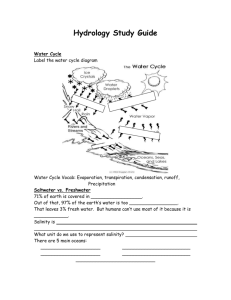
Salinity, Currents, and Tides Unit Test Review Sheet
advertisement

Salinity, Currents, and Tides Unit Test Review Sheet 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. 27. 28. 29. 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. 35. 36. 37. 38. 39. 40. 41. 42. 43. Why is water able to mix with other substances such as salt or sugar? List the properties of water that make it unique. What types of bonds hold water together? Why is this a weak bond? What colors of the spectrum get absorbed first and which ones the deepest? Give examples of polar and non-polar substances. Why is pH important to ocean organisms? What is the pH of the ocean? How do we express salinity as a measurement? What is the average salinity of the ocean? How is the salinity at the poles different from the salinity at the equator? What main gases are regulated in the ocean? Where is the oxygen minimum zone found? What role do bicarbonate ions play in the ocean? What two main factors control the density of the water? What is a zone of rapid temperature change called? Explain the Coriolis Effect in great detail. What force is mainly responsible for creating waves? What are Tsunamis? Describe the three types of tides. Explain the difference between spring and neap tides. How do they correlate with the phases of the moon? List five ways in which tides affect the ocean. How much later do tides occur each day? What is the difference between osmoconformers and osmoregulators? What are the three main gases in the ocean? What holds more gas cold or warm water? The amount of gas depends on what three factors? What percentage of sunlight is actually absorbed by the Earth? Why are surface currents important? What produces gyres? How many are there? List them. Which current is the strongest? How fast does it move? What two currents directly affect Florida? What are the main driving forces of surface currents? What four things control surface currents? What organism relies on the Gulf Stream for survival? A current can move fast or slow explain its oxygen and nutrient content. What is another name for the Global Conveyor Belt? What is the difference between upwelling and downwelling? Why is upwelling important? How much of the commercial fishery relies on upwelling areas? Why is downwelling critical to deep sea creatures? Where in the world has the most drastic tide? Why do tides occur? How often does the moon orbit the Earth? 44. When the moons gravity pulls the ocean towards the moon it causes a what? What happens on the other side of the earth?