Nouns, Pronouns, Verbs Grammar Worksheet
advertisement

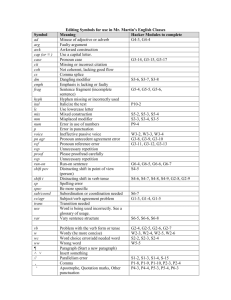
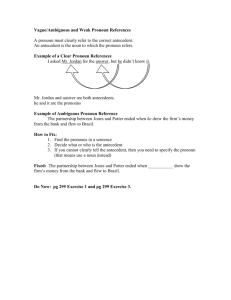
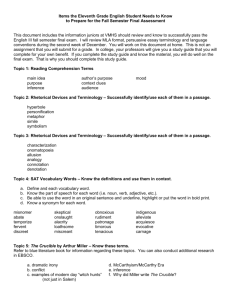
Grammar Unit 2—Nouns, Pronouns, and Verbs Nouns A noun is a word that denotes a person, place, or thing. In a sentence, nouns answer who and what. Example: The dog ran after its ball. An antecedent is the word, phrase, or clause to which a pronoun refers, understood by the context. Agreement-A pronoun must agree with its antecedent in three ways: Person refers to the quality of being. Number is the quality that distinguishes between singular (one entity) and plural (numerous entities). Gender is the quality that distinguishes the entities as masculine or feminine. Examples: Incorrect in Person: If a person wants to succeed in corporate life, you have to know the rules of the game. Incorrect in Number: If anybody wants to succeed in corporate life, they have to know the rules of the game. Incorrect in Gender: If a person wants to succeed in corporate life, he has to know the rules of the game. How would you fix the above errors? Pronouns A personal pronoun takes the place of common and proper nouns. First person= the person or people speaking or writing Second person= the person or people being spoken or written to Third person= the person, people, or things being spoken or written about First Person Second Person Third Person Singular I, me, my, mine you, your, yours he, him, his, she, her, hers, it, its Plural we, us, our, ours you, your, yours they, them, their, theirs Verbs A verb is a word that denotes action, or a state of being, in a sentence. Example 1: Beth rides the bus every day. Example 2: Paul was an avid reader. In example 1, rides is the verb; it describes what the subject, Beth, does. In example 2, was describes Paul’s state of being and is therefore the verb. Being Verbs am, is, are, was, were, been, being, be There may be multiple verbs in a sentence, or there may be a verb phrase consisting of a verb and a helping verb. Example 1: She turned the key and opened the door. Example 2: Jackson was studying when I saw him last. In example 1, the subject she performs two actions in the sentence, turned and opened. In example 2, the verb phrase is was studying. Nouns, Pronouns, Verbs Practice Name: Hour: Part I Directions: Circle the antecedent for the underlined pronoun in each sentence. If the pronoun has no antecedent, write “no antecedent”; if the antecedent is not clear, write “not clear”. Example: The boy wore his yellow raincoat. 1. Everyone at the party enjoyed her evening. 2. The car has a leak in its transmission. 3. Wearing a hat when it snows is wise. 4. I get worried when the neighbors let their dog out. 5. The cow twitched its tail at the fly. Part II Directions: Fill in the blank with the appropriate personal pronoun. 6. The children were frightened when the pony chased 7. When Tony dated , Sylvia was sixteen years old. 8. Marco admitted that was the one who made the phony phone call. 9. It was our turn to get the hot dogs, so 10. Theresa said to Judy, " . piled into Alan's car. are the only one who will understand my problem." Part III Directions: Circle the correct pronoun(s) in the following sentences. 11. (I, me) will pick up the groceries. 12. (She, he) sent (I, me ) her package in the mail. 13. Are you going to visit (he, him) this evening? 14. They told (us, we) to meet (them, they) in the parking lot. 15. Between you and (I, me), I prefer In N’ Out Burger over Fatburger. Part IV Directions: Circle the verb(s) in the following sentences. 16. Rosa accompanied her on rhythm guitar, while Josie sang in harmony. 17. They formed a musical group with two other friends. 18. They had many rehearsals and practice sessions. 19. After several months of practice, the group sounded very professional, and looked professional with their new uniforms. 20. Suddenly, the lead vocalist, Tasha, moved to another city. 21. Alice took Tasha’s place.