Fall Semester Final Exam Review
advertisement

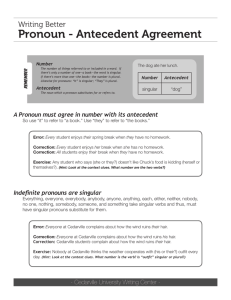
Items the Eleventh Grade English Student Needs to Know to Prepare for the Fall Semester Final Assessment This document includes the information juniors at VMHS should review and know to successfully pass the English III fall semester final exam. I will review MLA format, persuasive essay terminology and language conventions during the second week of December. You will work on this document at home. This is not an assignment that you will submit for a grade. In college, your professors will give you a study guide that you will complete for your own benefit. If you complete the study guide and know the material, you will do well on the final exam. That is why you should complete this study guide. Topic 1: Reading Comprehension Terms author’s purpose context clues audience main idea purpose inference mood Topic 2: Rhetorical Devices and Terminology – Successfully identify/use each of them in a passage. hyperbole personification metaphor simile symbolism Topic 3: Rhetorical Devices and Terminology – Successfully identify/use each of them in a passage. characterization onomatopoeia allusion analogy connotation denotation Topic 4: SAT Vocabulary Words – Know the definitions and use them in context. a. b. c. d. Define and each vocabulary word. Know the part of speech for each word (i.e. noun, verb, adjective, etc.). Be able to use the word in an original sentence and underline, highlight or put the word in bold print. Know a synonym for each word. misnomer abate temporize fervent discreet skeptical onslaught alacrity loathsome miscreant obnoxious rudiment patronage timorous tenacious indigenous alleviate acquiesce evocative carnage Topic 5: The Crucible by Arthur Miller – Know these terms. Refer to blue literature book for information regarding these topics. You can also conduct additional research in EBSCO. a. dramatic irony b. conflict c. examples of modern day “witch hunts” (not just in Salem) d. McCarthyism/McCarthy Era e. inference f. Why did Miller write The Crucible? Topic 6: Language Conventions (Grammar/Syntax) Consult your grammar book for examples and additional information. Students need to know the following: sentence fragment – What are sentence fragments? Fragments are incomplete sentences. Usually, fragments are pieces of sentences that have become disconnected from the main clause. pronoun/antecedent - What is pronoun/antecedent agreement? Pronoun/antecedent agreement is when the pronoun agrees in number (referring to singular or plural) and person (referring to first, second, or third person) with its antecedent. An “antecedent” is defined as a word, phrase, or clause that is replaced by a pronoun or other substitute later, or occasionally earlier, in the same or in another, usually subsequent, sentence. Example: Jane lost a glove and she can't find it. Jane is the antecedent of she and glove is the antecedent of it. subject/verb agreement – What is subject/verb agreement? The subject and verb must agree in number: both must be singular, or both must be plural. Problems occur in the present tense because one must add an -s or -es at the end of the verb when the subjects or the entity performing the action is a singular third person: he, she, it, or words for which these pronouns could substitute. verb tense agreement/usage – What is verb tense agreement/usage? The basic principle is that singular subjects need singular verbs and plural subjects need plural verbs. Topic 7: Persuasive Essay Terminology and Concepts concede refute concession refutation Topic 8: Modern Language Association (MLA) Format 1.) Know how to correctly identify in-text citations: for sources with and without authors 2.) Know how to format Works Cited entries for the following source types: 1.) magazines, 2.) books and 3.) articles from an on-line database 3.) Know how to correctly format an MLA Works Cited page 4.) Know how to format Works Cited entries for the following source types: 1.) films and 2.) newspaper articles Topic 9: Grammar 1.) 2.) 3.) 4.) 5.) 6.) 7.) 8.) simple and compound subjects simple and compound predicates main clauses coordinating conjunctions compound sentences complex sentences compound-complex sentences subordinate conjunctions