H16 - WordPress.com
advertisement

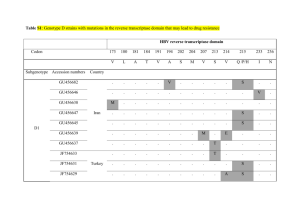
Molecular analysis of β-globin gene mutations in UKMMC using multiplex amplification refractory mutation system and flow-through hybridization kit: A comparison of two methods. NORUNALUWAR Jalil BSc (HONS)1, Khairiliah AUSIKHIN Khairuman3, RUSILAWATY Abdullah3, Raja Zahratul AZMA MBBS, MPATH2, EMIDA Mohamed PhD3, HAFIZA Alauddin MBBS, MPATH2, AZLIN Ithnin MBBchBAO, MPATH2, ZARINA Abdul Latiff MBBS, MMed (Paed)3, HAMIDAH Alias MD, MMed (Paed)3, RAFEAH Tumian MD, MMed4, Noor FARISAH Abdul Razak BSc (HONS)1, MALISA Mohd Yusoff Dip MLT1 and AINOON Othman MBBS, Dr Med Sc1,6 Departments of 1Laboratory Diagnostic Services and 2Pathology, UKM Medical Centre, Kuala Lumpur. 3 Department of Medical Laboratory Technology, Universiti Teknologi MARA, Puncak Alam. 4 Departments of Paediatric & 5Medicine, UKM Medical Centre, Kuala Lumpur. 6 Department of Medical Sciences II, Faculty of Medicine, USIM, K. Lumpur. Abstract Introduction: β-thalassaemia causes expression defects mainly by point mutations on chromosome 11. The aim of this study was to characterize β-globin gene mutations by using multiplex ARMS polymerase chain reaction (MARMS-PCR) as compared to flow-through hybridization (FTH) kit. Method: 56 β-thalassaemia cases were selected based on hypochromic microcytic red cell indices and raised HbA2 level. Mutations analysis was performed using nine primers of common β-globin gene mutations for MARMS-PCR and correlated with 25 mutations on designed FTH kit. Results: MARMS-PCR successfully detected β-globin gene mutations in 49/56 (87.5%) of samples. 24/49 (49.0%) were due to the common IVS 1-5 and Cd 41/42 mutations. The rest were IVS 1-1, Cd 17, Cd 26, IVS 2-654, Cd 8/9 and -28. There was one patient with compound heterozygous for Cd 41/42 and Cd 26 mutation. Seven samples are negative for the mutations tested. FTH results were in agreement with MARMS-PCR in 47 cases, except for the two cases where Cd 8/9 mutation was not part of FTH panel. FTH detected additional mutations (51/56 cases (91.1%)) as the panel incorporated more mutational primers in. These comprised del45, 619bp del and polyA mutation. However, 619bp del was needed for a further reference test which is sequencing as a confirmation since it was not common. Some of these mutations were seen to be compoundly inherited with other more common β-globin gene mutations hence more severe phenotypes of the affected patients. Discussion: Both MARMS-PCR and FTH techniques are reliable and laborious, but FTH is able to detect 25 mutations in the single test for one patient. However, hybridization is costly for large sample sizes. Thus, MARMS-PCR is more cost effective to characterize the spectrum of β-thalassaemia mutations. Keywords: ß-thalassaemia mutations, MARMS-PCR, Flow-through hybridization