qrs: it`s not complex ecg strips analysis
advertisement

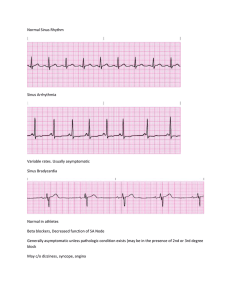
CARDIAC SESSION QRS: it's NOT complex ! Part 3 ECG Strips Analysis by Dr. Dan Ohad The following 3 strips (A through C) were recorded from a large, 9 year old mixed breed male dog with a chronic organic heart disease, with resultant progressive atrial enlargement. Strip B was recorded 3 months following Strip A, and Strip C was recorded 2 years later. All 3 strips were recorded in Lead II at 25mm/sec (10mm=1mV). What is your diagnosis for each strip? Also, we encourage you to send us any cardiac cases with which you need consultation: ECGs, radiographs, echograms, historical and physical examination findings are welcome. Cases of teaching value will be publicly discussed in this web site, with your permission About the Author Dr. Dan Ohad DVM - Koret School, Hebrew University. PhD - Hebrew University in applied cardiac electrophysiology Diplomate ACVIM Specialty of Cardiology Hints Hint for Strip B: There is an Atrial Premature Complex (APC) (labeled as "1"), seen as a seemingly "non-conducted" P w after the 5th QRS complex from the left. It is followed by another (seemingly "conducted") APC tha labeled as "2". In fact, the first P-wave ("1") is the one that is responsible for the following QRS complex contrast, the second premature P-wave ("2") found the AV-node still totally refractory, and therefore co not result in the following QRS. There is then a normal sinus beat ("3"), another APC ("4") that is follow by a normal sinus beat ("5"), and finally a run of "Paroxysmal Atrial Tachycardia". It is defined "paroxysmal" because its onset is sudden (right after the sinus beat labeled "5"), rather than gradual. Thi atypical of rhythms originating in the SA-node (such as sinus tachycardia), and is very typical of an ecto rhythm such as would originate in an atrial focus, away from the SA-node. This atrial ectopic activity prompted a therapeutic decision of using a Digitalis glycoside. Hint for Strip C: Note the absence of P-waves and the presence of flutter waves on the baseline (labeled as "f" waves). Th are regularly spaced (as opposed to fibrillation waves that would have been highly irregular, appearin unpredictable and chaotic and usually much shorter time-intervals). Although the ventricular (Q complexes seem irregular and unpredictable, as one would expect in atrial fibrillation, the R-to-R interva actually always an exact multiplication (in this case between 2 to 9 times) of the basic f-to-f interval. overall heart rate is within normal limits (rather than a typically fast ventricular rate during untreated a fibrillation or flutter) due to the chronic therapeutic control through Digitalis. Diagnoses Arrhythmia. Strip A: Normal Respiratory Sinus