Standard Grade Biology
advertisement
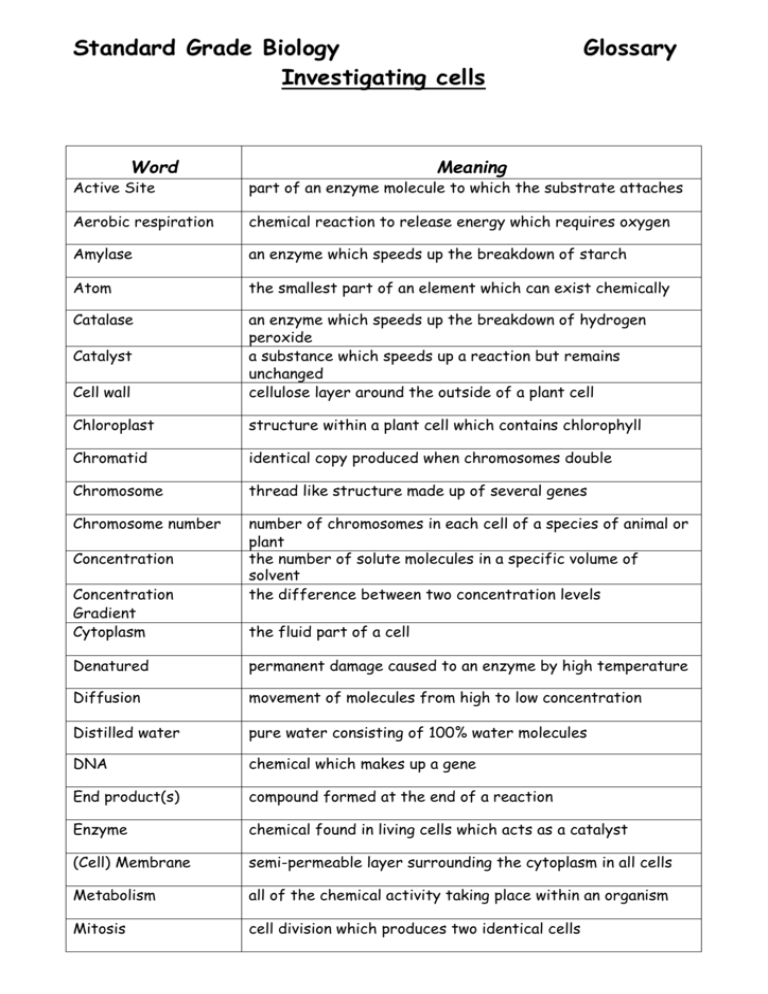
Standard Grade Biology Investigating cells Word Glossary Meaning Active Site part of an enzyme molecule to which the substrate attaches Aerobic respiration chemical reaction to release energy which requires oxygen Amylase an enzyme which speeds up the breakdown of starch Atom the smallest part of an element which can exist chemically Catalase Cell wall an enzyme which speeds up the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide a substance which speeds up a reaction but remains unchanged cellulose layer around the outside of a plant cell Chloroplast structure within a plant cell which contains chlorophyll Chromatid identical copy produced when chromosomes double Chromosome thread like structure made up of several genes Chromosome number number of chromosomes in each cell of a species of animal or plant the number of solute molecules in a specific volume of solvent the difference between two concentration levels Catalyst Concentration Concentration Gradient Cytoplasm the fluid part of a cell Denatured permanent damage caused to an enzyme by high temperature Diffusion movement of molecules from high to low concentration Distilled water pure water consisting of 100% water molecules DNA chemical which makes up a gene End product(s) compound formed at the end of a reaction Enzyme chemical found in living cells which acts as a catalyst (Cell) Membrane semi-permeable layer surrounding the cytoplasm in all cells Metabolism all of the chemical activity taking place within an organism Mitosis cell division which produces two identical cells Word Meaning Molecule two or more atoms joined together by chemical bonds Nucleus control centre of a cell Optimum conditions conditions in which an enzyme works most efficiently Osmosis diffusion of water molecules across a semi- permeable membrane Pepsin an enzyme which breaks down protein pH a measure of acidity/alkalinity Phosphorylase an enzyme which synthesizes starch Selectively permeable allows some molecules to pass through but not others Solute substance which is dissolved in a liquid Solvent liquid used to dissolve another substance Specific Activity each enzyme only acts on one substrate Spindle fibrous structure which pulls chromosomes apart Stain coloured dye used to show up cell structure more clearly Substrate the molecule on which an enzyme works Synthesis building up a larger molecule Vacuole cavity in the cytoplasm of a plant cell