CHM1 Review for Exam 6 The following are topics and sample
advertisement

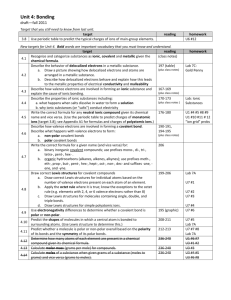
CHM1 Review for Exam 6 The following are topics and sample questions for the first exam. Topics 1. Types of Bonding a. Covalent – Sharing electrons between nonmetal atoms i. Nonpolar covalent ii. Polar covalent b. Ionic – Cations and anions (metals and nonmetals) i. Ionic formulas – Criss-cross ii. Polyatomic ions 2. Physical properties a. Covalent i. Low melting and boiling ii. Nonconductors of heat and electricity iii. Localized bonding between two atoms b. Ionic i. High melting and boiling ii. Good conductors of electricity in solution or liquid phase, but not in the solid phase iii. Usually crystalline solids c. Metallic bonding i. Mobile nonlocalized electrons explain good electrical conductivity ii. Usually solids but range from soft to very hard depending upon the number of valence electrons 3. Lewis Dot structures a. Ionic b. Molecular c. Compounds containing polyatomic ions Multiple Choice Questions 1. What is the correct Lewis electron-dot structure for the compound magnesium fluoride? CHM1 Review for Exam 6 2. Which type of bond is formed when electrons are transferred from a metal to a nonmetal to form ions? (1) covalent (2) ionic (3) hydrogen (4) metallic 3. Which type of chemical bond is formed between two atoms of bromine? (1) metallic (2) hydrogen (3) ionic (4) covalent 4. Which formula correctly represents the formula that results from combining Fe3+ and O2-? (1) FeO3 (2) Fe2O3 (3) Fe3O (4) Fe3O2 5. Which element has atoms that can form single, double and triple covalent bonds with other atoms of the same element? (1) hydrogen (2) oxygen (3) fluorine (4) carbon 6. The bond between N atoms in a N2 molecule is (1) ionic and is formed by the sharing of six valence electrons (2) ionic and is formed by the transfer of six valence electrons (3) covalent and is formed by the sharing of six valence electrons (4) covalent and is formed by the transfer of six valence electrons 7. Which of the following will conduct electricity when dissolved in aqueous solution? (1) H2 (2) NaCl (3) CH3OH (4) C6H12O6 8. What is the molecular shape of CH4? (1) linear (2) bent (3) triganol (4) tetrahedral CHM1 Review for Exam 6 9. Which of the following correctly represents the ions that are in the ionic compound whose formula is Fe2(SO4)3? (1) Fe2+ and SO4(2) Fe3+ and SO34- (3) Fe3+ and SO42(4) Fe2+ and SO43- 10. How many valence electrons does a nitrogen atom have? (1) 2 (2) 3 (3) 5 (4) 8 11. Which of the following compounds does not contain ionic bonding? (1) Na2O (2) Al2O3 (3) F2 (4) NH4Cl 12. What is the H-C-H angle in methane, CH4? (1) 180° (2) 120° (3) 109° (4) 90° 13. Which of the following is most likely to conduct electricity in the solid state? (1) Co (2) CO2 (3) N2 (4) NaCl 14. How many oxygen atoms are in the formula of the compound that results from combining Ca2+ with PO43-? (1) 2 (2) 4 (3) 8 (4) 12 15. Which of the following ions polyatomic? (1) OH(2) F- (3) O2(4) Ti4+ 16. What type of element is most likely to form a cation? (1) an alkali metal (2) a nonmetal (3) a metalloid (4) a halogen CHM1 Review for Exam 6 17. Which of the following contains polar covalent bonds? (1) H2 (2) NaCl (3) H2O (4) O2 18. Based on the Lewis dot structures, which of the following contains a nonbonding pair of electrons? (1) H2 (2) NH3 (3) CH4 (4) BH3 19. Based on the Lewis dot structure, which of the following would be the shortest covalent bond? (1) a single bond (2) a double bond (3) a triple bond 20. Which of the following diatomic elements does not contain a single bond? (1) hydrogen (2) oxygen (3) fluorine (4) chlorine Short Answer Questions. Show all work. 21. What is the formula of the compound that results from combining the following ions? (a) Al3+ and SO42- (b) Ti4+ and C4- (c) Ca2+ and NO3- (d) NH4+ and SO42- 22. Write the Lewis dot structures for the following molecular compounds. (a) O2 (b) CO2 (c) CH4 (d) OF2 CHM1 Review for Exam 6 23. Write the Lewis Dot structures for the following ionic compounds. (a) NaCl (b) CaO (c) NH4Cl (d) Al(OH)3 24. Briefly describe metallic bonding and what physical properties this description is most useful to explain? 25. What is the octet rule and how does it apply to both ionic and molecular compounds? 26. What cause the forces of attraction in compounds that exhibit ionic bonding? CHM1 Review for Exam 6 Answers 1. 3 2. 2 3. 4 4. 2 5. 4 6. 3 7. 2 8. 4 9. 3 10. 3 11. 3 12. 3 13. 1 14. 3 15. 1 16. 1 17. 3 18. 2 19. 3 20. 2 21. (a) Al2(SO4)3 (b) TiC 22. (a) ::O=O:: (b) ::O=C=O:: .. 23. (a) [Na]+ [:Cl:] .. .. (b) [Ca]2+ [:O:] .. (c) Ca(NO3)2 (d) (NH4)2SO4 H .. .. .. (c) H-C-H (d) :F-O-F: .. .. .. H H .. .. 3+ (c) [H-N-H]+ [:Cl:] .. (d) [Al] 3 [:O-H] .. H 24. The metallic solid consists of a regular repeating pattern of metal atoms in which the valence electrons are forming delocalized bonds in which the electrons are shared between the metal atoms. This is useful in describing the electrical conductivity of a metal. 25. The octet rule states that atoms will generall need eight valence electrons to complete the valence shell with an electron configuration of ns2np6. 26. Ionic bonds are due to the charge interactions between the cations and anions.