초록_박미현
advertisement

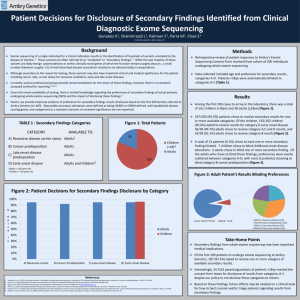
Whole exome sequencing combined with linkage analysis identifies N88S and novel S90W BSCL2 mutations in Charcot-Marie-Tooth families Mi-Hyun Park1, Hae-Mi Woo1, Byung-Ok Choi2, Ki Wha Chung3, Soo Kyung Koo1 1 Division of Intractable Diseases, Center for Biomedical Sciences, National Institute of Health, Cheongwon-Gun 363-951, Korea; 2 Department of Neurology, Ewha Womans University School of Medicine, Seoul 158-710, Korea; 3Department of Biological Science and Research Center for Biotechnology, Kongju National University, Gongju 314-701, Chungnam, Korea Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT) is a genetically and clinically heterogeneous hereditary disorder involving motor and sensory peripheral neuropathies. We investigated the diseasecausing mutation in two unrelated families with autosomal dominant axonal CMT neuropathy (FC51 and FC305) using exome sequencing in combination with linkage analysis, and we examined the genotype-phenotype associations. Through whole exome sequencing, we identified the average 20,152 coding variants from two individuals within each family. And we also identified the evidences of linkage mapped to chromosome 11p11-11q13.3 with LOD scores of 3.0 (FC51) and 3.6 (FC305), respectively. Among these variants in linkage region, we detected two causative heterozygous mutations (N88S and S90W) of BSCL2 gene, after filtering 31 Korean control exomes and integrating the results from the two individuals. The clinical features of families were confirmed by electrophysiologic and pathologic findings. Interestingly, patients of FC305 family with novel mutation (S90W) had similar sural nerve histopathologic features, showing a distinct difference from previous reported mutations. We demonstrate that exome sequencing is crucial for drawing more accurate genotype-phenotype evaluating, and it could be efficiently applied to the genetic diagnostic testing and counseling in a heterogeneous disorder. We also suggest that the identified mutation in BSCL2 expands the phenotypic spectrum of this gene.