Determination of an Rotameter Static features
advertisement
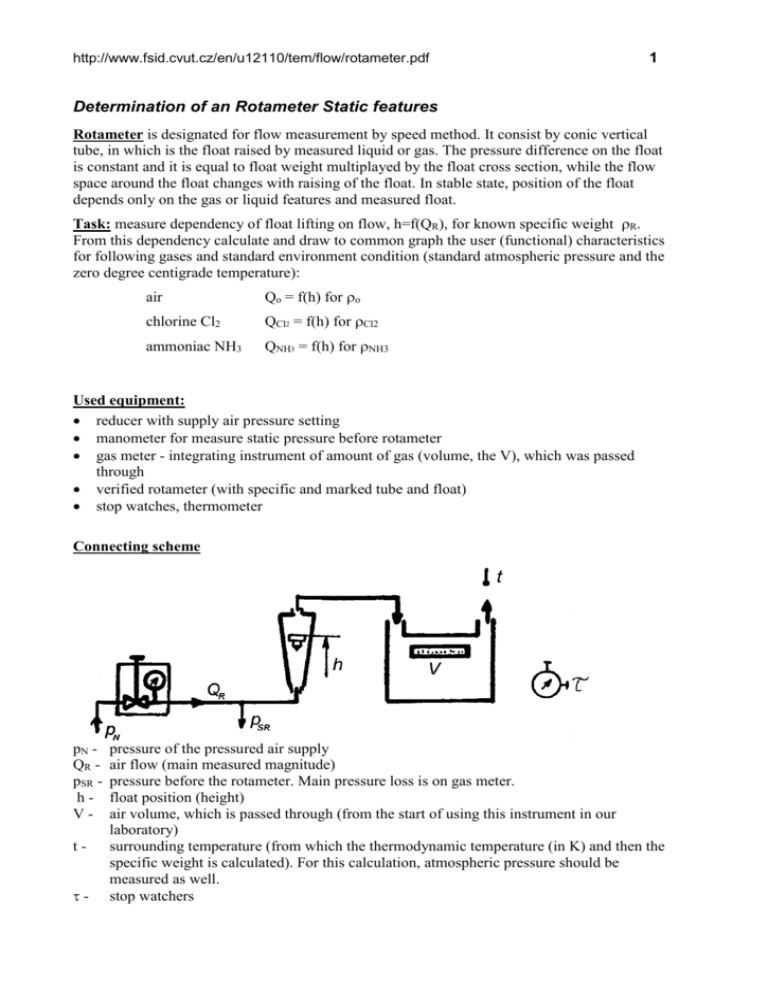
http://www.fsid.cvut.cz/en/u12110/tem/flow/rotameter.pdf 1 Determination of an Rotameter Static features Rotameter is designated for flow measurement by speed method. It consist by conic vertical tube, in which is the float raised by measured liquid or gas. The pressure difference on the float is constant and it is equal to float weight multiplayed by the float cross section, while the flow space around the float changes with raising of the float. In stable state, position of the float depends only on the gas or liquid features and measured float. Task: measure dependency of float lifting on flow, h=f(QR), for known specific weight R. From this dependency calculate and draw to common graph the user (functional) characteristics for following gases and standard environment condition (standard atmospheric pressure and the zero degree centigrade temperature): air Qo = f(h) for o chlorine Cl2 QCl2 = f(h) for Cl2 ammoniac NH3 QNH3 = f(h) for NH3 Used equipment: reducer with supply air pressure setting manometer for measure static pressure before rotameter gas meter - integrating instrument of amount of gas (volume, the V), which was passed through verified rotameter (with specific and marked tube and float) stop watches, thermometer Connecting scheme pN QR pSR hVt- pressure of the pressured air supply air flow (main measured magnitude) pressure before the rotameter. Main pressure loss is on gas meter. float position (height) air volume, which is passed through (from the start of using this instrument in our laboratory) surrounding temperature (from which the thermodynamic temperature (in K) and then the specific weight is calculated). For this calculation, atmospheric pressure should be measured as well. stop watchers 2 http://www.fsid.cvut.cz/en/u12110/tem/flow/rotameter.pdf Comments Measure in ten points in all settable range of flow, not for zero. The volume of air by gas meter measure for at least two minutes for each float position. Avoid unstable behaviour of float (must be smoothly rotated). Used equation Air specific density equation R 3,484 p1R T1 [kg.m-3, kPa, K] ; p1R = psR + pbo In the gas meter, consider half of the pressure measured by manometer. Conversion of flow for other gases with regard to specific weight: Qo QR R o , Q Cl 2 Q R R Cl 2 , Q NH3 Q R R NH3 Specific weight for standard conditions, i.e. po=101325 Pa, To = 273,15 K ( = 0 oC) is: air o = 1,293 kg.m-3 chlorine Cl2 Cl2 = 3,22 kg.m-3 ammoniac NH3 NH3 = 0,771 kg.m-3 calculating the pressure from length of a column form inclined manometer: pSR = e . N . g . l (e - inclined manometer conversion, in our case e=1, filling - distilled water) Table of measured and calculated values: h psR V1 [mm] [mmH2O] [m3] V2 V=V1-V2 QR Q0 QCl2 QNH3 [m3] [s] [m3] [m3.s-1] [m3.s-1] [m3.s-1] [m3.s-1]