Name Class
advertisement

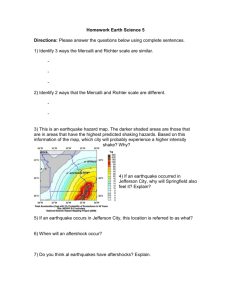
NB # ____________ Name ______________________________ Class _____________ DATE ___________ 1.) _Earthquakes occur when movement along a fault is quick and sudden 2.) The ___strength______ of an earthquake depends on the distance over which blocks of rock move 3.) Along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, two tectonic plates are moving away from each other. In this area, earthquakes likely occur along ____Normal Faults____ 4.) Compared to a shallow-focus earthquake, a Deep focus Earthquake____with the same magnitude and epicenter tends to cause less damage 5.) Secondary Waves____ can travel though rocks 6.) Three seismograms from different seismic stations are needed to locate an earthquake’s epicenter 7.) An earthquake’s epicenter is located directly above its focus 8.) Using the moment magnitude scale, an earthquake with a magnitude of 5 releases about how much more energy than a magnitude 4 earthquake? 32X 9.) Scientists can usually predict the earthquake risk of an area 10.) How could you reduce earthquake damage to a three-level parking garage by adding cross braces to the garage 11.) A mountain belt is formed when two continental plates collide 12.) Folded mountains form at tectonic boundaries where plate move toward each other 13.) Blocks of rock that have tilted along faults are common along Ocean spreading Centers 14.) A Volcano is an opening through which lava, rocks and gases erupt 15.) A Pyroclastic Flow is so dangerous because of its speed and temperature 16.) Volcanoes form at converging boundaries , diverging boundaries, and hot spots 17.) Rising temperature in volcanic lakes is a sign that might indicate that a volcano might soon erupt 18.) volcanic Ash clouds can be dangerous to people that live hundreds of km away from an erupting volcano 19.) An increase in acid rain and a decrease in Earth’s temperature are some of the effects of volcanic eruption on Earth’s atmosphere 20.) A fumarole releases steam and other gases For # 21 – 23, label each diagram with the type of fault that it represents. Draw arrows on the diagram to show the directions of stress that caused the faults. 21.) Normal Fault 22.) Reverse Fault 23.) Strike Slip For # 24 – 26, label each diagram with the type of volcano that it represents. 24.) Cinder cone 25.) composite cone 26.) shield volcano Using the drawings above, answer the following questions. 27.) Where are cinder cone volcanoes often found? On the sides of other types of volcanoes. 28.) Why are composite cone volcanoes taller than cinder cone volcanoes? Composite cones are larger because their structures are strengthened by hardened lava. 29.) What is the connection between a shield volcanoes shape and the lava that formed it? Shield volcanoes are formed when lava flows onto Earth’s surface. Because it flows easily it can spread out to form many thin layers. These thin layers crate gently sloping sides. 30.) Which volcano will most likely erupt violently? Explain. Composite because trapped gasses in the rising magma and because their openings may have been plugged by hardened lava from earlier eruptions.