6th Grade Earth Science: Water in Earth's Processes Syllabus
advertisement

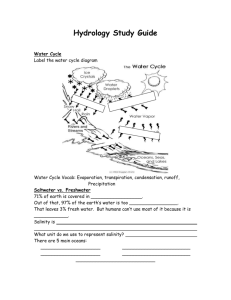
J.T. Reddick Middle School 6th Grade Earth Science Course Syllabus 2014-2015 Course: Unit 4 “Water in Earth’s Processes” Textbook: Prentice Hall Science Explorer – Georgia Earth Science (pages 314-317, 334-339, 432-433, and 530-531) Unit Overview: Students will understand and be able to explain the types of water on Earth, how it is distributed (sources of where each type is found), how the movement of water from the surface to atmosphere results from the transfer of energy around the planet, and how the movement of water through the crust, ocean, and atmosphere affects climate and weather. In addition, students will investigate and explain the formation and effects of various types of ocean water movement – waves, currents, and tides. Standards: S6E3. Students will recognize the significant role of water in earth processes. (Unit 4) a. Explain that a large portion of the Earth’s surface is water, consisting of oceans, rivers, lakes, underground water, and ice. b. Relate various atmospheric conditions to stages of the water cycle. c. Describe the composition, location, and subsurface topography of the world’s oceans. d. Explain the causes of waves, currents, and tides. S6E6. Students will describe various sources of energy and with their uses and conservation. a. Explain the role of the sun as the major source of energy and its relationship to wind and water energy. Objectives (What are OUR goals, and what will YOU learn in this unit?): 1. Explain how Earth’s water is distributed (types of water and locations/sources). 2. Explain what is meant by the term salinity. 3. Explain how the ocean became salty. 4. Explain how and why the salinity of cold ocean water and warm ocean water differs. 5. Explain how glaciation would affect the salinity of the ocean. 6. Describe the basics of the water cycle (know the energy source and processes involved). 7. Describe the basic characteristics of a wave. 8. Explain how ocean waves are formed. 9. Explain how ocean currents are formed. 10. Understand and explain how the interaction between the Earth, sun, and moon forms tides. 11. Compare and contrast spring and neap tides. 12. Compare and contrast ocean waves, currents, and tides. 13. Discuss water as a natural resource, and describe methods of conserving water. Assessments (Quizzes, Tests, Projects) Weekly Vocabulary Quiz (Formative) Concept Quiz “Distribution of Water and Water Cycle” (Formative) Concept Quiz “Waves, Currents, and Tides” (Formative) Unit 4 Summative Test (Summative) Unit 4 Culminating Project (Summative) – Create a “Pirate Training Manual” Vocabulary: underground water (groundwater) glaciation polar ice caps conduction convection radiation atmosphere condensation evaporation precipitation wavelength crest trough wave height current gulf stream Coriolis effect salinity tides conservation