heparin C. Unfractionated heparin D. Inferior vena cava filter E. Echocardiography to look for right heart strain 2. A 27 year-old woman who underwent arthroscopic knee surgery one week ago presents to the emergency department complaining of right-sided pleuritic chest pain that began within the last 24 hours. She has a nonproductive cough but she denies fever or chills. She has mild dyspnea that she attributes to her inability to take a deep breath. She is taking ibuprofen for knee pain but she does not use any other medications. Her past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. On physical exam, the patient appears anxious but not acutely ill. Her heart rate is 86 BPM, the blood pressure is 116/84 mm Hg, her temperature is 38.1°. Pulmonary exam demonstrates normal breath sounds in all fields but there is some splinting on the right side. The incision over the right knee is healing well and there is no swelling or pain in the lower extremities. The white blood cell count is 13,000. Which of the following is the most appropriate at this time? A. B. C. D. E. transesophageal echocardiography ventilation perfusion scan helical computed tomography of the chest compression ultrasonography of the lower extremities quantitative D-dimer testing Post Module Evaluation Please place completed evaluation in an interdepartmental mail envelope and address to Dr. Wendy Gerstein, Department of Medicine, VAMC (111). 1) Topic of module:__________________________ 2) On a scale of 1-5, how effective was this module for learning this topic? _________ (1= not effective at all, 5 = extremely effective) 3) Were there any obvious errors, confusing data, or omissions? Please list/comment below: ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 4) Was the attending involved in the teaching of this module? Yes/no (please circle). 5) Please provide any further comments/feedback about this module, or the inpatient curriculum in general: 6) Please circle one: Attending Resident (R2/R3) Intern Medical student