Section 2-4 “Chemical Reactions and Enzymes”
advertisement

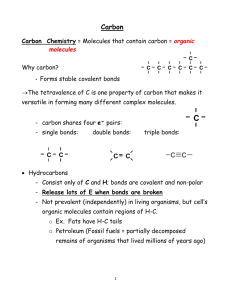
Section 2-4 Chemical Reactions . Key Concept: Life depends on thousands of chemical reactions occurring in the body Main Ideas: 1. Chemical reactions involve the breaking and forming of bonds between atoms. 2. Chemical reactions either release or absorb energy. What is a Chemical Reaction? Chemical Reaction – the process of breaking the bonds between atoms and then reforming them so that the atoms are arranged into new types of molecules. http://www.cartage.org.lb/en/themes/sciences/chemistry/inorganicchemistry/chemicslformula/Equation/chemicalequation/FG03_003.GIF Chemical reactions always involve the breaking of bonds in reactant molecules and the formation of new bonds in the product molecules. Parts of a Chemical Reaction Chemical Equation – Shorthand way to describe the overall chemical reaction. Reactants – Elements or compounds that are the “starter materials” for a reaction Products – Elements or compounds produced by a chemical reaction Ex. Chemical equation for photosynthesis 6CO2 + 12H2O + sunlight 6O 2 + C6 H12O 6 + 6H2 O Reactants Products Bond Energy in Chemical Reactions What happens when bonds break and bonds form? Energy must be added to break bonds that hold the reactant molecules together. This is called activation energy (Ae). This amount of energy is what “activates” or gets the reaction started. Once the bonds are broken, the atoms are freed up and can make new molecules. When bonds form between the atoms to make new molecules, energy is released. The specific amount of energy that is needed to break a bond, or is releases when that same bond forms, is called bond energy. Two Categories of Chemical Reactions based on Energy Changes 1. Exothermic Reaction - a reaction that releases more E than what it absorbed. Exo – Out of Thermic - Heat Example: Combustion/Cell Respiration 2. Endothermic Reaction - a reaction in which more E is absorbed that released. Endo - Inside Thermic - Heat Example: Photosynthesis