File - AICE Biology
advertisement

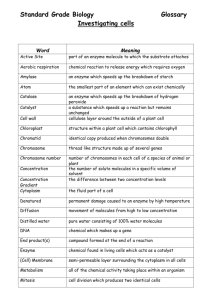
Katherine Loera Pd.5 AICE Biology Vocabulary Chapter 1: 1. Cytology- A branch of biology dealing with the structure of a cell, functions, multiplication, pathology, and life history of cell. 2. Cell Theory- Basic unit of structure and functions of all living things. 3. Electron Microscope uses electrons as source of radiation. 4. Membrane- Partially permeable 5. Light Microscope- Uses light as a source of radiation 6. Nucleus- Largest cell organelle stains intensely, controls activity of cell. 7. Organelle- Small structure with in cytoplasm, functionally and structurally distinct part of a cell. 8. Cell wall- Gives cell a definite shape, prevents cell from bursting by osmosis reinforce extra strength. 9. Plasmodesmata- Links neighboring plant cells by fine strands of cytoplasm passes through pore like structure in the walls. 10. Large Central Vacuole- Stores food and water 11. Chloroplast- Collects sunlight and transfers into energy 12. Tonoplast- Controls exchange between the vacuole and cytoplasm 13. Grana- Absorbs light in photosynthesis, in chloroplast, mainly in leaves 14. Nucleolus- Manufactures ribosome, using information from its DNA 15. Genes- Control the activity of the cell inheritance Chapter 2 1. Macromolecule- Giant Molecule 2. Peptide bond- the bond that is formed between amino acids 3. Hydrophobic- Dislike of water 4. Monosaccharide- Sugars that are building blocks of carbohydrates 5. Hydrophilic- water loving 6. Fibrous- Proteins form long strands and do not curl into a ball 7. Covalent Bond- Are types of bonds formed because of a sharing of electron 8. Isomers- Two forms of the same chemical 9. Condensation- process of two sugars joining together 10. Glycogen- is the storage of carbohydrates in animals 11. Starch- is the major form of glucose storage in plants 12. Amylose- made by condensation between a-glucose molecules 13. Triglyceride- when three fatty acids are combines with glycerol 14. Hydrolysis- Addition of water that breaks apart sugars 15. Saturated- Having the maximum number of hydrogen attached Katherine Loera Pd.5 Chapter 3: 1. Biological Catalyst – Enzymes which are protein 2. Active site – Region, usually cleft or depression to which another molecule or molecules bind 3. Substrate- The molecules that binds with enzyme 4. Enzyme-substrate complex- Temporary bond which form between the substrate and some of the r groups of the enzyme amino acid. 5. Products- the outcome when a substrate either joins or separates due to the interaction of R groups of enzyme and atom of the substrate. 6. Activation energy- Energy that is temporarily given to the substrate in order to convert into product 7. Initial Rate of reaction- the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction is always fastest at the beginning. 8. Denatured- when enzyme molecule begins to lose its shape and activity and is irreversible 9. Optimum Temperature- Temperature in which enzyme catalyses a reaction at the maximum rate 10. Inhibitor- this inhibits the enzyme function by blocking the binding of substrate with enzyme 11. Competitive inhibition- where inhibitor and substrate compete to bind with substrate and which ever has more concentration ends up binding with enzyme 12. Specific- the enzyme has an active site for a specific substrate 13. Non-competitive inhibitor- Enzyme function is blocked no matter how much substrate 9s present 14. End product- what controls an enzyme from running wild 15. Non-competitive irreversible inhibitor- no matter how much substrate there is the inhibitor is blocking enzymes function and is unable to be reversed. Chapter 4 1. Micelles- phospholipids shaken up with water they can form stable structures in the water 2. Bilayers- two-layered structure 3. Fluid Mosaic model- model for the structure of a membrane 4. Cholesterol- help regulate the fluidity of the membrane 5. Glycolipid- short carbohydrate chains 6. Receptor molecules- bind with particular substances 7. Diffusion- net movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to an area of low concentration 8. Facilitated diffusion- diffusion taken place between channels created by protein Katherine Loera Pd.5 9. Osmosis- the movement of water molecules from a region of higher water potential to lower water potential 10. Turgid- when plant cell is fully inflated with water 11. Plasmolysis- protoplast continues to shrink it begins to pull away from cell 12. Active transport- energy consuming transport of molecules 13. Endocytosis- engulfing of the material by plasma membrance 14. Phagocytosis- “CELL EATING” Uptakes solid material 15. Pinocytosis- “CELL DRINKING” uptakes liquid Chapter 5: 1. Nucleotides- the smaller molecules from which DNA and RNA molecules are made are nucleotides 2. Semi-conservative replication- original molecules is kept in each new molecule 3. Conservative replication- one completely new double helix qouls bw made from the old one 4. Dispersive replication- each new molecule would be made of old bits and new bits scattered randomly through the molecules. 