the urinary system
advertisement

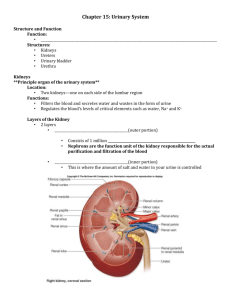
THE URINARY SYSTEM IDENTIFICATION OF TERMS – USE RED BOOK OR DEVICES Albumin Catheter Cytoscope Dialysis Enuresis Excretion Micturition Urea Parts of the urinary system A. ______________ – pair of bean-shaped organs located on the posterior abdominal wall behind the peritoneum at about the level of the first lumbar vertebra contains little filter’s called ____________________. B. _____________ – tubes extending from the kidneys to the urinary ___________. C. ________________ – muscularly bag in which _________ collects D. _______________ – tube passing from urinary bladder to ___________ of the body Functions of the urinary system A. Maintains ____________ by regulating the composition and _________ of the blood by removing and restoring selected amounts of ____________ and ________________. B. Maintains _________________ by influencing ____________________ of the blood C. Helps in ______________ processes 1.____________________ during times of starvation 2. secretes erythropoietin which stimulates the production of ________________ 3. participates in the synthesis of ___________________ (the active form of vitamin D) Formation of urine A. Blood flows to kidney by means of _________________ B. Waste products such as _______, ___________, ____________, and various salts are filtered from the blood by structures within the kidney C. The waste is called _______ and flows from the kidney by means of the _________ to the urinary ________________ D. The_________ blood returns to the ______________ blood Disorders of the urinary system A. _________ – complete urinary suppression or ________________ of kidney function B._____________ - inflammation of the ___________ usually occurring secondary to ascending urinary tract infections C. Diabetes Insipidus – ______________ and___________ caused by inadequate secretion of vasopressin (ADH) by the posterior pituitary gland (Neurohypophysis) D. Dysuria – ____________ urination E. ____________ – condition in which body tissues contain an excessive amount of tissue fluid F. Glycosuria – presence of _____________ in the urine G. _________________________ – inability to retain urine H. ____________________ – calculus or crystalline masses present in the pelvis of the kidney composed primarily of urates, oxalates, phosphates, and carbonates of varying size I. Nephritis – severe ____________________ of the kidney J. ______________________ – diminished amount of urine formed K. Polyuria – _______________ secretion and discharge of urine L. _____________________ – failure of the kidneys to perform their essential functions. Usually less than _______ of total kidney function M. ____________ – condition in which wastes normally excreted by the kidney are retained in the _________________ N. Urethritis – _____________________ of the urethra O. _____________________________________ – infections of the urinary tract (kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra) by microorganisms Dialysis and transplants A. _______________________ – treatment for patients who have defective kidney function. The blood is _____________________ by passing it through an artificial filter instead of the kidney B. ____________________________ – replacement of a diseased kidney with a healthy kidney provided by a ___________________.