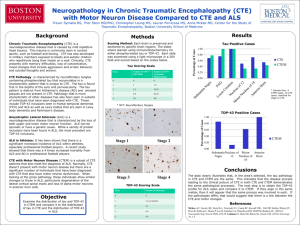
Table: Distribution of tau and TDP-43 pathology in brains and spinal
advertisement

Supplemental Table: Summary of Distribution of tau and TDP-43 Pathology in Brains and Spinal Cords of Patients with CTE, ALS, and CTE with MND CTE without ALS without CTE with MND Controls (N = 12) MND (N = 9) CTE (N = 12) (N = 3) Brain* – tau Abundant (1, 2) Not stated ** Extensive Not stated (2)+ Brain* – TDP-43 Extensive, less Not stated ++ Abundant Not stated; known than CTE/ MND from other sources cases; or absent. to be absent The great majority was not tau positive. There were no inclusions in the dentate gyrus. Spinal cord - tau Occasional Rare neurites in Present, most Rare neurites, in 4 neurites and 1 of 12 cases, but frequently in 2 of of 12 controls NFTs no NFTs the 3 cases Spinal cord – Occasional, in 2 Present in all Abundant TDP-43 of 5 cases cases None CTE – chronic traumatic encephalopathy; MND – motor neuron disease; ALS – amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; FTLD – frontotemporal lobar degeneration; PDC – parkinsonism-dementia vomplex; PSP – progressive supranuclear palsy; CBD – corticobasal degeneration; NFT – neurofibrillary tangles; N – number of patients (controls). * Includes cerebrum, deep gray nuclei and brainstem. ** The cortices of most patients with ALS or with ALS/FTLD are tau-negative; Guamanian ALS/PDC is an exception. There are tau-positive forms of FTLD that overlap with PSP and CBD. + Tau pathology is generally absent in normal control cerebral cortex. ++ TDP-43 immunoreactivity is abundant in motor cortex of patients with sporadic ALS, with greater cortical distribution (extending beyond primary motor cortex) in patients with ALS/FTLD. 1. McKee AC, Cantu RC, Nowinski CJ, et al. Chronic traumatic encephalopathy in athletes: progressive tauopathy after repetitive head injury. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2009;68:709-35 2. McKee AC, Gavett BE, Stern RA, et al. TDP-43 proteinopathy and motor neuron disease in chronic traumatic encephalopathy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2010;69:918-29