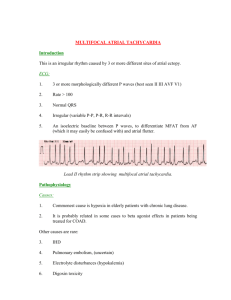
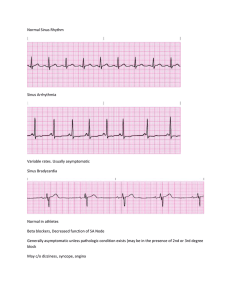
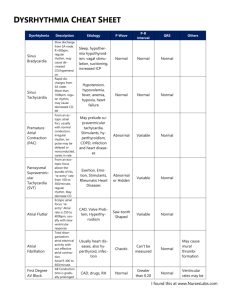
rhythms originating in the atria
advertisement

Any atrial area may originate an impulse. Rhythms have upright P waves preceding each QRS complex. Not as well-rounded Heart rates usually from 60 to 100 beats/min Atrial flutter Atria contract too fast for ventricles to match Resemble a saw tooth F waves get blocked by AV node, creating several F waves before each QRS complex Atrial flutter (cont’d) Caused by hypertension, coronary artery disease, and cardiomyopathy . frequently degenerates into atrial fibrillation . Symptoms include shortness of breath, chest pains, lightheadedness or dizziness, nausea and, in some patients, nervousness and feelings of impending doom. Treatment is usually medication or electrical cardioversion. Atrial fibrillation Atria fibrillate or quiver Random depolarization from atria cells depolarizing independently Adapted from Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD. Atrial fibrillation (cont’d) Irregularly irregular appearance . Usually signs of serious heart problem . Tendency to cause clots . Prehospital treatment is rare. paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) Called paroxysmal SVT (PSVT) because of tendency to begin and end abruptly Tachycardic rhythm from pacemaker Regular rhythm, rate exceeding 150 beats/min QRS complexes: 40 to 120 ms. May have cannon “A” waves Adapted from Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD. Premature atrial complex A particular complex within another rhythm Upright P wave precedes each QRS complex Adapted from Arrhythmia Recognition: The Art of Interpretation, courtesy of Tomas B. Garcia, MD. Premature atrial complex (cont’d) Non-conducted PAC: P wave occurs early on the ECG and is not followed by a QRS complex. PACs occur when another region of the atria depolarizes before the sinoatrial node and thus triggers a premature heartbeat. Wandering atrial pacemaker Wandering pacemaker is usually caused by varying vagal tone . With increased vagal tone the SA Node slows, allowing a pacemaker in the atria or AV Nodal area, which may briefly become slightly faster. After vagal tone decreases, the SA Node assumes its natural pace.Upright P wave precedes each QRS (at least 3 shapes of P waves within a strip) Wandering atrial pacemaker (cont’d) Most common with significant lung disease Multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT) Pacemaker moves within various atrial areas Rate of more than 100 beats/min Upright P wave preceding each QRS complex P waves vary. Multifocal atrial tachycardia (cont’d) PR interval: 120 to 200 ms Most common with significant lung disease, but it can occur after acute MI, hypokalemia, and hypomagnesemia Therapies for SVT generally ineffective The P-waves and P–R intervals are variable due to a phenomenon called wandering atrial pacemaker (WAP). Then, if the heart rate exceeds 100 beats per minute, the phenomenon is called multifocal atrial tachycardia.