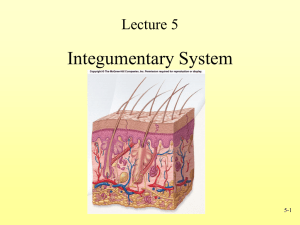
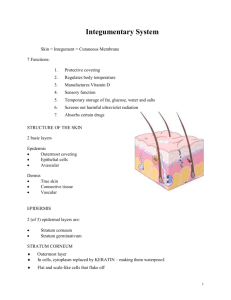
A. Outer, thinner layer or strata
advertisement
Ch. 6 Skin I. Integumentary System - Skin and its appendages II. A. Hair, nails, and _____________ ________________ B. Integument = "____________" C. Relatively flat organ; classified as a cutaneous membrane Structure of the Skin (Figs. 6-1, 6-2) A. Outer, thinner layer or strata - _________________ B. Inner, thicker layer of vascular c.t. - ______________ C. Beneath dermis lies loose subcutaneous layer; rich in fat and ________________ tissue - _________________ (not considered layer of skin) D. E. Thin and thick skin- refers to the epidermal layer 1. Thin - most covering body surface 2. Thick - palms of hands, soles of feet a. All ______ layers of epidermis present b. raised dermal papillae(_____________ or _____________) c. no ______________ Epidermis 1. Cell types a. Keratinocytes - filled with tough, ______________ protein = ______________; 90% of ep. Cells b. Melanocytes - synthesizes pigment melanin (color to skin); protects deeper layers from ________________ light c. Langerhan cells- (immune cells) macrophage like; arise from bone marrow; migrate to epidermis 2. Cell layers (Fig. 6-1) - 5 strata (layers) a. Stratum __________________ (horny layer) 1) most ______________________ layer 2) Shingle like dead cell 3) cytoplasm replaced by ____________________ 4) held together by desmosomes 5) Keratinization - process of cells formed from deeper layers, filled with keratin, and pushed to surface b. Stratum lucidum (____________ layer) 1) _____________________ are anucleated and clear 2) Cytoplasm filled w/Eleidin protein-bound lipid that will eventually be turned into keratin 3) Blocks water penetration 4) Occurs only in thick skin c. Stratum ___________________ (granular layer) 1) ____________________ begins here 2) 2-4 layers of flattened cells 3) cells filled w/ granules = ______________________ d. Stratum spinosum (______________ layer) 1) ___________ layers of irregularly shaped cells w/ prominent intercellular desmosomes 2) AKA prickle cells 3) Cells rich with ___________ for Protein synthesis- required for (keratin) e. Stratum _____________ (base layer) 1) Single layer of _______________ cells 2) mitosis only occurs here 3) cells originate here => migrate to different layer => shed f. Stratum ______________________ (growth layer) 1) used to describe the stratum ________________ and stratum ________________ together F. G. H. Epidermal growth and repair (p. 163) 1. ____________________ time - time period required for population of cells to mature & reproduce 2. time for new cell formation = rate old keratinized cells flake off 3. cells push upward => into each layer => die => become keratinized => ___________________ (fall away) 4. Regeneration time ~ 35 days Dermal-epidermal junction (p. 164) 1. Composed of ____________________ membrane 2. Also contains specialized fibrous elements & _______________________ gel that cement epidermis to dermis 3. partial barrier to the passage of some cells and large molecules Dermis or _______________________ 1. thicker than _______________________ 2. protective function against ____________________ injury 3. reservoir storage area for water & ________________________ 4. ____________________ sensory receptors (nerves & nerve endings) 5. muscle fibers, hair follicles, sweat & sebaceous glands & blood vessels 6. the rich vascular supply of the dermis plays a critical role in regulation of body temperature 7. Two layers: a. _________________ layer (Fig. 6-1) -thin 1) Loose, areolar CT with fibers 2) dermal papillae - bumps that project into epidermis 3) creates distinct ridges on epidermis finger and toes (fingerprints) 4) ___________ surfaces b. Reticular layer (Fig. 6-1) -thick 1) dense irregular c.t. 2. network of fibers - _________________ & elastic (when commercially processed = leather) 3) contains muscle - __________________ & smooth(allows for a point of attachment for mm) 4) __________________ - scalp movement & facial expressions 5) _________________ __________ muscles small bundle of smooth muscle that causes hair to "stand on end"- which causes the skin around it to raise = “goose bumps” 6) somatic sensory receptors for pain, _________________, touch, and ____________ I. Blisters (Box 6-3) 1. injury of epidermal cells or separation of dermal-epidermal jxn 2. damages __________________ - skin fall apart/away from body 3. causes of blisters- burns, friction, exposure to primary irritants III. Skin Color (p. 168) A. Pigments 1. Melanin (Fig. 6-5)- brown pigment a. quantity determines skin ________ b. melanocytes convert a.a. _____________ melanin w/ help from enzyme ___________________ c. melanocytes mostly found in stratum _____________ d. amt of melanin produced depends upon __________________, sun exposure, age, and hormones e. ________________ - enzyme tryrosinase is absent from birth; can not make melanin 2. _______________ - yellow pigment a. stratum corneum mostly b. palms and soles 3. Change in ____________ volume through the skin’s _______________ causes a temporary change in skin color a. skin blood vessels constrict => ____________ b. skin blood vessels dilate => ______________ c. ___________________ - when an excess of poorly oxygenated blood exists; skin appears bluish IV. Functions of the Skin (Table 6-1) A. Protection (p. 170) 1. barrier against _________________, harmful chemicals and mechanical _____________ to tissues 2. prevents _________________ 3. ________________ protects from harmful UV light 