Making sense of the ECG
advertisement

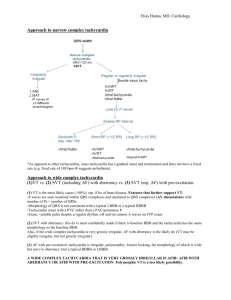
By Dr Saqib Mahmud MRCP(UK) MRCP(London) MRCGP Rate – normal, tachycardia or bradycardia Rhythm – sinus or irregular P waves present (II & V1 best leads to assess) PR interval QRS complexes & axis- widened QRS, Q waves, buddle branch block, voltage criteria for LVH ST segments – isoelectric, depression or elevation T waves – N, peaked or inverted What was the indication? age Symptoms-CP, palpitations, sob, syncope, dizziness Haemodynamically stable? Clinical signs- HF, poor peripheral perfusion Pre-morbid Hx-HTN, IHD, DM, CKD Medications- b-blockers, diltiazem etc Consider repeating for interval change Compare with previous ECG if available LVH – sum of S in V1 & R in V5 or V6 >35 RBBB – tall R in V1, QRS >0.12sec, R’sR pattern LBBB - QS-V1,V2, QRS>0.12 Axis - Axis leads-I&III or I&aVF, Normal axis- “double thumbs up’’(I&III+), RAD I –ve, III +ve, LAD I +ve, III –ve Inferior leads-------------II, III, aVF Antero-septal leads------V1,V2,V3&V4 Antero-lateral leads------I,aVL,V5,V6 Heart rate calculation-(rhythm regular) count the no of large squares b/w 2 consecutive QRS & divide into 300.HR=300/? Irregular – count no QRS in 30 large squares X 10 RBBB LBBB Thumbs up! Normal axis RAD LAD Sinus bradycardia Sick sinus syndrome 2nd or 3rd degree/CHB Escape rhythms- form of safety net to maintain heart beat if impulse generation fails or blocked Negatively chronotropic drugs – betablockers(don’t forget eye drops!), Ca antagonist; diltiazem, verapamil, digoxin Dizziness Syncope Recurrent falls in elderly Fatigue Breathlessness CP Palpitations O/E-look for hypotension, signs of HF & poor perfusion Relevant Investigations – U&Es , TFTs o o o o Narrow complex (<3 small squares) Broad complex (>3 small squares) Narrow complex tachycardias always supraventricular in origin Narrow complex tachycardias: Sinus tachycardia Atrial fibrillation Atrial flutter AV nodal re-entrant tachycardia Occurs if normal electrical impulses are abnormally or aberrantly conducted to the ventricles causing delay in ventricular activation & widening of QRS complex VT Torsades de pointes Accelerated idioventricular rhythm SVT with aberrant conduction Tachycardia causing hemodynamic disturbance requires urgent Rx Evidence of hemodynamic disturbance; Hypotension Cardiac failure Poor peripheral perfusion Investigations FBC U&Es TFTs BNP Hypothermia Hypothyroidism B-blockade Raised ICP Obstructive jaundice Uraemia Increased vagal tone Ischemia Structural SA node disease Sinus bradycardia Thyrotoxicosis Any cause of adrenergic stimulation including pain Hypovolaemia Anaemia Pregnancy Fever Myocarditis drugs;theophylines,salbut amol, vasodilator antihypertensives Sinus tachycardia Is it regular or irregular? Regular rhythms Sinus rhythm- P waves precedes every QRS complex with consistent PR interval Nodal or junctional rhythm- no P wave preceding QRS complex but narrow regular complexes Atrial flutter-saw tooth appearance, rapid & regular with a rate about 150bpm(2:1 block) SVT, AVNRT-if high rate 150-220bpm Sinus arrhythmia-P wave precedes QRS with constant PR interval but irregular The end Thank you