331PHO~1 - St. Robert CHS
advertisement

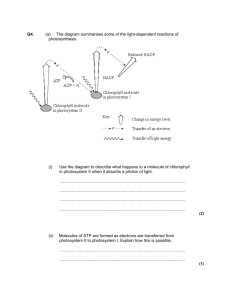
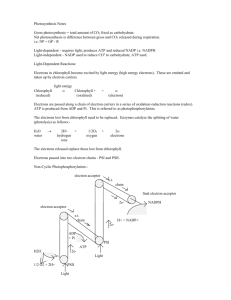
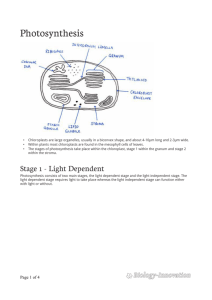
SBI 4U Photosynthesis Photosynthesis: The Details Introduction The heart of photosynthesis as it occurs in most autotrophs consists of two key processes: 1. the ____________________________________________________ 2. the_____________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________ The electrons (e−) and protons (H+) that make up hydrogen atoms are stripped away separately from water molecules. The electrons serve two functions: o They reduce _____________________ for use in the Calvin Cycle. o They set up an ______________________that provides the energy for pumping protons from the stroma of the chloroplast into the interior of the thylakoid. The protons also serve two functions: o They participate in the reduction of _______________________ o As they flow back out from the interior of the _____________________, by facilitated diffusion, (passing down their ________________________), the energy they give up is used for the conversion of ADP to ATP. o Because it is driven by light, this process is called _____________________. 1 SBI 4U Photosynthesis The Light Reactions The light reactions begin when photons strike a ______________________________ Steps in Light Reactions Steps 1. Photoexcitation 2. 3. Chemiosmosis Description Excited electrons are transferred through a series of membrane bound e- carriers, so a H+ is pumped through a photosynthetic membrane , which creates an ____________________ which will reduce an electron acceptor (NADP+) the phosphorylation of __________________________________ through ATP-ase complexes Photoexcitation When chlorophyll or accessory pigments absorb protons, the photon boots one of the pigment molecules’ electrons in its lowest energy state (ground state) to an orbital of higher potential energy (excited state). The excited state is unstable, so excited electrons quickly fall back to the ground state orbital, releasing excess energy in the process. Photosystems Each photosystem has an antenna composed of pigment molecules (chlorophyll and accessory molecules.) When a photon strikes a pigment molecule, the energy is passed from molecule to molecule until it reaches the reaction centre where ___________________ is found. An excited e- from the reaction-centre chlorophyll is captured by a specialized molecule called the ___________________________.(Called Pheophyton) The energy stored in the trapped electrons powers the synthesis of __________________. 2 SBI 4U Photosynthesis Types of Photosystems Photosystem II Photosystem I The reaction centre has a specialized The reaction centre has a specialized chlorophyll a which absorbs best at ____________________________ chlorophyll a which absorbs best at ____________________________ Note: P700 and P680 are identical chlorophyll molecules, but each is associated with a different ___________________. Noncyclic Electron Flow 3 SBI 4U Photosynthesis Another way to look at it 1. Ps II absorbs light, boosting excited e- to a higher energy levelcaptured by primary acceptor.(called _______________) 2. The Z protein completes Photolysis of water _________________________, (The electrons are used to replace the e- lost by chlorophyll P680.)(___________________ chloroplast as byproduct.) 4 SBI 4U Photosynthesis - 3. Photoexcited e pass from the primary electron acceptor of Ps II to Ps I via ____________ [consists of electron carrier ________________(PQ), a complex of two cytochromes and a protein called ________________________(Pc)] 4. Noncyclic Phosphorylation –chemiosmotic mechanism. As electrons move down the ETC, the energy released is captured by thylakoid membrane to produce NADPH. 5. When electrons reach the bottom of the ETC, they fill electron “holes” in the ________________________ molecule in the reaction centre of Ps I (replaces light energy that drives from the chlorophyll to the primary electron acceptor of Ps I). 6. The primary electron acceptor of Ps I passes the excited e- to ferredoxin (Fd). The enzyme NADP+ reductase then transfer e- from Fd to NADP+ (this is the redox rxn. that stores the high energy in NADPH-the molecule that will provide reducing power for the synthesis of sugar in the Calvin Cycle) Cyclic Electron Flow Involves only Ps I and generates ATP without producing ____________or evolving oxygen. When light is not the limiting factor, NADPH tends to accumulate in the stroma and there is a shortage of NADP+. The normal flow of electrons is inhibited b/c NADP+ is needed as a final acceptor of electrons. Cyclic photophosphorylation is required in order to make ATP When does cyclic phosphorylation occur? Cyclic phosphorylation occurs when: o NADP+ is absent due to __________________________________ o Cells need additional supplies of ___________________________ Chemiosmotic Mechanism of Photophophorylation 5 SBI 4U Photosynthesis As electrons pass from carrier to carrier during redox rxn. H+ removed from stroma are deposited in thylakoid compartment, storing energy as a proton-motive force (H+ gradient) Water is split by Ps II, as Pq transfers e- to Cyt. complex, protons are translocated across membrane, H+ is taken up by NADP+ reducing it to NADPH. The diffusion of H+ from thylakoid compartment to the stroma powers the _____________, and phophorylating ________________________ 6