Unit 4: Bonding draft—fall 2011 Target that you still need to know
advertisement
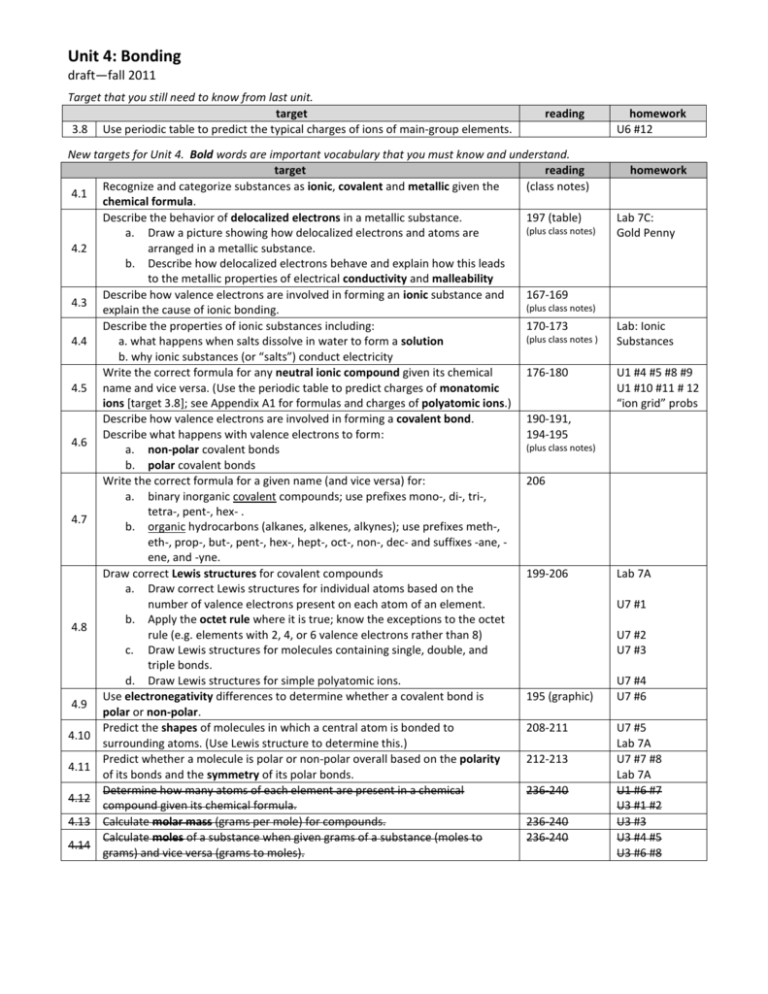
Unit 4: Bonding draft—fall 2011 Target that you still need to know from last unit. target 3.8 Use periodic table to predict the typical charges of ions of main-group elements. reading New targets for Unit 4. Bold words are important vocabulary that you must know and understand. target reading Recognize and categorize substances as ionic, covalent and metallic given the (class notes) 4.1 chemical formula. Describe the behavior of delocalized electrons in a metallic substance. 197 (table) (plus class notes) a. Draw a picture showing how delocalized electrons and atoms are 4.2 arranged in a metallic substance. b. Describe how delocalized electrons behave and explain how this leads to the metallic properties of electrical conductivity and malleability Describe how valence electrons are involved in forming an ionic substance and 167-169 4.3 (plus class notes) explain the cause of ionic bonding. Describe the properties of ionic substances including: 170-173 (plus class notes ) 4.4 a. what happens when salts dissolve in water to form a solution b. why ionic substances (or “salts”) conduct electricity Write the correct formula for any neutral ionic compound given its chemical 176-180 4.5 name and vice versa. (Use the periodic table to predict charges of monatomic ions [target 3.8]; see Appendix A1 for formulas and charges of polyatomic ions.) Describe how valence electrons are involved in forming a covalent bond. 190-191, Describe what happens with valence electrons to form: 194-195 4.6 (plus class notes) a. non-polar covalent bonds b. polar covalent bonds Write the correct formula for a given name (and vice versa) for: 206 a. binary inorganic covalent compounds; use prefixes mono-, di-, tri-, tetra-, pent-, hex- . 4.7 b. organic hydrocarbons (alkanes, alkenes, alkynes); use prefixes meth-, eth-, prop-, but-, pent-, hex-, hept-, oct-, non-, dec- and suffixes -ane, ene, and -yne. Draw correct Lewis structures for covalent compounds 199-206 a. Draw correct Lewis structures for individual atoms based on the number of valence electrons present on each atom of an element. b. Apply the octet rule where it is true; know the exceptions to the octet 4.8 rule (e.g. elements with 2, 4, or 6 valence electrons rather than 8) c. Draw Lewis structures for molecules containing single, double, and triple bonds. d. Draw Lewis structures for simple polyatomic ions. Use electronegativity differences to determine whether a covalent bond is 195 (graphic) 4.9 polar or non-polar. Predict the shapes of molecules in which a central atom is bonded to 208-211 4.10 surrounding atoms. (Use Lewis structure to determine this.) Predict whether a molecule is polar or non-polar overall based on the polarity 212-213 4.11 of its bonds and the symmetry of its polar bonds. Determine how many atoms of each element are present in a chemical 236-240 4.12 compound given its chemical formula. 4.13 Calculate molar mass (grams per mole) for compounds. 236-240 Calculate moles of a substance when given grams of a substance (moles to 236-240 4.14 grams) and vice versa (grams to moles). homework U6 #12 homework Lab 7C: Gold Penny Lab: Ionic Substances U1 #4 #5 #8 #9 U1 #10 #11 # 12 “ion grid” probs Lab 7A U7 #1 U7 #2 U7 #3 U7 #4 U7 #6 U7 #5 Lab 7A U7 #7 #8 Lab 7A U1 #6 #7 U3 #1 #2 U3 #3 U3 #4 #5 U3 #6 #8