Lecture 5
advertisement
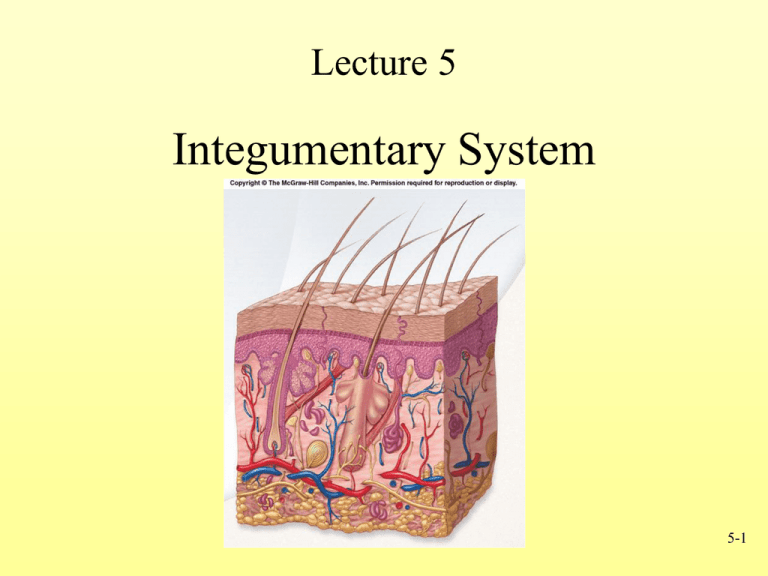
Lecture 5 Integumentary System 5-1 Integumentary System • Consists of: 1. Skin (Epidermis & Dermis) 2. Accessory structures • • • • Hair Nails Glands Functions – – – – – Protection Sensation Temperature regulation Vitamin D production Excretion Fig. 5.1 5-2 Epidermis and Dermis Fig. 5.2 5-3 Epidermal Cells • Cell types – Keratinocytes: Produce keratin for strength – Melanocytes: Contribute to skin color (pigment melanin) – Langerhans’ cells: Part of the immune system – Merkel’s cells: Detect light touch and pressure Fig. 5.2 •Keratinization: Cells die and produce outer layer that resists abrasion and forms permeability layer 5-4 Epidermal Strata • Stratum Basale – Deepest portion of epidermis and single layer – High mitotic activity • Stratum Spinosum – Limited cell division • Stratum Granulosum – In superficial layers nucleus and other organelles degenerate and cell dies Fig. 5.2 5-5 Epidermal Strata • Stratum Lucidum – Thin, clear zone • Stratum Corneum – Most superficial and consists of cornified cells – Squamous in shape, filled with keratin Fig. 5.2 5-6 Dermis • Structural strength • Two layers – Deeper layer dense connective tissue; stretch marks (striae) – Superficial layer underneath epidermis - loose connective tissue Fig. 5.6 5-7 Review Question The layer of keratinocyte cells of the epidermis with the highest rate of cell division is the (a) Stratum spinosum (b) Stratum basale (c) Stratum corneum (d) Stratum granulosum (e) Stratum lucidum 5-8 Hypodermis • Skin rests on this, but not a part • Also called – Subcutaneous tissue – Superficial fascia • Consists of loose connective tissue • Types of cells – Fibroblasts – Adipose (fat) cells – Macrophages Fig. 5.6 • Subcutaneous fat 5-9 Accessory Skin Structures • Hair – Found everywhere on human body except palms, soles, lips, nipples, parts of external genitalia, and distal segments of fingers and toes • Nails • Glands – Sebaceous or oil glands – Sudoriferous or sweat glands 5-10 Hair Structure • Composed of shaft and root – Shaft protrudes above skin surface – Root located below surface and base forms the hair bulb – Hair follicle consists of layer of dermis and epidermis • Arrector pili – Smooth muscle – Raises hair Fig. 5.9 5-11 Nails • Anatomy – Nail root proximally – Nail body distally: Eponychium or cuticle • Growth – Grow continuously unlike hair Fig. 5.8 5-12 Oil and Sweat Glands • Sebaceous glands – Produce sebum – Oils hair and skin surface • Sudoriferous glands (sweat) – Most commonly found in palms, soles and forehead – Also found in axillae (arm pit), genitalia, around anus – Ceruminous glands (cerumen or ear wax) – Mammary glands Fig. 5.10 5-13 Points to Remember • Two components to integumentary system – Skin (epidermis & dermis) – Accessory structures (hair, nails and glands) • Keratinization (accumulation of keratin) produces upper layer of cells of epidermis, hair and nails • Two types of glands in skin – Sebaceous (oily) – Sudiferous (watery) 5-14 Questions? 5-15