Chapter 3 – Ocean Motion

Chapter 3 – Ocean Motion
3.1
Ocean Water
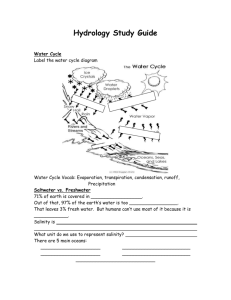
Origins of oceans – Earth’s surface had many different seismic activities occurring
volcanic eruptions – released water vapor, CO
2
, sulfur, etc into the atmosphere
vast amounts of meteorite impact o contained water crystals traveled from space
~ 4 billion ya
Cooled and condensed in clouds
Lots of rains occurred & formed oceans
Basins – low areas where water filled
Composition – 70% of Earth’s surface is ocean water
salts o Cl, S, Ca, Na, Mg, K o Come from dissolved elements from rocks & minerals o Carried to oceans by rivers
Salinity – most abundant elements in seawater
-
Na & Cl o Na
– rivers dissolving minerals o Cl
– from volcanic eruptions
Seawater evaporates
Na & Cl
form halite – salt to season food
Measures the amount of dissolved salts in seawater o g/kg of water o 1 kg of ocean water contains about 35g of dissolved salts
(~3.5%) o Equilibrium between salts dissolved
Element removal – new stuff added
element being removed
removed by becoming sediments & thru biological processes o sea animals & algae
form bones & shells (Ca)
Desalination – removal of salt from seawater
three ways o evaporation (collect water vapor) o electric current (collect salts) o freeze (salt doesn’t freeze)
3.2
Ocean Currents
Surface currents – move horizontally
powered by wind
cause huge circular patterns
related to circulation of wind on Earth
upper few hundred feet of seawater
sailors & plants depend on currents
Antarctic Circumpolar current is the strongest current
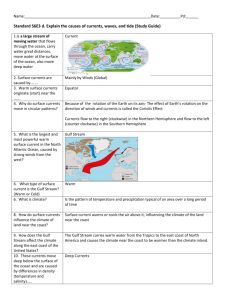
Gulf Stream o Records help us identify currents (1800’s) o 100 km wide o Was used to travel from NA to England o 1600’s – William Dampier wrote about the stream in
“Discoveries on the Trade Winds” o 100 yrs later, Ben Franklin published a map (received from
Gst. Tim Folger – whaler)
other factors o Coriolis effect – rotation of Earth causes this wind
Clockwise in N Hemisphere
Counterclockwise in S Hemisphere
Continents block this flow and create circular currents
Importance
can effect the climates of east & west coasts
West Coast East Coast
Cold current
Begins near poles
Cooler climate
Warm current
Begins near equator
Warmer climate
warmer waters release heat to the atmosphere – warms up- affects climate
water takes longer than land to heat up and cool down
Upwelling
– circulation in ocean that brings deep, cold water to surface
– Contains lots of nutrients from dead organisms
– Attracts fish to feed
– Places like Oregon, Washington, Peru, etc.
–
Typically off rocky coastlines
Density Currents
forms when more dense seawater sinks under less dense seawater
occurs deeper in the ocean
can increase or decrease in 2 ways: o salinity
o temperature
circulate slowly
Antarctica o Drop in temps freezes more water o Salinity increases o Water becomes more dense & sinks o Start spreading towards the equator o In Pacific – can take 1000 years to reach equator o In Atlantic – can take 275+ years
3.3 Ocean Waves & Tides
Waves – caused by winds, earthquakes, & gravitational force of sun &
Moon
a rhythmic movement that carries energy through matter & space
Wave movement
energy of wave moves forward but H
2
O particles stay in place
shallow places change shape of wave o more friction slows down wave o crest & trough come closer together o amplitude increases o less friction at top of wave than bottom allowing it to move faster o nothing underneath it so it collapses o called “breaker”
o gravity pulls H
2
O back to sea after it breaks
2 types of waves
Wind
- friction caused
- Increase wind, increase height
- Height depends on: speed of wind,
Distance over which it blows,
Length of time it blows
Tides
- Caused by a giant wave
- 1-2m high but
1000+ km long
- High/Low –
12hrs & 25min
- 2 High/2 Low –
24hrs & 50 min
Gravitational Effect of Moon
moon’s gravity exerts a pull
H
2
O responds to the pull
Bulge on opposite sides of Earth represents high tide
Earth rotates & bulges follow the moon o Different sections of the Earth goes through high & low tides
different places barely notice a change o ex. equator - H
2
O spread over a large area – can’t really tell difference in height of tide o smaller area would notice a greater change
Gravitational Effect of Sun
can increase or decrease the strength of the moon
alignment of the 3 bodies
Spring tides
higher high tides
lower low tides
Neap tides
high tides are lower
low tides are higher