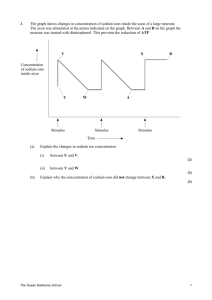
Synapses worksheet
advertisement

Volume 26, Number 2, November 2013 Activity Synapses Bill Indge Read the following passage. 5 Benzodiazepines are drugs that are widely used to treat anxiety and insomnia. They work by affecting the activity of a neurotransmitter called GABA. GABA is the most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain. In simple terms, benzodiazepines work by binding to GABA receptors present on the postsynaptic membranes of synapses. GABA receptors are examples of transmembrane ligand-gated ion channels. This results in an increased flow of chloride ions into the postsynaptic neurone. An increased influx of chloride ions affects the resting potential of the neurone so there is a larger difference between the resting potential and the threshold. The neurone is then less likely to generate an action potential. Treatment with benzodiazepines therefore helps to suppress worry, stress and anxiety. 10 The results of treatment with benzodiazepines mirror what you may see in a person who has been drinking ethanol. The action of ethanol on inhibitory GABA activity involves both the presynaptic and postsynaptic sides of the synapse. First, it increases the probability of vesicles fusing with the presynaptic membrane. Second, ethanol boosts the binding of GABA to its receptors on the postsynaptic membrane. 15 As well as increasing inhibition in the brain, ethanol decreases excitatory activity. Glutamate is the commonest excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain and is crucial for learning and memory. Ethanol acts on glutamate receptors and prevents the binding of glutamate. Glutamate cannot trigger the opening of the ion channels so excitation does not occur in the postsynaptic neurone. Use the information in the passage and your own biological knowledge to answer the following questions. 1 GABA receptors are examples of transmembrane ligand-gated ion channels (lines 4–5). Explain why. (3 marks) 2 (a) Explain the part played by sodium ions and potassium ions in establishing the resting potential in a neurone. (4 marks) (b) An increased influx of chloride ions affects the resting potential of the neurone (lines 6–7). Explain how. (2 marks) (c) A larger difference between the resting potential and the threshold results in a neurone being less likely to generate an action potential. Explain why. (3 marks) 3 Explain how the effects of ethanol on the presynaptic side of the synapse (lines 11–12) may affect GABA release. (2 marks) Philip Allan Updates © 2013 1 4 Memory loss can occur after drinking large amounts of alcohol. Use information in the passage to suggest an explanation for this memory loss. (2 marks) Suggested marking guidelines 1 (Transmembrane means that) the receptor spans the cell surface membrane; (Ligand-gated means that) the channel is opened by the binding of a specific substance, in this case GABA; (Ion channel means that) there is a pore running through the molecule through which ions such as chloride can pass; 3 A full answer to this part of the question requires an explanation of each of the three ideas — transmembrane, ligand-gated and ion channel. 2 (a) A lot of positive potassium ions diffuse out; Few positive sodium ions diffuse in; Therefore there are fewer positive ions inside the neurone; The inside of the neurone is now negative with respect to the outside; (b) 4 Chloride ions have a negative charge; This makes the resting potential more negative; 2 Recall on its own is of little value. To be really useful, it must be based on understanding. This question is designed to test understanding of the information required in part (a) of this question. (c) The same number of sodium ions entering; Will not reach threshold; Must reach threshold to generate action potential; 3 The first two elements to this answer might also be written in terms of requiring more sodium ions to reach the threshold. 3 GABA-containing vesicles are more likely to fuse with the presynaptic membrane; More GABA will be released; 2 The first step in this question is to locate the relevant material in the passage. It is better to express this idea in your own words rather than simply copying it out. 4 (The passage says that) ethanol prevents glutamate binding to receptors; No excitation of neurones associated with memory; 2 This question requires the use of information from the passage. It is a good idea to refer deliberately to the passage at some point in the answer. The question requires searching for the answer as there are no line references. Again, it is better to express this idea in your own words rather than simply copying it out. Philip Allan Updates © 2013 2