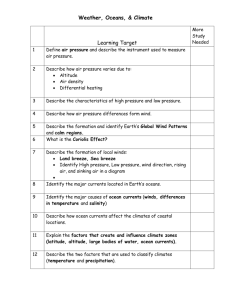
Global Wind Patterns
advertisement

Global Geography 12 Global Wind Patterns and Currents (Pages 60-67) 1. What two processes cause motion in the atmosphere and oceans? The two processes are the uneven heating of the Earth’s surface (warm at the Equator, cold at the poles) and the Coriolis Effect (Earth’s rotation causes “curves” in weather and currents) 2. Explain the main difference in how the atmosphere and oceans are heated. The atmosphere is heated by infrared (heat radiated from the Earth’s surface upward) while the oceans are heated by absorbing sunlight (from the surface downward) 3. Define convection cells. On the global scale, warm air rises, travels North or south – depending on location – then descends to the surface. 4. Define Coriolis effect and describe how it affects winds in both the Northern and Southern hemispheres. The curvature of the Earth’s surface affects the relative speed at different latitudes. As a result, winds in the north curve to the right (clockwise) and winds in the south curve left(counterclockwise). 5. What is a jet stream? Where do jet streams occur? It’s a fast moving current of air, high in the atmosphere. There are two in each hemisphere. (Text is not clear on location!) 6. What causes seasonal changes in winds? The tilt of the planet relative to the sun changes the location of the warmest areas (although these are always found between the two tropics). 7. Where do monsoon winds occur? Describe the seasonal pattern of these winds and the weather that results. Monsoons occur mainly in Southeast Asia. In (our) winter they blow from east to west, creating a dry season. In (our) summer they blow from West to East, creating a rainy season. 8. Describe similarities and differences between ocean currents and wind in a table. similarities differences Both are moving fluids One involves water, the other air Both are caused by heating Both are affected by Coriolis effect Ocean currents are affected by salinity as well as temperature Both are important to human activities Ocean currents are affected by the size of the ocean and shape of coastlines 9. Define spring and neap tides. Spring tides are very strong tides that occur when the sun and moon align Neap tides are exceptionally weak tides (when the sun and moons pull counteract) 10. Read the case study on page 63 -64. a. Describe several (3-5) impacts of flooding on the lives of people in Bangladesh. Homes are destroyed crops are lost No access to clean water Diseases spread Infrastructure is damaged b. Suggest 2-3 reasons why disasters have a stronger impact on people in less developed countries. Governments have less emergency funding available for rebuilding, and fewer services to assist during the crisis Heavy reliance on agriculture means there is a more direct impact on daily lives Populations are crowded, so many more people may be affected c. What two global processes or systems may have been the cause of the increased flooding? Higher sea levels Global warming Earthquakes in the Indian ocean