5. Triplet- the code is a three letter code 6. Genome- total set of genes in a cell 7. mRNA- complimentary copy of the code from a gene is made by building a molecule of a different type of nucleic acid 8. Anticodon- triplet bases 9. Codon- complimentary triplet on the mRNA molecule 10. Transcription-making of mRNA molecule which carries a complimentary copy of the code from part of the dna molecule 11. Translation- when DNA is translated into an amino acid sequence 12. Hydrogen bonds- the two strands are held together by this bond between the bases 13. Complimentary base pairing- A with T, C with G, important of polynucleotides 14. Macromolecule- DNA and RNA, like protein and polysaccharides 15. Adenine, thymine, guanine and cytosine- nitrogen containing bases in DNA and RNA, in RNA there is no thymine but instead uracil. Chapter 6: 1. Chromosomes- Thread-like structures 2. Karyotype- Cutting out individual chromosomes from a picture and rearranging them 3. Homologous pairs- Matching Pair of chromosomes 4. Sex Chromosomes- The two chromosomes which are displayed to one side Katherine Loera Pd.5 5. Autosomes- every other chromosomes that aren’t sex chromosomes 6. Diploid- two set of chromosomes (2n) 7. Haploid- one set of chromosomes (n) 8. Chromatids- two identical structures, makes up a chromosome 9. Centromere- holds two chromatids together 10. Locus- particular characteristics found in the same position 11. Nuclear divison- process in which mitosis and meiosis occur 12. Cytokinesis- constriction of the cytoplasm between the two new nuclei 13. Prophase- fist part of the mitosis cycle 14. Metaphase- all chromosomes line up in the middle, second phase 15. Anaphase- chromosomes get pulled apart by spindle fibers, third phase 16. Telophase- last phase pinching of cytoplasm Chapter 7 1. Ecology- The branch in biology that deals with the envioment 2. Habitat- place where an organism lives 3. Population- group of organisms of the same species, which live in the same place at the same time, and can interbreed with each other 4. Community- all the organisms, of all the different species, living in a habitat 5. Ecosystem- relatively self contained, interacting community of organisms, and the enviorment in which they live with which they interact 6. Niche- its role in the ecosystem 7. Producer- Photosynthetic organisms and green plant all fall under producer usually at the beginning of a food chain 8. Food chain- indicates the direction in which the energy flows 9. Decomposers- feed on detritus 10. Productivity- rate in which plants convert light energy into chemical potential energy 11. Gross primary productivity- total quantity converted by plants in this way 12. Net primary productivity- energy remains as chemical energy after plants have supplied their own needs in respiration 13. Nitrogen Fixation- nitrogen converted from N2 to some more reactive form such as ammonia 14. Nitrogenase- bacteria fix nitrogen with the help of an enzyme 15. Mutualism- two organism of different species live very closely together, each meeting some of the others need Chapter 8: 1. Cardiovascular System- The general layout of the main transport system of mammals that is the blood system. Katherine Loera Pd.5 2. 3. 4. 5. Tunica Media- Middle layer of the arteries Tunica Externa- Outer layer of the arteries Arterioles- small vessels that transport blood Capillaries- takes blood as close as possible to all cells, allowing rapid transfer of substances between cells and blood 6. Veins- To return blood to the heart 7. Plasma- Pale yellowish liquid 8. Homeostasis- The maintenance of a constant internal environment includes the regulation of glucose concentration, water, pH, metabolic wastes and temperature 9. Erythrocytes- Red blood cells 10. Haemoglobin- a globular protein that contains pigment 11. Buffer- Maintains the pH of the blood close to neutral 12. Semilunar valves- keeps blood flowing in the right direction 13. Arteries- transport blood, swiftly and at high pressure, to the tissues 14. Diffusion- Removal of waste products 15. Venules- large vessels that are formed when blood leaves capillary bed the capillaries gradually join with one another. Chapter 9: 1. Cardiac Muscle- Muscle in which the heart is made 2. Pulmonary Artery-Takes blood to the right and left lung, blood vessel leaving the heart 3. Aorta- Large arching blood vessel, largest artery, leads upward to the head and the main flow doubling back downwards to the rest of the body 4. Venae cavae- runs vertically on the right-hand side of the heart, two large veins, one brings blood downward other upward 5. Pulmonary veins- brings blood to the heart from the left and right lungs 6. Coronary arteries-on surface of heart, branch from aorta, deliver oxygenated blood to the walls of the heart itself 7. Septum-Wall muscle separated left and right chambers of heart 8. Ventricles- Lower Chambers, blood flows into ventricle from the artria then squeezed into arteries 9. Atrium- upper chamber on each side 10. Atrio-ventricular valves-atria and ventricles have valves between them 11. Mitral (bicuspid)- one on the left 12. Tricuspid valve- one on the right 13. Sinoatrial node- specialized patch of muscle in the wall of the right atrium 14. Electrocardiogram- essentially a graph of voltage against time 15. Atrial systole- time where heart is filled with blood and muscle in the atrial walls contracts Katherine Loera Pd.5 Chapter 10 1. Endodermis- the cell outer layer surrounding the stele, thick,waterproof,waxy band. 2. Casparian strip- forms an impenetrable barriers to water in the walls of the endodermis cells 3. Passage cell- water can continue to pass freely through this passage 4. Tracheids – the cells that are involved with the transport of water and their structure and function 5. Fibres- Elongated cells with lignified walls that help support the plant. Dead cells 6. Parenchyma- standard plant cells, have unthickened cellulose cell walls and