ISE467 - Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering
advertisement
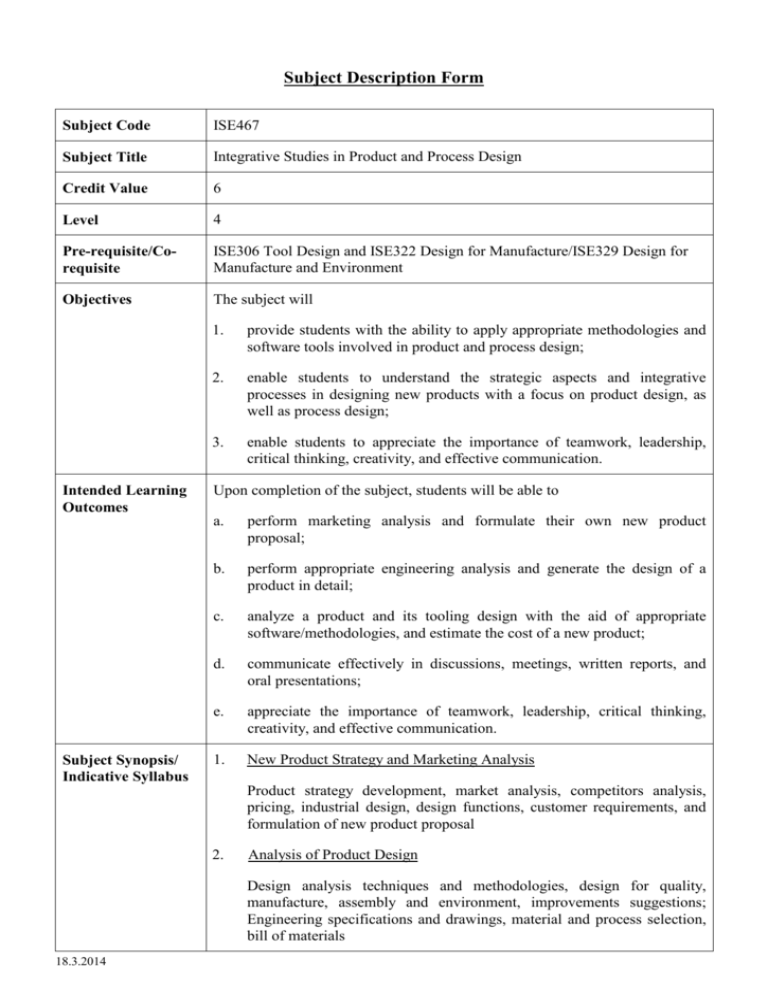
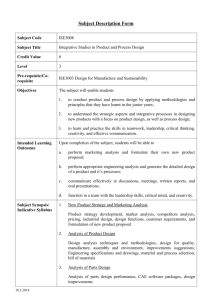
Subject Description Form Subject Code ISE467 Subject Title Integrative Studies in Product and Process Design Credit Value 6 Level 4 Pre-requisite/Corequisite ISE306 Tool Design and ISE322 Design for Manufacture/ISE329 Design for Manufacture and Environment Objectives The subject will Intended Learning Outcomes Subject Synopsis/ Indicative Syllabus 1. provide students with the ability to apply appropriate methodologies and software tools involved in product and process design; 2. enable students to understand the strategic aspects and integrative processes in designing new products with a focus on product design, as well as process design; 3. enable students to appreciate the importance of teamwork, leadership, critical thinking, creativity, and effective communication. Upon completion of the subject, students will be able to a. perform marketing analysis and formulate their own new product proposal; b. perform appropriate engineering analysis and generate the design of a product in detail; c. analyze a product and its tooling design with the aid of appropriate software/methodologies, and estimate the cost of a new product; d. communicate effectively in discussions, meetings, written reports, and oral presentations; e. appreciate the importance of teamwork, leadership, critical thinking, creativity, and effective communication. 1. New Product Strategy and Marketing Analysis Product strategy development, market analysis, competitors analysis, pricing, industrial design, design functions, customer requirements, and formulation of new product proposal 2. Analysis of Product Design Design analysis techniques and methodologies, design for quality, manufacture, assembly and environment, improvements suggestions; Engineering specifications and drawings, material and process selection, bill of materials 18.3.2014 3. Analysis of Parts Design Analysis of parts design performance, CAE software packages, design improvements 4. Manufacturing Process and Tooling Design Manufacturing process planning and evaluation, tooling design, tooling configurations, process simulation 5. Estimation of Product Cost Product cost analysis in terms of parts, materials, and manufacturing and overhead costs Teaching/Learning Methodology The student’s interest is stimulated through a problem-based learning approach. Case studies, self-learning modules, seminars/lectures, and guided studies are used. Task activities begin with an analysis of a newly proposed product from the marketing perspective. Students are required to conduct detailed product and parts design. Analysis techniques and methodologies are applied to study the product in terms of parts, material, manufacturing processes, tooling, environment, and cost. Throughout the study of this subject (apart from task briefing and introduction sessions), lectures, seminars, case studies, tutorials, and guided studies are used to enable students to acquire knowledge in a manner that allows them a high degree of learning flexibility. Students work in small groups of five to six to experience working team spirit. Formal group meetings with minutes taken are encouraged to enhance project progress and simulated learning. Assessment Methods in Alignment with Intended Learning Outcomes Specific assessment methods/tasks % Intended subject learning outcomes weighting to be assessed a b c d e 1. Written report 40% 2. Task presentations x 2 30% 3. Peer critiques x 2 15% 4. Learning journal 15% Total 100% The written report is a final report of all the task activities and technical analysis involved in the project. Each group prepares a written report, with individual contributions indicated. Task presentations are required so that students can orally present the progress and findings from the two tasks. Peer critiques are required to allow students to comment on other groups’ work for the purpose of learning. A final learning journal for assessing students’ understanding of the importance of teamwork, critical thinking, creativity, and effective communication is required after project completion. 18.3.2014 Student Study Effort Expected Class contact: Lecture/Seminar Laboratory/Tutorial/Case study 2 hours/week for 9 weeks 18 Hrs. 14 Hrs. 2 hours/week for 7 weeks Task activities/Group meetings/Consultations 45 Hrs. 3 hours/week for 15 weeks Other student study effort: Preparation for presentations, reports, and learning journals 52 Hrs. Project work and discussions 52 Hrs. Guided study/Self-learning 52 Hrs. Total student study effort Reading List and References 18.3.2014 233 Hrs. 1. Butterworth-Heinemann 2008 Product Development a Structured Approach to Consumer Product Development, Design and Manufacture, An imprint of Elsevier 2. Crawford, C and Di, B 2003, New Products Management, McGraw Hill 3. Shetty, D 2002, Design for Product Success, Society of Manufacturing Engineers, USA 4. Otto, K 2001, Product Design: Techniques in Reverse Engineering and New Product Development, Saddle River, N.J: Prentice Hall 5. Swift, K 2003, Process Selection – from Design to Manufacture, Oxford, Boston: Butterworth-Heinemann 6. Spitler, D, Lantrip, J, Nee, J, and Smith DA 2010, Fundamentals of Tool Design, 6th edn, Society of Manufacturing Engineers, Dearborn 7. 2005, Self Learning Modules for Product and Process Design, Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University