EKG Review - Rescue One
advertisement

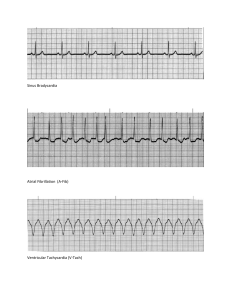
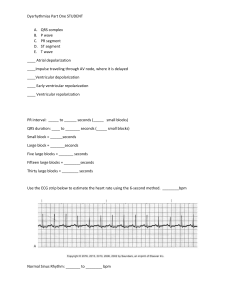
EKG Review Function of Heart • With any functioning unit you need: Electricity and Plumbing • ELECTRICITY: electrical current that stimulates the heart and tells it to beat or contract • PLUMBING: When the heart contracts it provides blood and oxygenation to vessels, tissue and organs • ***Keep in mind how electricity and plumbing affect each other!!! Electricity • SA AV Bundle of HIS BB PF • SA: 60-80bpm • AV: 40-60bpm • BH-BB: 20-40bpm “ACCIDENTS ON A HIGHWAY”- will be detoured around the blockage. increased distance to travel = increased time to get to location **Electrical current needs healthy tissue to conductdead tissue will not allow signal to pass through Plumbing Beats = contractions • Each beat requires atrial and ventricular contraction • Heart is like a sponge. It absorbs and squeezes out blood with each contraction. If it is not “rung out fully” with each squeeze- it cannot absorb it’s full potential. (preload, afterload) • Ventricular contraction- pushes blood into arteries to be sent to body, tissues, organs and lungs • Tissue needs oxygen and blood to survive. Without this, it cannot function Basic principals of EKG • Rate? FAST, SLOW, NORMAL • Complex? “P” in front of every “QRS” P- atrial contraction QRS- ventricular contraction qrs p T What is my rate: •Each Full complex is one beat •Most strips are 6 seconds long 1 2 3 4 (# of complexes in 6 sec strip) X (10) = Heart Rate (5 complexes) X (10) = 50 beats per minute 5 ARRYTHMIAS • Normal: 60-100 bpm • Slow: < 60 bpm • Sinus Bradycardia, Junctional • Fast: >100 bpm • Sinus Tachycardia, Supraventricular Tachycardia, VTach. -CARDIA : heart beat including contraction & relaxation Sinus Rhythm • Sinus rhythm is normal electricity and normal plumbing. • Electrical signal fires from ‘Sinus’ node. Rate is either slow, fast or normal. “P wave” is present in front of every “QRS” SLOW ARRYHMIAS • Sinus Bradycardia • SLOW sinus rhythm • Junctional Rhythm • “P” wave is inverted or absent FAST ARRYTHMIAS • Sinus Tachycardia • Fast sinus rhythm • Supraventricular Tachycardia • Supra-superior : “above” the ventricular • Rate is greater than 160 bpm, “QRS” is narrow. Ventricular rhythms • Ventricular Tachycardia • Tachycardia- firing from the ventricle • WIDE “QRS”, no “P” • Ventricular Fibrillation • Fibrillation or “quivering” of the ventricles- no contraction/relaxation. No organized rhythm Atrial Arrhythmias • Atrial Fibrillation • Underlying rhythm is sinus, with fibrillation between complexes/beats • Atrial Flutter • Look at sawtooth pattern between waves Asystole • No movement of heart muscle Just remember : “Dead meat don’t beat” EKG GRIDS Time (secs) V O L T A G E 5 Large blocks = 1 sec. on strip SMALL blocks: 0.04 sec LARGE blocks: 0.20 sec BLOCKS • Underlying rhythm is sinus, (must have P-QRS) • Normal P-R interval is .12-.20 sec (one big block) • • • • 1st degree: prolonged P-R interval (>.20) 2nd degree I: (WB) P-R gets longer, then drops beat 2nd degree II: more “P’s” than “QRS” (kids w/o parents) 3rd degree: total disassociation, no communication Premature Complexes • PAC- premature Atrial complex • P wave upright in front of QRS • PJC- premature Junctional complex • P wave is inverted or absent • PVC- premature Ventricular complex • Wide and bizarre, No “P” wave Other things to look at…. • S-T segment ***Classified as significant if > 1 mm • Depression- Ischemia or injury • Elevation- infarct or death of tissue **STEMI- is key point in ACS algorithm Pacemaker spikes • If Pacemaker is pacing the heart you will see a spike. To determine what is being paced, Look at location of spike Before P: pacing ATRIA Both- pacing both Before QRS: Pacing VENTRICLE