contain all the organelles you would expect a plant cell to contain 7. Lignin – substance in normal plant cell in whose wall substance as laid down 8. Lumen- when content of cell died, leaving completely empty space (lumen) 9. Xylem Vessel- non-living tube in vessel 10. Mesophyll- middle leaf, layers are not tightly packed. An internal structure of leaf 11. Stomata-Small pores in the leaf 12. Assimilates- substances which plant has made it self 13. Sieve Plate- formed when the end walls of two sieve elements meet 14. Co-transport- where sucrose molecules are carried through 15. Carbon-Dioxide- Photosynthetic plant cells require supply of carbon dioxide during the daylight Chapter 11: 1. Cartilage- In the trachea and bronchi keeps these airways open and air resistance low, and prevents them from collapsing or bursting as the air pressure changes during breathing 2. Mucus- lining the nasal passages and other airways 3. Goblet cells- what produces mucus in the trachea and bronchi 4. Elastic fibers- stretch during breathing and recoil during expiration to help force out air 5. Macrophages- Phagocytic white blood cells 6. Alveoli- located at the end of the pathway between the atmosphere and the bloodstream. 7. Pulse rate – identical to what is the heart rate 8. Cardiac output- the total volume pumped out per minute 9. Stroke volume- the volume of blood pumped out from each ventricle during each contraction 10. Diastolic pressure- the minimum pressure in the arteries 11. Systolic pressure- the maximum arterial pressure during this active stroke Katherine Loera Pd.5 12. Sphygmomanometer- what measures the blood pressure 13. Hypertension- If systolic and diastolic blood pressures are high at rest, this indicates that the heart is working too hard at pumping blood. 14. Ventilation rate- measure the effect of exercise on breathing is measured by calculating this rate 15. Residual Volume- The volume of air still remained in the alveoli and the airways during force exhalation Chapter 12 1. Tar: Mixture of aromatic compounds 2. Carbon Monoxide- diffuses across the walls of the aveoli and into the blood in the lungs 3. Chronic bronchitis- damage and blocking of the airways 4. Emphysema- Large spaces appear where they have burst and this reduces the surface area for gaseous exchange 5. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease- Progressively disabling diseases 6. Coronary heart disease- is a disease of these arteries that cause damage to, or malfunction of the heart 7. Plaques- contain cholestrol-rich artheroma. lining in the arteries, making them less elastic 8.Heart Failure- due to blockage of a main artery and the resulting gradual damage of heart muscle 9. Heart attack- Also known as myocardial infarction 10. Angina pectoris- main symptoms of which is severe chest pain brought on by exertion 11.Nicotine- is the drug in tobacco 12. Allergen- substance that causes allergies 13. Obstructive lung disease- includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema and asthma 14. Passive smoking- breathing someone elses cigarette smoke 15. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease- very rare in none smokers, attributed to smoking Chapter 13: 1. Carriers- Some people may spread a pathogen even though they do not have a disease 2. Transmission cycle- The way in which pathogen from one host another Katherine Loera Pd.5 3. Oral rehydration therapy- way that can help cure cholera if they are able to drink 4. Vector- What transmits the disease 5. Immune- when people become continually re-infected they can become immune 6. prophylactic- preventative drug, stops an infection from occurring if a person is bitten by infected mosquito 7. T helper lymphocytes- what controls the immune system's response to infection 8. Opportunistic infections- infection causes because of body bein unable to defend itself against infections 9. Contact tracing- Important part of HIV in the UK infected patients mention partners or people they might have infected 10. Broad spectrum antibiotics- effective against a wide range of bacteria 11. Narrow spectrum antibiotics- are active only against a few 12. Inhibition zone- where no bacteria grows 13. MRSA- resistant to at least four antibiotics due to their previous inappropriate and widespread use 14. Choleragen- if bacteria reaches the small intestine they multiple and secrete a this toxin 15. Chloera - caused by the bacterium vibrio cholerae Chapter 14: 1. Artificial passive immunity- antibodies have come from another person who has encountered the antigen 2. Passive immunity- B and T cells have no been activated and plasma cells have not produced any antibodies 3. Antigen- Any molecule which the body recognizes as foreign 4. measles- caused by virus which is spread by airborne droplets 5. neutrophils- A kind of phagocytes and form about 60%of white blood cells in the blood 6. Monocytes- develop into macrophages after they leave the blood and settle in the organs 7. colostrum- thick yellowish fluid produced by mothers breats 8. vaccine- preparation containing antigenic material 9. antibody - specific to an anitgen, which is acts against 10. herd immunity- interrupts transmission of disease in population 11. macrophages- phagocytes but larger than neutrophils 12. nistamine- chemical released when body responds to attack of cell 13. active immunity- lymphocytes are activated by anitgen Katherine Loera Pd.5 14. thymes- t cells leave the bone marrow and collect here 15. natural passive immunity- appears immediately in the blood