bacteria webquest answer key
advertisement

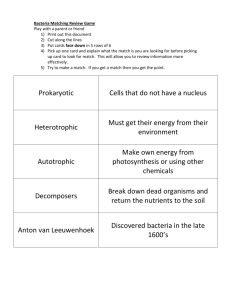
Bacteria: Good and Evil Name ___________________ Date ___________ Period __________ Score ______ Introduction: Bacteria are often maligned as the causes of human and animal disease. However, some bacteria produce antibiotics such as streptomycin and nocardicin; others live symbiotically in the guts of animals (including humans) or elsewhere in their bodies, or on the roots of certain plants, converting nitrogen into a usable form. Bacteria put the tang in yogurt and the sour in sourdough bread; bacteria help to break down dead organic matter; bacteria make up the base of the food web in many environments. Bacteria have been on earth longer than humans and will be here when we are gone. They are adaptive to all environments and very important to humans and all living things. Purpose: In this WebQuest, the goal is to gain insight into the overall role bacteria plays in relation to humankind. You will be directed to “click” down a preplanned trail of discovery. It is important that you follow the trail. This will aid you in realizing your goal to discover the good and evil roles bacteria plays in the survival and demise of humankind. Process: Use the links below to find the answers to the following questions. Evolution- http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/bacteria/bacteria.html 1. How old are bacteria? 3.5 billion years old Ecology- http://www.microbeworld.org/ 2. Where are bacteria found? Give 5 examples of where bacteria are found. Found in the intestines, food products, soil, causing diseases, in plants. 1 Bacteria: Good and Evil Name ___________________ Date ___________ Period __________ Score ______ Classification http://www.microbeworld.org/microbes/archaea/default.aspx http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/archaea/archaea.html http://www.biology.arizona.edu/cell_bio/tutorials/pev/page2.html 3. What two kingdoms belong to the domain Prokaryote? Archaeobacteria and eubacteria 4. What characteristics place an organism in the domain Prokaryote? No organelles-cell parts, have a cell wall, 5. What characteristics do Archae have that differ from Bacteria? They live in extreme environments, can make proteins, but have bacteria like genes Kingdom Bacteria. http://biology.clc.uc.edu/courses/bio106/bacteria.htm http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/bacteria/bacteriamm.html 6. Bacteria have three possible shapes. Name each shape and draw a picture of each. Coccus or cocci –round bacillus or bacilli-rod shaped spirlli-corkscrew Bacteria cell structure http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/bacteria/bacteriamm.html http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/bactcell.htm#surface 2 Bacteria: Good and Evil Name ___________________ Date ___________ Period __________ Score ______ 7. Draw and label a picture of the bacteria cell. You can do that 8. Give the structure and function of each of the following: a. b. c. d. e. f. g. Cell wall –protects bacteria from outside environment Capsule-protects the inside of the bacteria Nucleoid –the tangle of DNA in bacteria Flagella –tail like structure used by some bacteria for movement Pili –hairlike structures on bacteria that are used to attach to other cells Plasmids-small loops of DNA that can be exchanged Endospore-tough internal structures that protects bacteria genetic information Gram Stain -http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/bacteria/bacteriamm.html 9. What is the difference between a gram positive and gram negative bacteria? Gram positive would show a purple color when stained, gram negative do not show the color 10. How does the cell wall of a gram positive and gram negative bacteria differ? The cell wall of gram positive has more peptidoglycan proteins while gram negative have none or low amounts. Reproduction- https://micro.cornell.edu/research/epulopiscium/binary-fissionand-other-forms-reproduction-bacteria 9. How do bacteria reproduce? Draw a picture of this process. Binary fission or spores 3 Bacteria: Good and Evil Name ___________________ Date ___________ Period __________ Score ______ How do bacteria get their energy?http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/bacteria/bacterialh.html 10. Bacteria can be aerobic, anaerobic, or facultative anaerobes? What is the difference between these three types of bacteria? Aerobic-thrive with oxygen and require it Anaerobic-don’t like or use oxygen Facultative anaerobes-prefer oxygen but can live in both environments 11. How do heterotrophic bacteria get their energy? What do these bacteria feed on? They take in food from the environment-decaying material, fermentation 12. How do autotrophic bacteria get their energy? They fix carbon dioxide to make their own food 13. How do photoautotrophs differ from chemoautotrophs? Photoautotrophs use light to make food, chemoautotrophs use other elements or compounds to make food like sulfur, nitrogen, and methane The ecosystem, both on land and in the water, depends heavily upon the activity of bacteria. The cycling of nutrients such as carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur is completed by their ceaseless labor. 14. Explain the role of each of the following and how bacteria are involved in each. a. Decomposition Breakdown of dead organisms and the release of nutrients back into the environment b. Cycling of nitrogen in the ecosystem Nitogren fixing bacteria take nitrogen from the air and put it into soil for fertilizer 4 Bacteria: Good and Evil Name ___________________ Date ___________ Period __________ Score ______ c. Nitrogen fixation The way nitrogen becomes available to plants. d. Denitrification bacteria can be harmful and take out the nitrogen from the soil and make it bad for crops Now that you know some intimate details about bacteria, let's explore "the good, the bad, and the ugly" issues of bacteria. 15. Go to Bugs in the News. Click on "What the Heck is E. coli? Read the article and answer the following questions. http://people.ku.edu/~igmdoc/whatheck.html a. What does E. coli mean? Escherichia coli is found in our bodies b. Compare the "good and evil" E. coli. The good thrive in our bodies and help “us” digest and absorb nutrients, the bad can cause disease and diarrhea c. How do we acquire "good" E. coli? We get these bacteria after we are born d. How do we acquire "bad" E. coli?-from un clean food, drinks, unclean water e. How do we keep the good and avoid the evil? –wash hands and food 16. Now we will follow the Internet trail to Microbe Zoo. Visit each of the main attractions at the zoo and complete the activities below. http://commtechlab.msu.edu/sites/dlc-me/zoo/ Go to Dirtland: Select Root Cellar. Scroll down to Nitrogen Fixers. Explain how the bacteria Rhizobia helps plants make protein. They convert nitrogen in the air to ammonia which helps the plants make proteins Go to Animal Pavilion: Select Poo Corner. Discuss how human fecal matter is recycled so that humans are not buried in their own waste. The bacteria can be used in septic tanks, and sewage treatment plants 5 Bacteria: Good and Evil Name ___________________ Date ___________ Period __________ Score ______ Go to Snack Bar. Discuss the role of bacteria and other microbes in at least five different foods you eat. Yeast for bread, beer, and wine, lactis bacillis for chocolate, and yogurt Go to Water World. Discuss pond life from a bacterium's point of view. Photosynthetic bacteria-make own food, cyanobacteria, anoxygenphotosynthetic, heterotrophic, methanogen, sulfur reduction 17. Go to Microbe World, Every Day Roles, and click on the pictures to find 8 more good things that bacteria do! List your findings. http://www.microbeworld.org/ 6