Test
advertisement

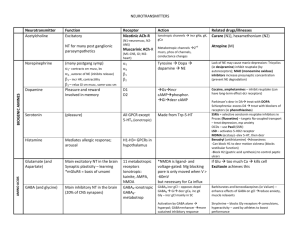
1 - Concerning new drugs that enhance the dopaminergic transmission in brain: A- They can be used as antipsychotics. B- They can increase prolactin secretion as a side effect. C- They can be used in treatment of parkinsonism. D- Both A & C. E- None of the above. 2 - Concerning new drugs that increase the levels of nor-epinephrine in brain: A- They can be used as antipsychotics. B- They can be used in treatment of depression. C- They may cause behavioral arousal and alertness. D- Both B & C. E- All of the above. 3 - Concerning new drugs that block cholinergic receptors in brain: A- They can be used in treatment of Alzeheimer’s disease. B- They may impair memory. C- They may used in treatment of parkinson’s disease. D- Both B & C. E- All of the above. 4- Concerning GABA receptors: A- Muscimol is a selective GABAB receptor agonist. B- Activation of GABAA receptors is associated with hyperpolarization due to opening of chloride channels. C- Barbituraes potentiate the action of GABAB receptors. D- Both A & B. E- None of the above. 5 - Concerning the use of new drugs that found to increase serotonin levels in brain: A- They can be used in treatment of depression. B- They are effective as antipsychotics. C- they may have anticonvulsant activity. D- Both A & B. E- All of the above. 6 – Which of the following mechanisms may explain the mode of action of antiepileptic drugs: A- Blocking GABA receptors. B- Inhibition of metabolism of GABA. C- Blocking glutamate (NMDA) receptors. D- Both B & C. E- All of the above. 7 - Concerning the expected side effects of centrally-acting new drugs: A- Drowsiness & muscle relaxation for drugs that enhance GABA action. B- Convulsions for drugs that block glutamate receptors. C- Hallucination & aggressive behavior for drugs that enhance GABA action. D- All of the above. E- None of the above. 8- Which of the following mechanisms may explain the effectiveness of new drugs that developed to treat depression? A- Inhibition of MAO enzyme. B- Inhibition of GABA-t enzyme. C- Inhibition of NE & 5-HT reuptake into central neurons. D- Both A & C. E- All of the above. 9- Concerning glycine neurotransmitter: A- Strychnine produces its convulsant effect by blocking GABA receptors. B- NMDA receptors are activated by glycine neurotransmitter. C- Drugs that block glycine receptors can be used as antiepileptics. D- Both A & C. E- None of the above. 10- Concerning GABA receptors: A- Baclofen is a GABAA receptor agonist. B- Bicuculine is a non-competitive GABAA receptor antagonist. C- Benzodiazepines are GABAA receptor agonist. D- Both A & C. E- None of the above. T F 1- Loss of dopaminergic neurons in basal ganglia may cause schizophrenia. T F 2- Drugs that increase central cholinergic transmission can be used to treat Alzheimer disease. T F 3- Drugs that block GABA reuptake into neurons can be used in treatment of epilepsy. T F 4- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors can be used in treatment of Parkinson’s disease. T F 5- Drugs that inhibit norepinephrine metabolism can be used in treatment of depression. T F 6- GABA agonists may cause convulsion as a side effect. T F 7- Anticonvulsant drugs may act by potentiating GABA action. T F 8- Dopamine antagonists may produce hallucination as a side effect. T F 9- 5-HT1A receptor agonists can be used to treat insomnia. T F 10- Drugs that block GABA can be used in treatment of anxiety.