word doc - Southgate Schools
advertisement

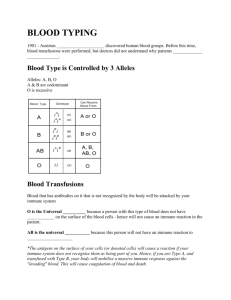
Name__________________________Date_________________Hour___________1 35.1 Summarize Koch’s Postulate What are symbionts and pathogens? 35.2 Defenses Against Infection Nonspecific Defenses The body’s first defense against pathogens is a combination of ____________________________and chemical __________________ 1.) 2.) 3.) 4.) 5.) 6.) These barriers are called _____________________________because they act against a wide range of pathogens. First Line of Defense The most widespread nonspecific defense is the_________________________. Very few pathogens can penetrate the layers of dead cells that form the skin’s surface. Other defenses protect parts of the body not covered by skin 1.) _________________2.) _______________3.) ___________ ___________________, ____________________, &_______________________contain lysozymes that breaks down bacterial cell walls. Mucus in your nose and throat traps_____________________. cilia push the mucous-trapped pathogens away from your lungs. Stomach secretions destroy many pathogens that are swallowed. Name__________________________Date_________________Hour___________2 Second Line of Defense If pathogens make it into the body, through a cut in the skin, the body’s second line of defense swings into action. These mechanisms include – ____________________________________ – ____________________________________ -____________________________________ Inflammatory Response The ___________________________________causes infected areas to become red, painful, and inflamed. Pathogens stimulate cells called mast cells to release chemicals ___________________. Histamines increase the flow of________________ and ___________________to the affected area. Fluid leaking from expanded blood vessels causes the area to swell. White blood cells move from blood vessels into infected tissues. Many of the white blood cells (__________________) engulf & destroy bacteria. All this activity may cause a local rise in____________________________. That’s why a wounded area sometimes feels warm. Interferons Viruses infect body cells, host cells produce proteins. These proteins help block__________________________. Interferons are ________________ that “interfere” with viral growth. Interferons slow down the progress of infection & “buy time” for immune defenses to respond. Fever The immune system also releases chemicals that increase body temperature, producing a______________________________. The increased body temperature may stop the growth of some pathogens. Higher body temperature also speeds up parts of the immune response. Nonspecific Defenses What are the body’s nonspecific defenses against pathogens? Answer below ________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Recognizing “Self” A healthy immune system recognizes all cells & proteins that _____________________the body as “_______________________.” Recognizing “self” is essential. Name__________________________Date_________________Hour___________3 The immune system controls powerful cellular and chemical weapons that could cause problems if turned against the body’s own cells. Recognizing “Nonself” –The immune system recognizes ____________________organisms as “__________________.” –Once the immune system recognizes “_________________,” it ________________ –After encountering a specific invader, the immune system “remembers” the invader –This_______________________, _________________, and ___________________-the immune response. Antigens –Antigen (__________________) -a _______________________that can stimulate an immune response. –Antigens are located on surfaces of_______________, ________________, or__________________________. –Immune system responds by _______________________that ________________the invaders or produce proteins –antibodies (________________________) 1.______________________(good guy) _________antigens (bad guy) for destruction 2.The body makes up to 10 billion different antibodies. 3.The shape of each type of antibody allows it to attach to one specific antigen. Lymphocytes The main working cells of the immune response are –B lymphocytes (____________________) –T lymphocytes (____________________). B cells are produced, & mature in, in___________________________. B cells have embedded _____________________and discover _______________________in body fluids. Lymphocytes T cells are produced in bone marrow mature in the ___________________________(endocrine gland.) T cells must be presented with an antigen by infected body cells or immune cells that have encountered antigens. Lymphocytes –Each ________cell and ____________ cell recognizes one specific antigen. –A person’s ______________________determine the particular B and T cells that are produced. –Both types of cells travel to ___________________and the ___________________, where they will encounter antigens. Specific Defenses: The Immune System What is the function of the immune system’s specific defenses? Answer Below ________________________________________________________________________ Name__________________________Date_________________Hour___________4 Humoral Immunity Humoral immunity-The immune response that defends against antigens in body fluids 1.) _____________________2.) _____________________ –B cells play the ___________________________________ –When pathogens invades the body, its ____________________are recognized by ____________________________on the surfaces of the B cells. –Antibodies are the _______________________________ Humoral Immunity Antibody ~shaped like the letter _____ ~two _______________antigen-binding sites. The shapes of the binding sites lets an antibody recognize a specific antigen with a_______________________________________________. Humoral Immunity When an antigen binds to an antibody, __________cells stimulate the ____________cell to grow and divide rapidly. That growth and division produces many B cells of two types: 1.) ______________________________________ 2.) ______________________________________ Plasma Cells *Plasma cells produced *Plasma cells release _____________________________ *Antibodies are carried through the________________________. *Antibodies recognize & bind to ___________________________ *When antigens are bound, they __________________________the immune system to ________________________& ____________________________the invaders. *Some types of antibodies can disable invaders until they are destroyed. Memory B Cells Plasma cells _____________________after an infection is gone some B cells that recognize a particular antigen remain alive. These cells, called________________________________, react quickly if the same pathogen enters the body again. Memory B Cells Memory B cells rapidly produce ______________________________to battle a returning pathogen. This secondary response occurs much ___________________________than the first response to a pathogen. Immune memory helps provide long-term immunity to certain diseases and is the reason that vaccinations work. Name__________________________Date_________________Hour___________5 Cell-Mediated Immunity Another part of the immune response is called_____________________________. This immune system defends the body against _______________, ______________, and single-celled__________________________________. T cells also protect the body from its own cells when they become________________________________________. When a cell is infected by a pathogen or when a phagocyte consumes a pathogen, the cell ______________________________a portion of the ______________________on the outer surface of its membrane. This membrane attachment is a signal to circulating _____________________called helper T cells. Activated helper T cells divide into more ________________________ They go on to activate ________________________ which activate _____________________________________ & produce _______________________________________ Cytotoxic T (killer T cells) cells ________________________body cells infected with a particular antigen and kill the cells. They kill infected cells by puncturing their membranes or initiating apoptosis (_______________________________________). Memory helper T cells enable the immune system ___________________________if the same pathogen enters the body again. Another type of T cell, called suppressor T cells, inhibits the immune response once an infection is under control. They may also be involved in preventing autoimmune diseases. Although cytotoxic T cells are ___________________in the immune system, they make the acceptance of ___________________________________________________ When an organ is transplanted from one person to another, the normal response of the recipient’s immune system would be to recognize it as___________________. T cells and proteins would damage and destroy the transplanted organ in a process known as rejection. To prevent organ rejection, doctors search for a donor whose cell markers are nearly identical to the cell markers of the recipient. Organ recipients must take_______________________—usually for the rest of their lives—to suppress the_____________________________________________. The Immune System in Action What are the body’s specific defenses against pathogens? Answer__________________________________&_____________________________ Name__________________________Date_________________Hour___________6