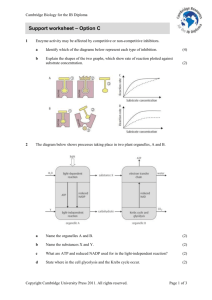
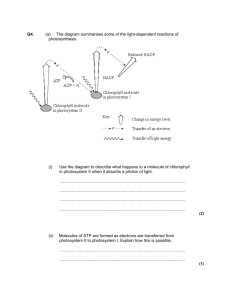
light dependent stage (advanced
advertisement
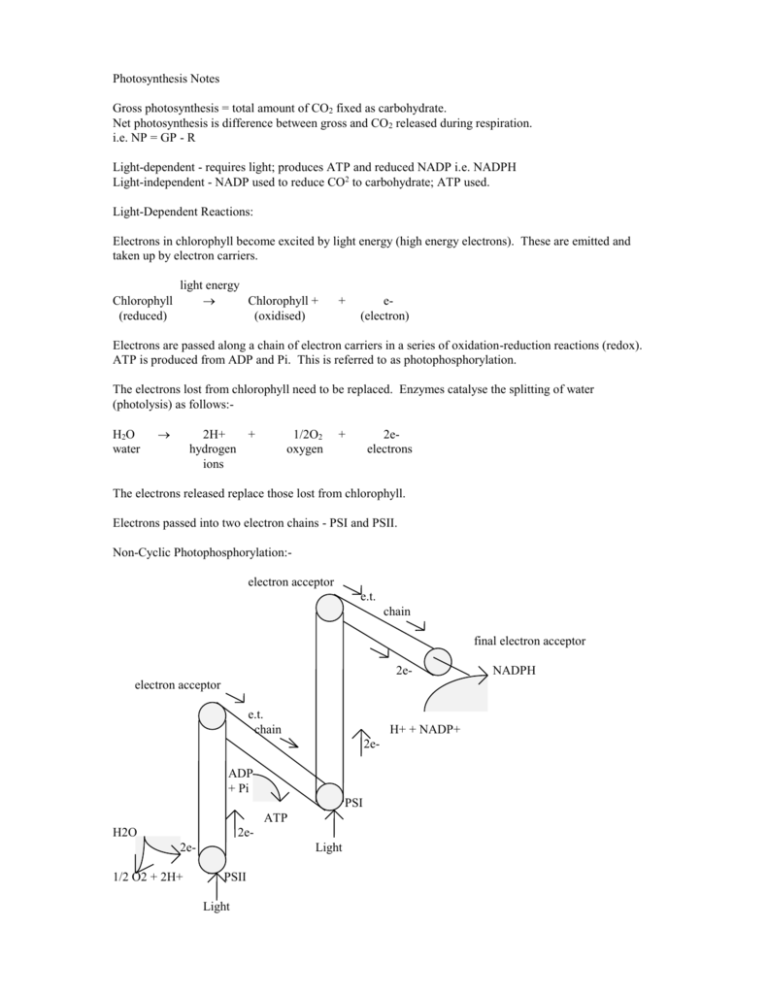
Photosynthesis Notes Gross photosynthesis = total amount of CO2 fixed as carbohydrate. Net photosynthesis is difference between gross and CO2 released during respiration. i.e. NP = GP - R Light-dependent - requires light; produces ATP and reduced NADP i.e. NADPH Light-independent - NADP used to reduce CO2 to carbohydrate; ATP used. Light-Dependent Reactions: Electrons in chlorophyll become excited by light energy (high energy electrons). These are emitted and taken up by electron carriers. Chlorophyll (reduced) light energy Chlorophyll + (oxidised) + e(electron) Electrons are passed along a chain of electron carriers in a series of oxidation-reduction reactions (redox). ATP is produced from ADP and Pi. This is referred to as photophosphorylation. The electrons lost from chlorophyll need to be replaced. Enzymes catalyse the splitting of water (photolysis) as follows:H2O water 2H+ + hydrogen ions 1/2O2 oxygen + 2eelectrons The electrons released replace those lost from chlorophyll. Electrons passed into two electron chains - PSI and PSII. Non-Cyclic Photophosphorylation:electron acceptor e.t. chain final electron acceptor 2eelectron acceptor e.t. chain H+ + NADP+ 2e- ADP + Pi PSI ATP H2O 2e2e- 1/2 O2 + 2H+ Light PSII Light NADPH The above processes supply reduced NADP for the light-independent reaction. Each photosystem raises two electrons to higher energy levels and higher chemical potential energy levels. Cyclic Photophosphorylation:The above processes do not provide sufficient ATP to drive the light-independent reactions. Cyclic photophosphorylation only involves PSI. Excited electrons are passed back to the electron transport chain between PSII and PSI. Extra ATP is produced and the electrons simply pass back to PSI. No oxygen is produced.....why?? The Light-Independent Reactions: