i. function of the urinary system
advertisement

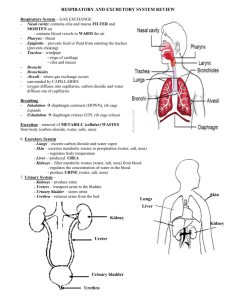
THE URINARY SYSTEM (pp. 985 - 989) I. FUNCTION OF THE URINARY SYSTEM A. Excretion - Excretion is the elimination of _waste products____ from _metabolism_______. The urinary system is the body’s main excretory system. When _proteins_______ are metabolized, a waste product called _urea____ is formed. If urea accumulates in the blood, it is _toxic_____. Urea is removed from the blood by the _kidneys_______, the main organ of the urinary system. B. Homeostasis - The urinary system maintains homeostasis in the body by monitoring the _composition___, _volume____, and pH of the blood. II. THE BLOOD WASHING PROCESS Oxygenated, “dirty” blood on its way to be washed leaves the _left ventricle___ of the heart by way of the _aorta_______ → _renal artery__ → _kidney_____. Each kidney contains approximately one million _nephrons____, the “washing machines” of the blood. A. Blood-Washing Inside the kidney blood enters a _nephron____ and _urea___ is filtered out of the blood. Although the blood is now “clean”, its oxygen has been used up by the kidney for _cellular respiration_____, so it must return to the _heart_____. The clean blood flows into the _renal veins____ → _vena cava___ → _right atrium______. B. Elimination of Urine The “dirt” that has been washed from the blood forms urine, consisting of _urea__ & other wastes. It is pooled with the urine produced in other _nephrons____, and leaves each kidney by way of tubes called the _ureters__ → _urinary bladder__ → _urethra___. The urinary bladder is a muscular sac that collects and stores urine until it is expelled from the body. When the urinary bladder is approximately _1/3____ full, a message is sent by way of a _sensory neuron_ to the _cerebrum_____. The urine ultimately leaves the body via the _urethra_____. THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM (pp. 997 - 1008) There are two systems that regulate the body. The nervous system relays information to the body using _electrical impulses__________________ that travel very _quickly______, but the messages are short-lived. The endocrine system uses _hormones________, or _chemical_______ messages that travel through the _blood____ to relay information to the body. The endocrine system is slower-acting, but the action of hormones is __longer-lasting___________. The _hypothalamus__________, which maintains homeostasis in the body, controls most of the glands of the endocrine system. I. HORMONES A. Hormone Production Most hormones are produced by _endocrine______ glands, secreted into _capillaries______, and transported by the _circulatory____ system to their destination. The destination is known as the _target_________. A hormone may have only one target, or it may have several. B. Control of Hormone Production Hormone release is regulated by a mechanism known as _negative feedback________. Information about the effect of the hormone is “fed back” to the gland …. when the desired condition is reached, the gland _shuts off______________ II. SELECTED GLANDS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Gland Location Hormone Pituitary Brain Growth Hormone Effect Stimulates _growth____; undersecretion results in _dwarfism_______; oversecretion results in _gigantism_____ Thyroid Base of Throat Thyroxine Regulates _metabolism_______; requires _iodine____ for normal function Pancreas Under Stomach Insulin Pancreas Under Stomach Glucagon Adrenal Glands Above Kidneys Epinephrine (also known as _adrenaline_) Testes Scrotum Testosterone Ovaries Either side of uterus Estrogen/ Progesterone _Decreases________ blood _glucose______ concentration by stimulating cells to take up glucose; triggers storage of glucose as _glycogen_________; not produced in individuals with _Diabetes mellitus, Type I________ _Increases________ blood glucose concentration by breaking down _glycogen______ stored in liver to glucose Known as _”fight-or-flight”____ hormone _Bronchioles____ dilate to increase air flow for __cellular respiration_______ _Glycogen____ in the liver is broken down to glucose for _cellular respiration____ _Heart____ rate is increased Blood flow to the _skeletal______ muscles increases Blood flow to the _digestive__ system is decreased Triggers development of secondary sex characteristics; _meiosis____ to produce _haploid____ sperm cells. Triggers development of secondary sex characteristics; __meiosis_____ to produce _haploid___ egg cells.