Genetics - Jocha
advertisement

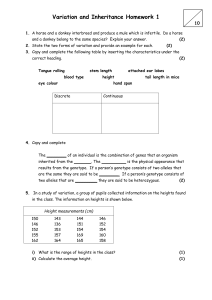
STUDY GUIDE LAB: Genetics 1. Explain what the difference is between… Diploid (2N) Genotype Homozygous Dominant (alleles) vs. Haploid (N) vs. Phenotype vs. Heterozygous vs. Recessive (alleles) 2. Imagine, you have two cells undergoing cell division, the first cell is undergoing mitosis, and the second cell is undergoing meiosis. The first cell is going to be a somatic cell of course, while the second one will be a sex cell. If you could “see” the contents, the inside of the cell, after both process were over, what differences would you see between both cells? 3. If a man has a genotype AO for the blood type… what will be the sex cells this person can produce regarding the blood type? 4. If a man has genotype AO for blood type and genotype Dd for dimples, which are caused by a dominant allele D, answer the following a) What is the diploid (2N) number for this problem? In other words, considering this problem, how many letters will you have in the somatic cells produced by this man? b) What are the genetic traits or characteristics you are considering here? c) What are the phenotypes for both traits? d) What will be the haploid (N) number when sex cells are produced? In other words, considering this problem, how many letters will you have in the sex cells produced by this man? e) What are the possible sex cells this man will produce containing information for BOTH blood type and dimples? 5. In humans, freckles (F) on the skin show dominant/recessive behavior as indicated by Mendel, if you do not have freckles you only have the recessive allele f. A man who has freckles marries a woman that does not have freckles f) Do you have enough information to determine the man’s genotype? Explain g) Do you have enough information to determine the woman’s genotype? Explain h) Ho does your answer change if you are told his mother did not have freckles? Explain 6. Compare the different types of genetics interactions seen during the lab… in all of them only two (2) alleles are present at the same time in one individual, each one coming from a different parent. Consider the following points for each genetic situation… Whether the alleles are located in sex chromosomes or autosomes (“normal” chromosomes) The number of possible alleles How many possible genotypes can be formed from the combination of alleles How many possible phenotypes are possible as a result of the interaction between alleles Now, answer the following questions… a) How is incomplete dominance different from Mendel? b) How is sex or x-linked different from Mendel? c) How does the multiple alleles interaction differ from Mendel? Instructor: Dr. Jose Bava