4. _______________ - flexible; waterproofing proteins 5. Surface film - ep.cells + secretions from sebaceous & sweat glands => functions=> ______________ and antifungal activity, lubrication, hydration of the skins surface B. Sensation (Fig. 6-3; Chapter 15) 1. _______________ ________________ serve as antennas that detect stimuli, ex. Pressure, ___________, temperature, __________ and vibration C. Movement and growth without injury d/t elastic fibers D. Excretion 1 regulates total fluid __________________ and ______________ products 2. waste products include uric acid, ammonia, ___________ E. Vitamin D production (endocrine function) F. Immunity - specialized cells are present in skin Ex. _______________ cells with help of helper _____ cells G. Homeostasis of body temperature 1. Heat production - ________________ of food and ________________ activity & glands (especially the liver) 2. To prevent heat loss, dermal blood vessels _________________ => more warm blood circulating deeper in body 3. To increase heat loss, dermal blood vessels ___________________ => inc. skin supply of warm blood => lost to external environment by physical process evaporation, radiation, conduction, and convection 4. Homeostatic regulation of heat loss Fig. 6-7 a. _______________ _____________ loop - affects sweat glands and blood vessels to return temperature back to set point 37 degrees C b. __________________ is control center V. Burns (p. 174) A. Tissue damage (Proteins denature) and cell death caused by heat, _________, UV radiation, or _____________ B. Estimating body surface area (Figs. 6-8, 6-9) 1. "Rule of _____________" - palm size = _____% if body surface 2. "Rule of _____________" C. body surface divided into _______ areas of 9% b. area around genitals 1% - perineum Severity of burns 1. 2. 3. VI. a. _____________ degree burns - typical ______________ a. only epidermis is damaged b. skin is red and swollen, no blistering Second degree burns a. Epidermis and ____________ are damaged b. damage to _____________ glands, ___________ follicles, and sebaceous glands c. __________________, severe pain, _______________ and scarring common Third degree burns (______________ thickness burns) a. destruction of __________________ and dermis b. tissue death extends below ___________ glands and _____________ follicles c. burning may involve fascia, ______________, and ____________ d. Insensitive to pain immediately after due to destruction of ________________ endings Appendages of the Skin (p. 176) A. Hair (Figs. 6-10, 6-11) B. Nails (Figs. 6-12, 6-13) - heavy _______________ epidermal cells C. Skin glands (Fig. 6-14) 1. Sweat glands (_______________)- most common 2. Sebaceous glands (Box 6-10)- oil for hair & skin 3. VII. ________________ glands Mechanisms of Disease: Skin Disorders (p. 181) A. Dermatosis - "skin condition" 1. Skin infections (viruses, bacteria, & fungi) a. Impetigo - bacteria (___________________) infection in young children; reddish discoloration that develops into vesicles (blisters) and ________________ crusts b. Tinea (Fig. 6-15) -______________ infection; Ringworm, jock itch, and _____________ _______ 1) s/sx - erythema (________________), scaling, & crusting c. Warts – ________________ viruses 1) usually _____________, can become malignant 2) transmitted by _____________ contact 3) Tx - ________________, drying, laser therapy d. Boils (furuncles) - local ____________________ 1) infection of hair follicles 2) Lg, inflamed pus-filled lesions 2. Vascular and inflammatory skin disorders a. Decubitus ulcers (_________________) (Fig. 6-16) 1) lesion caused by ______________ blood flow to skin area 2) ulcer forms 3) Tx -frequent changing positions and soft surfaces b. Urticaria (_______________)- raised red lesions = -wheals 1) causes - leakage of fluid from __________ blood vessels 2) severe _____________ 3) _______________ rxn, physical irritant, & systemic disease c. Scleroderma - autoimmune dz affecting ________________ vessels and c.t of skin 1) patches of _________________, hardened skin d. Psoriasis (Fig. 6-17) - _________________ inflammatory dz 1) ________________ basis 2) cutaneous inflammation, followed by ____________________ lesions e. Eczema – most common _________________ disorder of skin 1) inflammation, ______________, blisters, & crusts 2) usu. s/sx of underlying cond'n 3) allergic rxn or poison ivy B. VIII. Abnormal body temperature (Fig. 6-18) 1. Fever 2. Malignant hyperthermia (MH) 3. _______________ exhaustion 4. Heat stroke 5. _________________ 6. Frostbite Skin Cancer (Box 6-4) A. m/c form of CA in humans B. Basal cell carcinoma C. 1. most common type of _______________ cancer 2. arises from stratum basale 3. nose and ________________ 4. patient usually > _____________ years old 5. least _____________________ and rarely metastasize ___________________ cell carcinoma 1. slow growing and arises from st. __________________ 2. middle-aged and ________________ 3. sun-exposed areas (_______________, forehead, backs of hands 4. D. some forms may metastasize Malignant ____________________ 1. Most ________________ of all skin CA 2. older individuals (~53 y/o), light skin, eyes, and hair 3. may develop from pigmented mole (_________________) 4. Use ABCD rule for detection a. ____________________ 1) benign moles symmetrical 2) malignant moles ___________________ b. Border 1) B9 - distinct border 2) malignant - border irregular/indistinct c. ________________ 1) B9 - even color of brown 2) malignant - unevenly ______________, mixture of shades d. Diameter 1) malignant usually larger than ______ mm