8-7 Notes to go with power point
advertisement
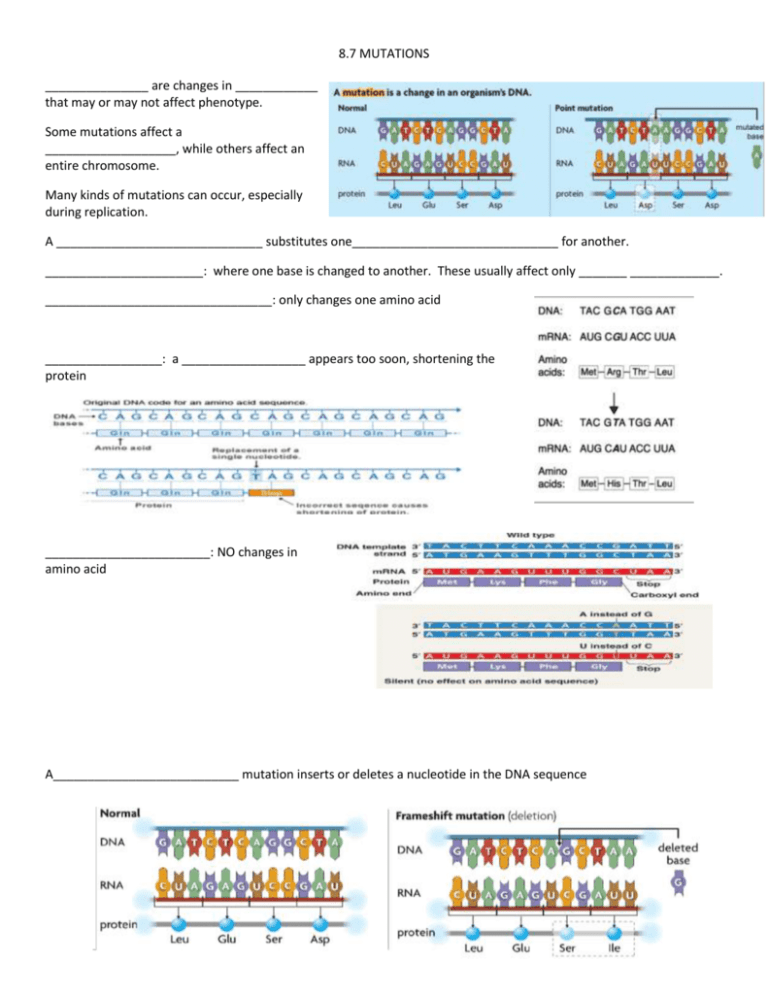
8.7 MUTATIONS _______________ are changes in ____________ that may or may not affect phenotype. Some mutations affect a ___________________, while others affect an entire chromosome. Many kinds of mutations can occur, especially during replication. A ______________________________ substitutes one______________________________ for another. _______________________: where one base is changed to another. These usually affect only _______ _____________. _________________________________: only changes one amino acid _________________: a __________________ appears too soon, shortening the protein ________________________: NO changes in amino acid A___________________________ mutation inserts or deletes a nucleotide in the DNA sequence These usually affect a ____________ part of the protein. Remember, bases are read in groups of three, but if one base is added or removed, this shifts the “reading frame” of the genetic code and can change __________________________ after the site of the mutation ______________________________________________: involve changes in the number or structure of the chromosomes. Can change the locations of genes on chromosomes ___________________: reverses the direction of parts of the chromosomes ____________________: part of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another. Can change the number of copies of some genes _________________: a part of the chromosome is lost ____________________: there is an extra copy of part of the chromosome Mutations may or may not affect phenotype. _____________________________ mutations tend to have a big effect. Mutations can be caused by several factors. _______________________________ can cause mutations. Mutagens, such as __________________ and ________________________, can cause mutations. Some cancer drugs use mutagenic properties to kill cancer cells.